Nodular mastopathy and breast cancer
The reasons for the development of nodular mastopathy are:
- adrenal and thyroid dysfunction;
- hysteria;
- depression;
- fatigue;
- abortions;
- genetic predisposition;
- irregular sex or lack thereof;
- liver diseases;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- lack of breastfeeding;
- inflammatory diseases of the ovaries;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- physical trauma to the chest;
- tight underwear;
- lack of iodine;
- hormonal contraception;
- early onset of menstruation;
- late menopause;
- large amounts of estrogen;
- lack of progesterone;
- chronic hepatitis;
- no pregnancy before age 30.
The key to women's health is regular sex, having children, breastfeeding, physical activity every day, positive emotions, proper nutrition and the absence of bad habits.
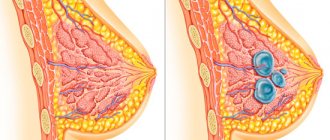
Nodular mastopathy, which is observed in the mammary gland, is a precancerous stage. Not every patient would like to hear such a diagnosis. The causes of cancer development are always varied. Common causes include various disorders in the formation of tissues or the functioning of organs, as well as hormonal disorders.
Nodular mastopathy most often affects women aged 35-50 years, but there are cases of development in younger representatives. The size and shape of the breast gradually change, which indicates pathological formations.
An insufficient amount of estrogen in the blood shifts monthly cycles, days of ovulation and possible pregnancy. The blood in the body is not renewed, which leads to the need for “nutrition” from the existing blood elements.
The causes of nodular mastopathy are:
- Depression.
- Abortion.
- Dysfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
- Liver diseases.
- Fatigue.
- Hysteria.
- Diabetes.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Obesity.
- Intestinal dysbiosis.
- Smoking.
- Absent or irregular sex.
- Chest injuries.
- Lack of breastfeeding.
- Tight underwear.
- Late menopause.
- Inflammation of the ovaries.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Lack of iodine.
- High levels of estrogen.
- Hormonal contraception.
- Chronic hepatitis.
- Early onset of menstruation.
- Progesterone deficiency.
- No pregnancy before age 30.
Treatment for nodular mastopathy that does not rupture includes herbal medicines, where the dosage of hormonal drugs is gradually reduced.
The causes of nodular mastopathy are not fully understood, but it is certain that it is associated with fluctuations in hormone levels.
The following factors contribute to the accumulation of fibrocystic changes in breast tissue:
- early onset of menstruation;
- first birth after 30 years;
- in a woman who has given birth;
- diseases leading to hormonal imbalance (diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, chronic ovarian inflammation, etc.).
“Thinking about the bad,” women at an appointment with a mammologist often ask the question, “Does breast cancer always occur against the background of nodular mastopathy?” Answer. Nodular mastopathy does not have the potential to develop into breast cancer and does not increase your risk of developing cancer. But, changes in breast tissue may present with symptoms that resemble cancer in the early stages.
Since cancer can be hidden under the symptoms of nodular mastopathy and sometimes women cannot recognize it on their own, it is advisable to regularly visit a doctor to examine the mammary glands.
It is important for women to learn how to properly perform self-examination of the mammary glands in order to determine in time what changes have appeared in it again and, the first time they are detected, contact a mammologist
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of nodular mastopathy varies in each individual case. Therapy is determined taking into account the physiological characteristics of the female body, the form and complexity of the disease and other factors that are directly or indirectly related to this pathology.
Conservative methods are aimed at bringing hormonal levels back to normal and treating associated gynecological and other abnormalities. Specialists prescribe medications that help eliminate hormone imbalances in the body. One of the most effective today is lymphomyositis. Surgery involves removing individual tumors without affecting surrounding tissue.
A surgical method may be required in cases where there is a suspicion that benign cysts are developing into malignant ones. Doctors may insist on surgery if conservative therapy does not produce positive results. Intensive growth of lumps, changes in their structure, blood discharge from the nipples - all this serves as a reason for surgical intervention. In some cases, during surgery, doctors remove part of the connective tissue that is located close to the lesion.
About 10% of cases of nodular mastopathy acquire a malignant form. Timely examination and treatment will help avoid negative, irreparable consequences.
On a note
Women who have given birth several times and breastfeed their children are much less likely to suffer from mastopathy of various forms. Folk remedies
Symptoms
The course of breast disease varies. More often than not, at the beginning of development, women do not detect any signs and symptoms. Signs of PMS, mood swings, sensitivity and discomfort in the breasts are associated with the approach of menstruation. Nodal seals cannot be palpated because their size is less than 3 mm.
Late symptoms of nodular mastopathy:
- 15% of patients have no pain syndrome;
- in a standing position, 1 or more lumps measuring 0.5–3 cm are palpated;
- in the supine position, the nodes are not palpable;
- 85% of women experience dull, aching, cyclical or persistent pain in the area of the node;
- pain can radiate (radiate) to the arm, shoulder blade, shoulder, under the armpit or behind the sternum;
- heaviness, engorgement, and tenderness of the breasts (mastodynia) are observed 7–14 days before menstruation;
- there are migraines, vomiting, anxiety, fear of developing cancer;
- bloody, transparent, whitish, yellowish or green discharge appears from the nipple;
- pathological fluid flows from the gland on its own or after pressure;
- it is possible to change the contour and size of the breast;
- inflammation is manifested by increased temperature, redness of the skin, swelling, and enlargement of nearby lymph nodes;
- Sometimes swelling of the arm on the side of the chest with nodular mastopathy is noted.
Symptoms and manifestations
- The most important symptom is the presence of round or oblong lumps in the mammary gland with clear contours.
- When palpating these places, severe pain appears. The pain may be dull and aching. They appear especially often during menstruation.
- Due to swelling of the connective tissue, breast enlargement occurs.
- Pressing on the nipple of a sore breast causes discharge, which can be clear, white or yellowish.
- With mastopathy, nodules and lumps cannot be felt in a lying position.
IMPORTANT If there is blood in the discharge, you must see a doctor. This symptom may indicate the onset of a cancer process.
Clinical picture and diagnosis of pathology
The diffuse or initial stage of mastopathy has the following histological varieties:
· Initial mastopathy, the main component of which is glandular tissue. This form is also called mammary adenosis.
· Initial mastopathy, the main component of which is fibrous tissue.
· Initial mastopathy with the development of cystic formations.
· Mixed type.
· Sclerosing form of adenosis.
This classification is based on the clinical and radiological characteristics of the disease. This suggests that to accurately diagnose the initial stage of mastopathy, they resort to the method of x-ray examination.
Female patients diagnosed with a diffuse form of mastopathy consult a doctor with the following complaints:
· feeling of heaviness, distension and tension in the causal area;
· increase in volume of the mammary gland.
In addition, the patient may complain of pain in the chest, which intensifies before menstrual flow. Sometimes women do not attach much importance to this because... The breasts almost always swell and hurt a few days before menstrual flow. However, over time, these changes only intensify. The pain becomes so severe that palpation of the breast is not possible. The pain is often localized not only in the mammary glands - it can spread to the shoulder blades, armpits or shoulder area.
The initial stage of mastopathy is usually diagnosed in women under 35 years of age. In addition to the above symptoms, patients complain of headaches, sleep disturbances, anxiety and fear associated with the possibility of developing malignant lesions in the chest.
In addition to the x-ray diagnostic method, an examination is used, one of the components of which is palpation. The palpation method allows you to determine not only the pain of the affected area, but also a diffuse increase in density. Palpation also shows roughness of the lobules in the upper outer quadrants of the gland. These roughened areas respond with moderate pain to touch, have unclear outlines, and may be finely grained or cord-shaped. Also, palpation examination reveals a clear, greenish or colostrum-like discharge from the nipples of the gland. To do this, the doctor presses on the dark areola.
Typically, the pain symptom, thickening and coarsening of areas of the mammary gland increases sharply before menstrual flow (several days). After menstruation subsides, these symptoms decrease. However, the gland does not return to its normal physiological state, the density of the gland and soreness remain, but it becomes less bright.
To confirm the diagnosis of mastopathy, mammologists and gynecologists recommend resorting to the following diagnostic methods:
1. Mammographic examination of the breast.
2. Pneumocystographic study.
3. Ultrasound research method.
4. Determination of the concentration of estrogen and prolactin in a woman’s bloodstream.
If, due to the disease, secretion is released from the nipples, then it is recommended to conduct a ductographic examination. This method allows you to identify a defect in the ducts and determine the size of cystic formations. In addition, studying a cytological smear allows one to exclude diseases such as actinomycosis, tuberculosis or syphilis of the mammary gland.
It is imperative that a woman be able to independently examine and palpate the mammary gland. If even minor changes appear in the breast (pain, tightness), you should definitely consult a doctor. This is done in order to identify the disease at the initial stage and prevent the development of serious complications.
If there is a suspicion of concomitant pathology, then it is recommended to undergo testing for thyroid hormones and sex hormones. You also need to determine the level of liver enzymes, seek advice from a gynecologist-endocrinologist and undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. In doubtful situations, it is recommended to carry out magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), histological examination of the material taken for biopsy, and also determine the level of CA 15-3 (oncological marker) in the bloodstream.
Nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland
Although it is a benign process, dishormonal disorders in the glandular tissue of the breast should not be underestimated. The mammary gland, like the uterus and ovaries, is a hormone-dependent organ: any endocrine disorder can cause the formation of the disease. Mastopathy can be diffuse and nodular: in the first case, the risk of cancer is minimal, in the second, the probability of degeneration is quite high, especially in women with risk factors for breast cancer.
Nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland is often combined with gynecological diseases (uterine fibroids, endometriosis, ovarian cystoma, endometrial hyperplasia), which indicates the presence of endocrine disorders in the female body.
Types and forms of nodular mastopathy
Nodular mastopathy is diffuse in nature, in which healthy breast tissue is damaged. Here are the different forms and types of the disease that you should know about.
Shapes:
- Nodular is a dangerous disease that occurs in multiple or single nodes in one or both breasts. This form can cause cancer.
- Diffuse - a harmless form, in which granular compactions are noted throughout the breast and swelling of the mammary glands.
Nodular mastopathy is observed in women from 35 to 45 years old. It is a precancerous condition, which increases the risk of developing cancer by up to 32%.
Since the nodular form can be a consequence of the diffuse form, the following symptoms of their manifestation are distinguished:
- Temperatures over 37.5°C.
- Graininess in the chest.
- Flaky skin.
- Pronounced lobular division.
- Pain in the chest outside the glands.
- Secret extraction.
- Feeling of heaviness in the mammary gland.
- Chills and fever.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Unusual breast shape.
Forms of fibrocystic mastopathy are distinguished by severity:
- Leaf-shaped tumors are a fibro-epithelial malignancy.
- Cyst simple - formation of a cavity nature with liquid contents.
- Lipogranulomas are small necrosis of the fatty tissue of the breast.
- Clinical fibroadenoma is a benign formation formed from breast tissue.
- Lipomas are benign formations from the fatty tissue of the breast.
- Intraductal.
- Hamartomas are a consequence of disturbances in processes in the embryonic membranes, which provokes benign formations.
- Clinical papillomas are benign formations on the skin in the form of a nipple-shaped growth.
- Angiomas are benign forms on the surface of the breast in the form of nodules.
The types that are divided depending on the amount of predominant tissue in one form or another of mastopathy are considered separately:
- Lobular.
- Fibrocystic.
- Cystic.
- Cystic proliferating.
- Fibrous-nodular (glandular).
- Cystic papillary.
Definition and reasons
Nodular mastopathy is a benign disease of the mammary glands, the pathogenesis of which is based on hormonal imbalance in the female genital area.
Doctors identify a number of reasons why nodular mastopathy may develop:
- Insufficient sexual activity.
- Diseases and various types of genital defects.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Metabolic diseases.
- Endocrine pathologies.
- Predisposition to the disease, both genetic and acquired.
- Difficult environmental situation in the woman’s place of residence.
- Abuse of contraceptives and hormonal drugs.
- Bad habits.
- Unhealthy eating.
- Immoral lifestyle.
Each of these points can disrupt the exchange of hormones in the female body and provoke the development of pathology. In particular, we are talking about an increase in the concentration of estrogen and prolactin against the background of a decrease in the level of hormones produced by the thyroid gland.
Most cases of detection of nodular mastopathy occur in women aged 30 to 50 years. The fewest cases of development of this pathology are observed in women who have several children who were breastfed.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
Nodular mastopathy is similar in symptoms to cancer, so at the first suspicion, additional examination is required. At the appointment, the mammologist asks the patient about symptoms and main complaints, after which he begins a visual examination of the mammary glands. With this type of mastopathy, dense formations with clear boundaries, lobular, granular or smooth surface (with a cyst) are palpable. In the case of a cyst, when pressed, a cavity with fluid is felt. With intraductal lesions, fluid of various colors is discharged from the nipples.
Next, mammography is performed, where in case of nodular mastopathy, areas of darkening with a homogeneous structure and high intensity are noted.
When a cyst is detected in the mammary gland, a puncture is performed with further cytological analysis of the contents (puncture biopsy method), after which pneumocystography is performed, which can be used to identify the presence of intracystic hyperplastic and tumor neoplasms.
Ductography is necessary for intraductal changes.
Nodular mastopathy can be diagnosed by performing an ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound, which allows one to examine the location, size and vascular growths, and structure of neoplasms in the breast tissue.
For additional diagnosis of the condition, methods for determining the level of thyroid hormones, estrogen, progesterone, liver enzymes can be used, and they can also additionally resort to consultation with specialists from an endocrinologist and gynecologist.
Diagnostics
First of all, an experienced specialist will conduct a thorough survey and find out all the complaints and feelings of his patient. Then a thorough examination of both breasts takes place to palpate lumps and other noticeable changes. The doctor makes an initial diagnosis, after which an intensive examination of the internal tissues of the chest is prescribed.
Thanks to the rapid pace of development of modern medicine, there are many ways to differentiate nodular mastopathy from other pathologies of the mammary glands. The most effective of them:
Mammography allows you to diagnose the disease in the early stages, provides complete information about the condition of the mammary glands as a whole, as well as individual areas. Ultrasound diagnostics - gives a clear picture of the localization of cystic tumors. In addition, ultrasound allows you to assess the general condition of the tissues located next to the lesions.
Pneumocystography - diagnoses large capsular tumors. Aspiration biopsy is an examination of breast tissue for histology. Computer and magnetic resonance imaging is a layer-by-layer examination of the chest tissue.
If a cyst is detected, its contents are sent for cytological examination. It is necessary in order to exclude the presence of cancer cells in the tumor. Pneumocystography will help determine the nature of the neoplasm. It can be granular, lobular or smooth. When intraductal changes are detected, ductography is performed.
Symptoms of nodular mastopathy
Manifestations of nodular mastopathy are characterized by tumor-like compactions in the breast tissue, which have clear boundaries and are not fused to the nipple and skin. Such lumps can be detected by the woman herself during a self-examination of the glands.
During the premenstrual period, the lumps and the entire mammary gland become painful, tense, and increase in size due to swelling. The pain may radiate to the shoulder or shoulder blade. After the premenstrual edema subsides, the nodes become painless. Sometimes with nodular mastopathy no pain occurs, and then the glandular nodule becomes an accidental finding.
Nodular mastopathy is characterized by a negative Koenig symptom - the inability to palpate breast nodes in a lying position. Regional lymph nodes are not enlarged in nodular mastopathy. In the nodular form of mastopathy, individual drops may be discharged from the nipples when pressed, or quite abundant transparent, yellowish-brown or bloody contents may be observed.
Manifestations of the disease
Symptoms of nodular mastopathy are manifested by dull or aching pain in the breasts and armpits, especially in the period before menstruation. During palpation, you can detect seals that have an irregular shape and clearly defined edges. During an exacerbation, they can be easily grabbed with your fingers. In a supine position, the nodules “hide” and become invisible to the touch.
With nodular mastopathy, a woman’s breasts become greatly enlarged, pressure is felt from within, bringing heaviness and discomfort. When pressed, a peculiar liquid is released from the milk ducts, most often yellowish in color, without a characteristic odor. With the arrival of critical days, the pain subsides, and the formations decrease or disappear completely.
Important
If you notice bloody discharge from your nipples, you should immediately consult a specialist. Such manifestations of the disease may indicate the presence of cancer.
Inflammation of the axillary and subclavian lymph nodes with mastopathy is an accompanying symptom. As a rule, the disease does not interfere with the menstrual cycle, but in some cases, due to the luteal phase, it may be longer than usual.
Manifestations of the disease vary depending on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body. Often the weaker sex perceives mastopathy as a harbinger of PMS and does not attach much importance to it. The presence of the above symptoms is a good reason to consult your doctor.
Many women are interested in a completely natural question: are nodular seals always cancer? It is safe to say that in most cases, neoplasms are benign and can be treated. In order to undergo an effective course of treatment for nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland, it is important to consult a mammologist in a timely manner.
What helps with mastopathy
In search of an answer to the question of how to cure mastopathy with folk remedies, women try many folk recipes. It is worth noting that not all of them are equally effective. Any medicinal plant can act on the body in different ways. Some women notice the appearance of side effects after the first use. In this case, to avoid complicating mastopathy, treatment with folk remedies at home is stopped. In general, for the treatment of mastopathy using folk recipes, the following can be used:
- herbs;
- oils;
- decoctions;
- infusions
Herbs for mastopathy
When talking about folk remedies for treating mastopathy in women, experts put medicinal plants in the first place. Their availability, ease of use and effectiveness explain the high popularity of this group of products among women. In most cases, several herbs or a whole collection are used simultaneously for effective therapy. Among the plants effective against mastopathy:
- Borovaya uterus
- contains a large amount of phytoestrogens. These components are similar in composition to female sex hormones, so they are a good alternative to hormonal medications. - Red brush
– has pronounced immunostimulating properties, restores the synthesis of sex hormones. - White cinquefoil
- promotes the rapid removal of toxins from the body, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, and has a pronounced antitumor effect. - Celandine
– helps reduce and resolve cysts. It is necessary to use the herb for decoctions carefully; the juice of the plant is poisonous. - Golden mustache
– has a general strengthening effect, improves metabolic processes in the body.
Oils for mastopathy
According to women who have recovered from the disease, essential oils for mastopathy are an effective means of combating the disease. Among the tools used in this group are:
- Flaxseed oil
is rich in phytoestrogens. The lignin it contains helps restore hormonal levels in women, having an estrogen-like effect. - Camphor oil
has a pronounced analgesic effect. Used for compresses and lotions on the chest. - Evening primrose oil (evening primrose)
- helps improve blood flow, dilate blood vessels, and restores the skin. - Burdock oil
has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. Apply to the chest during the day, thereby reducing pain and discomfort.
Products for mastopathy
Using natural remedies for mastopathy, patients manage to avoid possible side effects from medications
It is worth noting that nutrition is also important in the complex treatment of the disease. Experts have found that mastopathy is directly related to intestinal function. Its weak activity, with chronic constipation, leads to the reabsorption of estrogens excreted in bile
Its weak activity, with chronic constipation, leads to the reabsorption of estrogens excreted in bile.
Taking these features into account, doctors recommend that patients with mastopathy drink plenty of fluids and eat more fiber. The following products should be present in the diet:
- lean meat (turkey, horse meat, rabbit, beef);
- fish;
- vegetable and butter;
- vegetables (spinach, cabbage, tomatoes);
- berries and fruits (apricots, blueberries, lingonberries, oranges).
Prevention
The best prevention is close attention to your health, regular visits to the gynecologist at least twice a year, especially for women over 30 years of age. Long-term breastfeeding also protects well against problems with the mammary glands, so you should not switch your baby to formula without medical indications, allowing the milk to burn out
Regular sex life, proper nutrition, avoiding stressful situations, moderate exercise, giving up bad habits and artificial abortion are the best ways to maintain women's health and protect yourself from various diseases and serious consequences.
Prolonged breastfeeding also protects well against problems with the mammary glands, so you should not switch your baby to formula without medical indications, allowing the milk to burn out. Regular sex life, proper nutrition, avoiding stressful situations, moderate exercise, giving up bad habits and artificial termination of pregnancy is the best way to maintain women's health and protect yourself from various diseases and serious consequences.
Treatment of mastopathy
When preparing therapy, the physician always relies on what type of disease has been identified and what is the root cause of the disease.
At the same time, specialists often try to prescribe conservative types of treatment at an early stage. Only in the presence of certain factors are women offered surgical intervention.
Often, drug therapy is carried out if a diffuse form of the disease is found in the patient. This allows you to prescribe a course of hormonal drugs to the patient, after which positive dynamics will be visible.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=jIPo_UFwvRU
Medication
In order to equalize hormonal levels and regulate the menstrual cycle, patients are prescribed hormone therapy. Due to this effect, the breast tissue is freed from previously identified nodules.
To improve the condition, the following is prescribed:
- Women who have not crossed the threshold of 35 years are prescribed oral contraceptives. This could be Janine or Marvelon, which will be used according to the scheme as a means of preventing unwanted pregnancy.
- Antiestrogens. Fareston and Tamoxifen were recognized as the most common and effective. Usually a 3-month course is enough to improve the condition. It is worth remembering that longer therapy may lead to side symptoms.
- Gestagens. In the second phase of the cycle, women are prescribed Utrozhestan and Duphaston.
- Inhibitors of prolactin production. The drug is also prescribed during the period from 15 to 25 days of the menstrual cycle. Usually Parlodel is prescribed as the main drug.
- Androgens. Prescribed on the same days as the medications described above. Methyltestosterone is a priority among doctors, but its prescription is very rare. Almost all patients complain of too much hair on their body after the course of treatment.
Almost all women after 40 years of age suffer from the fact that they have a lot of concomitant ailments; for this reason, hormone therapy is not always indicated.
Conservative treatment for mastopathy can be carried out using non-hormonal medications. They can be combined with hormonal forms or used as monotherapy.
If the patient led a healthy lifestyle, and her illness is at an early stage, then there is a high probability that the disease will soon recede. For non-hormonal therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamin complexes and herbal remedies are used.
Among herbal remedies, Mastodinon deserves special attention, as it helps reduce prolactin levels in patients.
Moreover, it was noticed that the development of the pathological process in the mammary gland was stopped.
With its help, you can gently regulate the cycle and eliminate the severe symptoms of mastopathy. Acceptable to use
Mastodinon is long-term, for example, patients use capsules for about 90 days without a break. The drug is well tolerated, side effects are rare.
Surgical
The operation is performed if the patient has nodular mastopathy or fibroadenoma. In this case, the nodules should exceed 2 cm in volume. In very rare cases, the help of a surgeon is required if a cyst occurs in the chest.
If fibrous mastopathy is not large in size, then it is observed by a mammologist and a visit to a surgeon is not required.
For this disease, 2 types of surgical intervention are practiced:
- In the first case, the woman has not only the tumor removed, but also the mammary gland. We are talking about sectoral resection.
- In the second case, the patient needs enucleation or enucleation, then the cystic formation or tumor is excised.
When is surgery indicated:
- if the patient has noticed abnormal growth of fibroadenoma;
- the histology result indicates the malignant nature of the neoplasm;
- when a single cyst forms, it is necessary to remove fluid from its cavity using a puncture, but in case of relapse, enucleation is recommended.
The speed of healing and the rehabilitation process will depend on the patient’s lifestyle and the condition of her body. During the recovery stage, it is not recommended to indulge in coffee, tea, chocolate and cocoa. Due to some substances in their composition, increased pain may occur.
Moreover, in the future it is better to give up the harmful addiction to tobacco and alcohol consumption. The patient should take care of her state of mind, sleep more, and walk more often. Lean meat, boiled fish and foods of plant origin are added to the diet.
It is advised to pay special attention to the choice of underwear that will be worn after surgery. Due to an incorrectly selected bra, breast deformation or problems with ligaments may be noticed.
Treatment
Based on the test results and examinations performed, the doctor prescribes treatment, which directly depends on the type and root cause of mastopathy and is selected individually, taking into account all the characteristics of the woman’s body.
Conservative therapy is used in fairly early cases of detection of mastopathy and at the initial stage of development of the disease. Treatment is aimed at balancing and correcting hormone levels, eliminating disorders caused by pathology, especially in the genitourinary area and the endocrine system of the woman’s body.
Surgical intervention
The main treatment for nodular mastopathy is still surgery. The prognosis of this treatment is almost always favorable, since it is possible to completely remove the pathological focus in the mammary gland. The scope of the operation and the course of the recovery period directly depend on the stage of development of the tumor and its location.
Treatment of cystic mastopathy is mainly carried out using manipulation aimed at removing the cyst with a special instrument through a small incision in the skin. In this case, there is a possibility of a relapse of the disease, which should be treated with radical enucleation (removal) of the tumor.
In these cases, sectoral resection is performed - removal of a certain area of tissue and muscle of the mammary gland along with the neoplasm, to prevent hyperplasia and the transition of cells of these tissues to malignant ones. Such surgical interventions are carried out in a hospital, under local anesthesia.
The next day after the operation, the patient can go home, she will be prescribed treatment with anti-inflammatory and painkillers. A week after the operation, if the incision site has healed normally, the woman will have the postoperative sutures removed.
Traditional methods
Treatment of nodular mastopathy can also be carried out using folk recipes, the effectiveness of which will be noticeable in the early stages of the development of the disease. In more advanced cases, to prevent the development of harmful pathological processes, treatment by a specialist is still recommended, since there is a risk, and sometimes increases significantly under the influence of certain factors, of malignant degeneration of the neoplasm.
Traditional methods of treatment are suitable for almost everyone and are absolutely safe, causing virtually no side effects, which often occur after taking certain medications containing hormones. When relying on the effectiveness of traditional medicine, it should be remembered that a positive result appears only within a few weeks, and in some cases, treatment may not be effective at all.
The most common components of folk recipes are medicinal herbs:
- red brush;
- motherwort;
- burdock root;
- series;
- yarrow;
- mint;
- chamomile;
- evaleriana.
They are used in the form of tinctures, decoctions and alcohol solutions;
Compresses made from raw grated beets mixed with honey, or raw cabbage leaves and burdock leaves applied to the affected mammary glands are effective, best at night.