- Fever
- Weakness in the hands
- Numb hands
- Swelling of the affected joint
- Redness of the skin at the site of the lesion
- Pain in the affected joint
- Pain when touching the affected joint
- Motor dysfunction
- Tingling in the affected area
Bursitis of the shoulder joint is an inflammation of the joint capsule with fluid that is localized between the bone and tendon in the shoulder joint. This inflammatory process most often occurs due to the impact of heavy loads on the shoulder joint. But this is not the only reason for the progression of the pathology. This disease can be caused by shoulder injuries, improper fusion of bones after a fracture, arthritis, and some autoimmune diseases.
- Etiology
- Varieties
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
Most often, the disease is accompanied by a symptom such as numbness of the arm from the shoulder to the hand. It can be treated in various ways, which directly depend on the form of the disease. The therapy method is selected only by a qualified doctor.
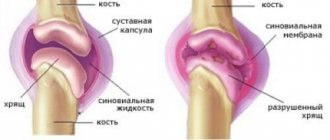
In a healthy state, the bursa looks like a small slit that contains a little fluid. In total, there are more than one and a half hundred of these types of bags in the human body. During inflammation, the bag increases in size and produces a large amount of fluid, the composition of which can be different and depends on the form of the disease. If left untreated, shoulder bursitis is complicated by the accumulation of calcium salts in the inflamed area.
Very often the disease affects men who are forced to lift heavy weights every day, as well as athletes. Women are much less susceptible to the disease. With proper, and most importantly, timely treatment, all symptoms of inflammation disappear within a few weeks.
Shoulder bursitis does not cause any complications for human health; the only trouble that can happen is the formation of a chronic type of illness.
Causes of the disease
Bursitis of the shoulder joint is a fairly common disease that can begin to progress due to many reasons, including:
- excessive physical stress on the shoulders;
- injuries, bruises, sprains, cuts or abrasions;
- allergic reactions;
- metabolic disease;
- prolonged tension in a particular joint in the shoulder;
- autoimmune lesion;
- intoxication of the body;
- the effect of alcoholic beverages or tobacco smoke on the body;
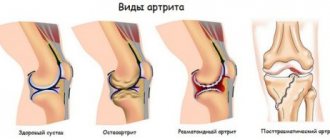
- arthritis.
Violation of the structure of the shoulder joint can be caused by either one reason or a combination of them.
The mechanism of the disease
Due to the anatomically determined specific structure of the shoulder joint, its synovial bursa in the form of a thinned section of the articular capsule does not communicate with the articular cavity. Their location is under the muscles or tendons surrounding the shoulder joint. The surface of the bursae is lined with synovial cells, which produce synovial fluid to lubricate the surface of the bones and ensure their optimal gliding.
Very often in medical practice, it is the bursa of the shoulder joint that is damaged, which limits any movement or rotation of the arms. Accumulations of fluid often contain admixtures of blood, pus and are enriched with protein. There are a total of eight articular capsules in the human shoulder, and damage can occur in one of them or in several at the same time. In this regard, both subacromial and subdeltoid bursitis can develop.
Varieties
Depending on how the disease progresses, bursitis can be:
- sharp;
- subacute;
- chronic;
- infectious.
Based on the composition of the fluid, the disease is:
- purulent;
- fibrous;
- serous;
- with blood impurities.
In addition, in the medical field, there are other types of shoulder bursitis, which have similar causes, but differ in course:
- calcareous bursitis of the shoulder joint, which is also called stone bursitis - accumulations of calcium salts are transformed into lime;
- calculous - calcium deposits are localized so deeply that surgical intervention is used to restore the functionality of the shoulder;
- subacrominal - which is characterized by acute pain when the joints are tense, and when the arm is lowered down, hanging freely, all unpleasant sensations go away;
- tendobursitis – combines the inflammatory process with thinning of the tendon structure.
Causes of pathology
Bursitis of the shoulder or elbow is an occupational disease of tennis players, track and field athletes, swimmers, and representatives of strength sports. Excessive loads and regular microtraumas cause wear and tear of the joint capsule and its inflammation. Similar processes in the shoulder joint occur in people engaged in monotonous physical labor - loaders, assembly line workers.
Factors that increase the likelihood of bursitis:
- chronic infectious foci in the body;
- injuries, blows, open wounds, shoulder abrasions;
- acute infectious diseases;
- presence of arthritis;
- osteomyelitis;
- osteoarthritis;
- gout and other diseases associated with metabolic disorders.
Separately, it is worth highlighting such a type of disease as calcareous bursitis, in which calcium salts begin to be deposited in excess quantities in the joint. The disease occurs as a result of metabolic abnormalities, is difficult to treat and gradually leads to a decrease in joint mobility.
Symptoms
Bursitis of the shoulder joint
In addition to the main symptom of shoulder bursitis - pain of varying intensity, the disease has the following symptoms:
- swelling and tingling sensation in the affected area;
- redness of the skin at the site of inflammation;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- weakening and rapid fatigue of the hand.
Such signs are characteristic of the acute form and stone type of the disease. With the chronic course of the pathological process, these symptoms intensify slightly and appear in waves - periods of increased pain alternate with periods of their subsidence.
Tendobursitis is characterized by symptoms such as dull pain with a specific location, which the patient can easily point to, and a decrease in motor functions. Externally, no changes in the shoulder are observed. This form of bursitis can only be detected on an x-ray.
Subacrominal bursitis is accompanied by symptoms such as:
- severe pain that appears not only when moving, but also at rest;
- weakness in the hand;
- touching the affected area causes discomfort;
- The fluid in the shoulder bursa contains pus and blood.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies can be used as additional treatment. They help relieve pain and swelling.
Cabbage compress. Place the cabbage leaf in boiling water for a few seconds, then drain and squeeze a little. Apply to the shoulder and secure with a bandage. Remove after 3-4 hours.
Preheat camphor oil in hot water. Rub the affected area, place a piece of cloth on top and secure it with a bandage. Remove the bandage after a few hours.
Cut a few leaves from the Kalanchoe plant. Grind them thoroughly. Apply the resulting pulp to the sore joint.
A course of treatment using physical procedures is carried out only after acute symptoms have been eliminated. The following methods are used for treatment:
- Electrophoresis.
- Manitotherapy.
- Ultrasound.
The result of treatment is the complete elimination of the main manifestations of bursitis.
Massage also worked well. The massage technique involves a specialist influencing the area of the affected joint in order to improve blood circulation and relieve muscle tone.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing bursitis of the shoulder joint is not difficult for an experienced doctor. The diagnostic process consists of a whole range of activities:
- examining the affected area for redness and swelling;
- collecting information about the causes and timing of symptoms;
- Carrying out radiography - from the image you can determine the form of the inflammatory process;
- puncture of the affected joint capsule, thanks to which you can find out the composition of the fluid, the presence of purulent or blood impurities;
- use of ultrasound and MRI data of the affected shoulder joint.
Methods used in treatment
Treatment of shoulder bursitis should be comprehensive and include the following methods:
- conservative treatment;
- local impact;
- surgical intervention;
- treatment with traditional methods.
Treatment of acute bursitis, which can be detected in the early stages of the disease, comes down to providing the patient with complete rest, applying a pressure bandage, possibly with Vishnevsky ointment, and applying heat.
In chronic forms of the disease, it is advisable to perform surgical intervention, in which special punctures are made and accumulated exudate is removed through them. Next, the cavity of the bag is drained with solutions of antiseptics or antibiotics.
If bursitis of the shoulder joint occurs as a result of an injury, it is effective to inject a hydrocortisone solution into the cavity of the joint capsule using aseptic technique, which will help avoid serious consequences and complications.
Purulent bursitis is treated using puncture, and in cases of ineffectiveness of this method, opening the inflamed joint capsule is justified, during which the pus is removed. Further treatment of a purulent wound is carried out using traditional methods for this disease. In some cases, a course of antibiotic therapy and the administration of sulfonamide drugs are prescribed. In especially severe cases, this method of treatment is distinguished by its longest duration and morbidity.
The following surgical methods can be used:
- excision of the inflamed bursa and its opening with further processing and introduction of chemicals into its cavity;
- opening and tamponing of the inflamed bursa;
- removing the wall of the bursa and lubricating its cavity with an antiseptic - an alcohol solution of iodine;
- Complete removal of the inflamed bursa without opening it is the most radical method of treatment.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, the use of dry heat or UHF, are very effective in promoting rapid resorption of exudate. After localizing the inflammatory process, patients are prescribed a course of massage and exercise therapy.
For chronic or subacute bursitis, radiation therapy, such as x-ray therapy, is used. This method has proven itself to be an excellent anti-inflammatory agent. It also relieves pain and allows you to quickly restore damaged trophism. In this case, depending on the severity of the disease, the optimal rhythm and daily doses of radiation are selected.
As for traditional methods of treatment, they must be considered as an addition to traditional treatment and must be agreed with the attending physician
. The most common remedies for bursitis of the shoulder joint, in folk medicine, are considered to be compresses from fresh vegetables (cabbage, potatoes, beets), compresses with sugar heated in a frying pan, and lotions made from propolis tincture. Celery tea is considered as a general tonic, which helps the patient’s body cope with inflammation.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of bursitis of the shoulder joint is carried out using many methods, from therapy with folk remedies to surgery.
Not all types of bursitis are treated with surgery, but only a few:
- stone, because deposits of calcium salts acquire the structure of lime or stone, which cannot be cured with medications;
- calculous - since calcium collects much deeper than in other forms, and the functioning of the shoulder can be normalized only by removing the salts surgically;
- tendobursitis - it is possible to cure and restore the functionality of the arm only through surgery, during which calcium deposits are removed and the joint is artificially strengthened;
- purulent - the operation is aimed at removing purulent fluid (sometimes mixed with blood) from the shoulder joint bursa.
In addition to this drastic remedy, bursitis can be treated by rubbing in medicinal ointments and taking anti-inflammatory and antibacterial medications. Also, therapeutic massages and physical exercises are used to strengthen and restore motor functions. All the time, until complete recovery, the patient needs to wear a tight bandage or bandage on the injured shoulder (grabbing the elbow), so that after the operation the tissue fusion takes place in the correct form.
Bandage for shoulder bursitis
Treatment of bursitis of the shoulder joint can be carried out at home using folk remedies, the effect of which will be noticeable only if they are used in conjunction with other methods.
So, folk remedies consist of medicinal compresses, which are made from:
- cabbage leaves;
- Kalanchoe;
- burdock leaves;
- salt - for this, salt is soaked in boiling water, a scarf or towel is dipped into the resulting solution, and the sore spot is tied.
Also, treatment with folk remedies consists of preparing decoctions, which include burdock root, propolis and butter.
You can use warming methods using flax seeds, which are heated, then placed on a towel while still hot, tied so as not to spill the seeds, and applied to the sore spot.
The latest folk remedy for treating bursitis is medicinal pine baths, which must be taken daily until the disease completely subsides. The duration of the bath is no more than twenty minutes.
Traditional treatment for shoulder bursitis
Therapeutic methods are prescribed based on research results. Traditionally, medications, physiotherapy, and therapeutic exercises are used. In difficult cases, surgical operations are prescribed. Massage, acupuncture and traditional methods of treatment help speed recovery. The goal of all treatment options is to reduce pain symptoms and restore full movement in the shoulder joint. During the treatment period, you should adhere to the following rules:
- The affected joint should be immobilized with a tight bandage or plaster.
- In case of purulent or hemorrhagic inflammation, the exudate is removed using a puncture.
- Loads on the shoulder are avoided during therapy.
Drug therapy
Acute symptoms of bursitis are relieved with topical medications. If necessary, systemic therapy is carried out. The effectiveness of external preparations lies in the fact that ointments, gels, emulsions, tinctures, mash are applied directly to the inflamed area without affecting healthy tissue. Systemic drugs (tablets, capsules, solutions for intravenous/intramuscular injection) are prescribed for severe cases of the disease, because they act much faster. Such drugs are absorbed into the general bloodstream and are active throughout the body.
During drug therapy, the patient is provided with complete rest; a warm compress is applied to the moving bone joints. During the treatment of bursitis, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Antibiotics. Antibacterial drugs are used to treat bursitis of infectious origin. Therapy is carried out using intramuscular injections into the periarticular bursa. For the purulent form of the disease, tablets or capsules are prescribed for oral use. In cases of weak immunity, intravenous antibiotics may be required. More often, doctors prescribe antibacterial drugs such as Dicloxacillin, Clindamycin, Cephalexin.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Medicines in this group are prescribed to eliminate inflammation and improve mobility of the shoulder joint. NSAIDs are used both systemically and externally. In orthopedic practice, it is customary to use Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, Ibuprofen.
- Painkillers. Such drugs are used in the form of tablets and intramuscular injections to eliminate pain symptoms. They are often combined with antibiotics. The best medicines from this group are Baralgetas, Analgin.
- Corticosteroids. These drugs have a rapid anti-inflammatory effect. They are prescribed, as a rule, in the form of injections. Popular drugs in this group are Diprospan, Triamcinolone hexacetonide.
Article on the topic: Ketoprofen - instructions for use, release forms, indications, side effects and price
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy is carried out after the disappearance of acute symptoms, swelling, pain relief, and cessation of the purulent process. To treat bursitis, the following physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed:
- UHF. The procedure involves exposing the affected area to high frequency electromagnetic fields. Thanks to special equipment, heat penetrates deep into the tissue, changing the structure of cells at the molecular level. UHF reduces swelling, relieves pain and symptoms of inflammation, and stimulates blood circulation.
- Ural Federal District. Ultraviolet irradiation is carried out during an infectious process. Short-wave radiation has a bactericidal and antiviral effect, during which the pathogen dies. At medium waves, ultraviolet radiation stimulates tissue trophism, improves local immunity, and activates the synthesis of vitamins.
- Applications with paraffin and ozokerite. These procedures allow you to warm up the inflamed area, relieve pain symptoms, increase immunity, and speed up recovery. For ease of application, paraffin is mixed with natural mountain resin (ozokerite). Applications from this mixture are easier to make, and the risk of burns is minimized.
- Phonophoresis. The use of low-intensity ultrasound waves aimed at the area of inflammation is considered effective in the treatment of shoulder bursitis. The energy is converted into heat, which penetrates several centimeters deep into the tissues. For better conductivity, use Hydrocortisone ointment. It blocks inflammation, relieves swelling and pain, and promotes rapid penetration of ultrasound.
Physiotherapy
Complete restoration of joint mobility is possible with the help of special therapeutic exercises. It is prescribed after pain and swelling have been relieved. For each patient, the rehabilitator selects an individual set of exercises. When conducting physical therapy, the following conditions must be met:
- It is important to start classes with static exercises.
- Dynamic exercises should initially contain small amplitudes and loads, and then they should be more complicated.
- Strength exercises and sudden movements must be completely avoided.
Surgery
If bursitis has caused complications, for example, tenobursitis of the shoulder joint has developed, more radical treatment is required. If drug therapy is ineffective, the patient is prescribed surgery. There are two types of intervention:
- removal of exudate using a catheter under local anesthesia (puncture);
- partial or complete excision of the bursa under general anesthesia (bursectomy).
Prevention
Preventive measures aimed at avoiding the occurrence of such inflammation consist of:
- reduction in physical activity (directed at the shoulder joints);
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle and giving up bad habits;
- good rest;
- performing gymnastic exercises in between hard work;
- a balanced diet, which should be enriched with vitamins and calcium;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of any infectious diseases.
What to do?
If you think you have shoulder bursitis
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: an orthopedist, an orthopedist-traumatologist, a surgeon.
Source
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
Diet
Limit your intake of dairy products for a speedy recovery!
Diet is especially necessary in the treatment of ossifying, calculous and calcareous bursitis of the shoulder. This includes limiting calcium-rich foods:
- milk;
- cheese;
- cottage cheese;
- kefir and yogurt.
The consumption of table salt is also limited. Food should be added salt only after it has been cooked. You can use no more than 1 tsp. table salt per day.
Causes
Bursitis of the shoulder joint is a common pathology that occurs in different age groups, regardless of gender. Bursitis is a polyetiological disease (has many causes), most often the disease is provoked by the following conditions:
- chronic overload of the joint with heavy weight or intense movements;
- fresh or long-standing injuries to the shoulder and collarbone, which were accompanied by swelling and a large area of damage;
- bacterial damage;
- allergic reactions to any irritants;
- autoimmune processes associated with the production of antibodies to one’s own tissues;
- intoxication and slagging of the body;
- developmental abnormalities of the bones that make up the joint;
- chronic diseases and amyloidosis.
Sometimes there may be several reasons at the same time that can provoke the development of the disease. For example, an autoimmune process occurs against the background of injury. In this case, the doctor must treat a disease that is more dangerous for the person.
Sometimes it is not possible to find out the exact cause, and such bursitis is called idiopathic (without an exact cause).
Symptoms of shoulder bursitis
The main characteristic symptom is acute pain. It has various manifestations, accompanied by accompanying symptoms:
- unbearable pain radiating to the scapula;
- pain on palpation, touching clothing;
- it hurts to carry a bag or satchel on the affected shoulder;
- sharp pain when trying to lift the upper limb upward;
- moderate pastiness of paraarticular tissues;
- mild hyperemia of the shoulder region;
- general hyperthermia during intoxication in the case of purulent bursitis.
The acute form of the disease develops rapidly. Occurs with acute clinical manifestations. When the mucous membrane of the bursa is infected, the pain does not stop, and the general condition worsens. The course of chronic bursitis due to long-term progression has a clinically poorly expressed picture. The pain is moderate, the general condition remains normal for a long time.
General signs
Symptoms of bursitis largely depend on the type of pathology and the nature of the course of the disease, but the disease still has common signs, they are as follows:
- due to the accumulation of exudate in the shoulder area, swelling appears;
- the site of inflammation is hyperemic (redness, increased local temperature);
- acute or aching pain syndrome (and any exercise or training aggravates the pain);
- reduction in range of motion (if the pathology becomes chronic, persistent contracture is possible).
The main symptom (edema, swelling of the joint) cannot always be seen visually, but sometimes the inflammation is hidden in the deep tissues of the joint and then the diagnosis of the disease becomes somewhat more complicated.
How intense the symptoms are depends on the stage of the pathology and the nature of the intra-articular exudate.
Reasons for the development of bursitis
The overwhelming number of purulent bursitis is associated with household injuries to the listed areas. At the same time, for the development of bursitis, microtrauma of the skin covering the area of the bursa may be sufficient.
Also, bursitis can occur after gunshot injuries to joints, open and closed fractures, as well as due to injection or surgical interventions (most often, injections of narcotic substances, self-opening of large abscesses at home, etc.). In patients with deforming arthrosis, rheumatoid polyarthritis or diabetic osteoarthropathy, post-injection purulent bursitis is often associated with the introduction of steroids into the joint cavity.
The introduction of infection from foci of purulent infection close to the bursa is also observed quite often (erysipelas of the limb, large boils, cellulitis, abscesses, infected bedsores, festering wounds, etc.).
The cause of the development of septic bursitis is any pyogenic flora that enters the cavity of the bursa as a result of injury. The most common causative agents of the inflammatory process in the bursae are staphylococci, streptococci, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter, Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
In patients with various immunodeficiency conditions, septic bursitis can occur due to Candida fungi or Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
In some cases, inflammation with bursitis can be aseptic in nature. Such inflammation develops with closed joint injuries that are not accompanied by infection and with systemic diseases (most often with gout, ankylosing spondylitis, SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus) or rheumatoid arthritis).