Inflammation of the subcutaneous connective tissue or bursitis of the elbow joint can be easily treated at home. Symptoms of this lesion appear gradually, which interferes with their diagnosis, therefore, if treatment is not started, over time this will lead to loss of ability to use the hands. The disease often develops in middle-aged men. The disease is also typical for students, athletes, people who, by the nature of their profession, overload their elbows: watchmakers, office workers, accountants.
What is elbow bursitis
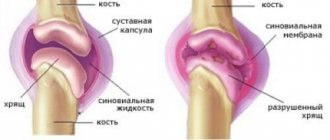
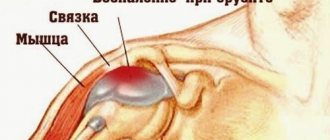
The inflammatory process that appears in the tissues of the synovial bursa (bursa) surrounding the olecranon is called bursitis. To understand how inflammation occurs, you should know that there are synovial bursa (bursa) filled with fluid around the joints. In normal condition, they play the same role as lubricating materials in the engine and prevent parts from coming into contact.
Specifically, the elbow is surrounded by the interosseous, subcutaneous ulnar and interosseous ulnar bursae. Synovial bursae in normal condition do not allow joint friction during movement. Sometimes inflammation occurs in the cavity of several or one bursa at once, and the fluid in the elbow joint increases, its composition changes, and the arm may swell and begin to hurt. This condition is called bursitis. Diseases of the knee, elbow and shoulder joints are common.
Inflammatory process of the elbow joint bursa
Elbow bursitis
Elbow bursitis is an inflammatory process of the elbow joint bursa, the appearance of which makes it difficult to perform functional movement between the large humerus located above and the two bones ulna and radius, located lower on the upper limb, at the point of their connection. The pathological process is accompanied by an increase in fluid content in the joint cavity. Surrounding tissues may also be affected.
The peculiarity of the anatomical structure of the elbow area, even with the slightest inflammation in this area, makes it difficult to perform the functions of the hand:
-flexion and extension;
- normal rotation (along the longitudinal axis).
And the reaction that manifests itself in the area of damage to the structures of the elbow formation, resulting from damage at the cellular level, can quickly spread to other compounds.
Symptoms
Elbow bursitis sometimes appears for no apparent reason, it is completely painless, and does not interfere with the movement of the arms. During examination, a doctor can only detect one or several formations. The chronic form of the disease occurs in the absence of treatment. Any signs of inflammation can easily be confused with gout and polyarthritis, so even if you feel slightly unwell, you should seek help from a specialist. Olecranon bursitis has the following symptoms:
- redness of the skin around the elbow, sudden swelling;
- the occurrence of swelling;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- swelling, which may increase in volume over time;
- feverish condition;
- limitation of joint mobility;
- intoxication, accompanied by sweating, headaches, loss of appetite, apathy;
- high body temperature;
- formation of pus;
- severe pain when bending your arms;
- as the joint capsule enlarges, the mobility of the arm becomes limited.
If you do not begin timely treatment of elbow bursitis and continue to ignore damage to the synovial bursa, the disease will turn into a purulent form, and subcutaneous phlegmons and fistulas will appear at the site of inflammation. If you detect any of the symptoms, you should not try to make a diagnosis on your own and start treatment; it is better to immediately seek help from a specialist.
Causes
Chronic ulnar bursitis can appear for several reasons:
- for diabetes mellitus;
- as a result of arthritis of any nature - gouty, rheumatoid, psoriatic;
- due to idiopathic inflammation of the synovial bursa;
- if there is an infection inside;
- with mechanical injury to the elbow;
- the cause of suppuration may be metabolic disorders, weakened immunity, or use of steroid drugs;
- due to microtrauma received;
- in the presence of purulent foci (boils, abscesses, abscesses).
Classification
Elbow bursitis has several forms, each of which is characterized by specific changes in appearance and intensity of pain. The most common classification is the division of the disease into the following forms:
- Chronic. Accompanied by mild pain that persists for a long time. There is no tumor, but a dense, small formation can be felt.
- Spicy. Symptoms of the disease include intoxication and fever. This form is often called traumatic bursitis.
- Recurrent. Occurs when the integrity of the affected area is repeatedly violated. The symptoms of recurrent bursitis are similar to the acute form.
In addition, it happens:
- Specific bursitis (post-traumatic). This type of illness appears in people engaged in monotonous strength work.
- Non-specific. It is observed in patients who have tuberculosis, treponema, and syphilis.
Based on the composition of the synovial fluid, it may be:
- Hemorrhagic bursitis. With this type of disease, blood enters the fluid.
- Serous. The safest form. Characterized by slight pain and swelling, elevated temperature. The serous fluid takes on the consistency of serum.
- Purulent. The person begins to feel bursting pain and severe swelling is observed. The presence of pus indicates inflammation and the presence of pathogenic bacteria. Purulent bursitis requires urgent treatment with antibiotics.
Diagnostic methods
If you notice the first symptoms of infection of the cavity of the ulnar bursa, you must urgently consult an orthopedic traumatologist. Often the disease is determined through a simple examination. Although there are cases when there is no exact certainty about the presence of a disease, therefore the following methods are used to specify and clarify the disease:
- Ultrasound. Using an ultrasound examination, you can find out exactly how much fluid is inside and whether there is a need for surgery.
- Puncture of the joint capsule. It is carried out when the doctor does not understand the nature of the disease - inflammatory or infectious. The fluid taken during puncture helps determine its sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Radiography. After an x-ray, a specialist can definitely tell about the presence of inflammatory fluid.
- MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging is used only in extreme cases, when it is necessary to find out the degree of advanced disease. MRI determines the depth of the joint capsule.
Puncture
For purulent acute bursitis of the elbow, the doctor may prescribe a puncture of the bursa exudate. During this procedure, the contents of the bursa are removed. In addition, during puncture it is possible to administer corticosteroids and antibacterial drugs, which have an anti-inflammatory effect. Before starting the procedure, the arm is bent at an angle of 90 degrees. The needle is passed between the lower edge of the lateral epicondyle and the outer edge of the olecranon.
Diagnostics
The primary diagnosis of elbow bursitis can be made by any doctor, since the signs are characteristic and indicate damage to a specific joint. Which doctor you go to for treatment depends on the process: for example, with gouty bursitis you need to go to a rheumatologist, and with a purulent process, you need to go to a surgeon. The first step is to contact your local physician, who will refer the patient to the right specialist.
The following methods are widely used in the diagnosis of this disease:
- radiography of the joint;
- Ultrasound;
- if there is a suspicion of damage to the deep ligaments, an MRI of the joint;
- Puncture of the elbow joint for bursitis makes it possible to determine the nature of the exudate, and often, after bacterial culture, to isolate the pathogen that caused the inflammation.
General clinical tests, such as a complete blood count, can show inflammatory changes when the process is severe,
Treatment of elbow bursitis
If the pathology is a consequence of a bruise, then the disease can go away on its own by limiting the movements of the sore spot and applying a compress using Dimexide. At the early stage of the disease, you need to organize rest for the joint. In other cases, anti-inflammatory therapy will be needed. To begin with, a specialist may prescribe non-steroidal drugs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac). If the cause of inflammation is bacteria, then antibiotics are necessary. If there is a large accumulation of fluid, a puncture should be performed.
In addition, treatment of elbow bursitis involves the application of immobilizing (pressure, scarf, plaster) bandages. If the damage is open, the wound is subjected to surgical treatment, after which an antiseptic bandage is applied on top. Only a specialist should treat infectious inflammation. Conservative therapy in such cases is ineffective. After healing, the patient should undergo physical therapy. If, due to the neglect of the process, treatment is not successful, then surgery is prescribed.
Medicines
In case of severe inflammation of the elbow, it is necessary to treat the disease with antibacterial, antiseptic, and anti-inflammatory agents. In addition to this, homeopathic ointments are used. Local treatment at home with Dimexide helps. Severe pain is relieved with glucocorticoids, analgesics, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Elbow bursitis is accompanied by pain and severe inflammation. To relieve such symptoms, the doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. All of them have antipyretic and analgesic effects. For bursitis, non-steroidal drugs are used systemically. This group includes the following drugs:
- Diclofenac. The product can be used in the form of rectal suppositories and injections. It has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. Suppositories are administered whole at 50 mg twice a day. Diclofenac should be used with caution in the presence of stomach diseases.
- Ibuprofen. The drug has antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. To relieve pain, the drug is prescribed as an injection. The course of treatment is 10 days. The product may cause side effects: nausea, allergic reactions, dizziness.
Antibiotics for elbow bursitis
Initially, for hemorrhagic and purulent bursitis, the patient is prescribed antibacterial treatment. Antibiotics should be prescribed by a doctor after laboratory tests - culture of the synovial cavity in order to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics. Depending on the infection that triggered the inflammatory process, the following antibiotics may be prescribed:
- Lincomycin. The product slowly develops stability and is quickly distributed in tissues. The daily dosage of the drug is 2 g. Duration of therapy is 2 weeks. Taking the medication is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation due to the penetration of the active substance through the placental barrier.
- Amoxiclav. Combined antibiotic medication. Belongs to the pharmacological group of penicillins. Used in tablet form. The average course of treatment is 14 days. Amoxiclav is prescribed with caution for liver failure and severe renal impairment.
The modern pharmaceutical market offers a large number of ointments that are successfully used against inflammation of the elbow joint. The preparations contain specific components that increase capillary permeability: pepper extract, bee or snake venom, essential oils. They locally increase blood flow, cause tissue hyperemia, and cope well with the symptoms of inflammation of the joint capsule. All medications can be used at home, but they should only be prescribed by a doctor. The most effective are:
- Collagen Ultra. Ointment or cream for external use. Thanks to the free amino acids contained in the preparation, inflammation goes away faster when using the ointment. Collagen relieves pain, strengthens connective tissue, and eliminates muscle tension. Rub the ointment in with massage movements, without pressing on the affected area. Side effect: possible development of allergies.
- Voltaren. The drug is considered the most effective in eliminating pathological processes in joints and muscles. The ointment is quickly absorbed, especially if it is applied under a bandage. In addition, the effect of the drug on tissue lasts more than 12 hours, which helps to use Voltaren only 2 times a day. Side effects: anxiety, insomnia, headache.
Vishnevsky ointment for bursitis of the elbow joint
The composition of the well-known ointment includes castor oil, xeroform, and tar. The drug is an effective antiseptic, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agent. In addition, Vishnevsky ointment is an excellent mixture for treating the inflammatory process, because it quickly resolves the exudate. For bursitis, this remedy, due to its structure, is well absorbed into the skin. The ointment is easy to apply and make various compresses. This remedy can cure a disease accompanied by the accumulation of pus. Contraindication – severe tendency to allergies.
Nutritional Features
To help the body fight the disease, you need to eat foods with vitamins C, A, E, and eat more gelatin (at least 3 times a week). Therefore, you should eat more:
- products of plant origin: cereals, cabbage, viburnum, carrots, beets, sea buckthorn, currants, citrus fruits, nuts;
- You can also include jellied fish, jelly, jelly, jelly in your diet;
- products of animal origin: beef, chicken, liver, fish, seafood, dairy products.
Surgical intervention
For bursitis, surgery is performed in extreme cases when all traditional methods are ineffective. As a rule, surgical treatment is necessary for purulent-hemorrhagic inflammation, recurrent or persistent serous bursitis. During surgery, in some situations, purulent exudate or part of the bursa may be removed, and if the disease is advanced, then the entire bursa may be removed. The following methods exist:
Treatment
Limiting the motor activity of the elbow is where you need to start treating elbow bursitis. Treatment involves the application of immobilizing (kerchief, pressure, and sometimes plaster) bandages. If the damage is open, the wound undergoes surgical treatment and is then fixed with an antiseptic bandage. The patient is prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics.
If there is exudate in the ulnar bursa, it must be removed using a syringe under absolutely sterile conditions. To relieve the symptoms of inflammation, the following methods are used:
- A steroid-type hormone (for example, Kenalog) is injected into the cavity of the joint capsule;
- non-steroidal drugs are used, which are taken by the patient in combination;
- ointments are used (“Voltaren”, “Ibuprofen”);
Treatment of bursitis of the elbow joint involves the inclusion of immunostimulants with a variety of vitamin complexes in the treatment program. After the inflammation is cured, the patient must undergo physical therapy.
If conservative treatment is not successful due to the advanced stage of the process, then surgery is prescribed. The most effective operations:
- drainage of the joint capsule. Liquid is pumped out of it through a small incision;
- removal of the bursa. During rehabilitation, a new bursa will be formed in the body.
Treatment with folk remedies
You cannot self-medicate for bursitis, because... this will lead to complications. All therapy must be coordinated with your doctor. Although folk remedies cannot completely cure the disease, they can alleviate the symptoms of connective tissue inflammation. As a rule, treatment of elbow bursitis at home involves the use of an ointment made from aloe juice and honey. To prepare it you will need plant juice, several parts of alcohol and honey. All ingredients are thoroughly mixed and applied to the affected area 2 times a day. A few more popular recipes:
- Salt compress. To prepare it, you need to dissolve a large spoonful of salt in 0.5 liters of water, moisten a cloth with the solution and place it on the sore spot. Wrap the top with film and a warm scarf. The duration of the procedure is approximately 8 hours. This treatment is good at drawing out excess fluid from the inflamed bursa.
- Onion mixture with laundry soap and honey. To prepare the recipe you will need a medium onion, a bar of soap and 500 g of honey. All ingredients must be thoroughly mixed and used as a compress. It must be done before bed for three weeks.
Video
Source sovets.net
Bursitis of the elbow joint is an inflammatory lesion of the synovial bursa - bursa. Due to the close proximity of the neurovascular bundle and a thin layer of fatty tissue, the elbow joints are vulnerable to various traumatic factors, reacting sharply to even the slightest damage. In response to inflammation, the inner lining of the joint capsule begins to actively produce joint fluid, with an excess of which the bursa swells and increases in size. Clinically, this is manifested by local swelling, moderate to acute pulsating pain, forcing one to abandon any movements of the arm in the elbow joint.
The disease is more often diagnosed in young and middle-aged men. It is typical for athletes, students and people whose occupation overloads their elbows: accountants, office workers, watchmakers, miners. Those who suffer from gout or other types of arthritis are also susceptible to the disease.
Bursitis of the elbow joint usually does not pose a serious danger; the general condition worsens slightly. The prognosis is favorable even with surgical treatment with further rehabilitation. But this does not mean that the disease can be taken lightly: there are cases when the infection, due to purulent inflammation, spreads to nearby tissues or spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream, leading to serious consequences (phlegmon, sepsis, osteomyelitis, fistulas, lymphadenitis or persistent contractures) .
Next, we will consider in detail the causes and changes that occur in the synovial bursa during its inflammation, the characteristics of symptoms and treatment options for different types of elbow bursitis.
Why does the disease appear?
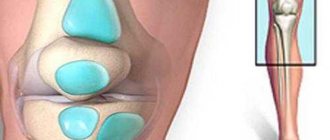
Bursitis is called inflammation of the periarticular bursae. Such synovial “capsules” - bursae - are elastic sacs filled with intra-articular fluid. They are located around the joints between muscles, bones and tendons in places that bear the greatest load. Hence their main task is to cushion joint structures during movement.
There are more than a hundred bursae in the body, but there are only three in the elbow joint: under the skin, between the ulna and radius bones, and near the distal (extreme) end of the humerus. Usually, when we talk about bursitis of the elbow joint, we mean the subcutaneous bursa, which is located near the olecranon process.
The occurrence of the disease is provoked by:
- injury to the elbow joint or tendon apparatus;
- inflammatory lesions of the elbow (arthritis, gout);
- infectious diseases (gonorrhea, tuberculosis, brucellosis, syphilis);
- wounds in the joint area;
- purulent pathologies (osteomyelitis, erysipelas, furunculosis, etc.);
- impaired metabolism or intoxication of the body (in case of poisoning with food, industrial toxins or alcohol);
- allergic or autoimmune conditions associated with “self-aggression” of immune mechanisms.
One or a combination of these factors puts increased pressure on the bursa. The latter stimulates cells, which subsequently begin to actively produce synovial fluid. When its quantity reaches its limit, the bag stretches, significantly increasing in size. The “swollen” bursa compresses the surrounding tissues and becomes inflamed, thereby causing symptoms of the disease.
The mechanism of development and features of elbow bursitis
The joint capsule is a slit-like capsule with synovial fluid inside, which acts as a lubricant to facilitate movement in the joint. It is a kind of shock absorber, protecting bones and periarticular tissues from friction or pressure.
When inflammation begins in the joint cavity for one reason or another, the production of synovial fluid increases, its nature and composition changes, pain appears, and bursitis of the elbow joint develops. The bag enlarges and swells, sometimes reaching significant sizes. If the exudate is mixed with blood, hemorrhagic bursitis occurs. If inflammation is caused by infectious pathogens that have entered the cavity, a purulent process develops, which can spread to neighboring tissues and even organs. With a long course of the disease, adhesions, foci of necrosis or calcification form.
Swelling of the elbow joint due to bursitis
The development and course of elbow bursitis has two characteristic features:
Firstly, the elbow joint is more susceptible to injury and overload, since it is not protected by either fat or muscles. Therefore, bursitis of the elbow joint is diagnosed more often than, for example, bursitis of the knee, and is in first place in terms of prevalence among inflammations of the bursae of other joints.
Secondly, with ulnar bursitis, of the three synovial bursae of the elbow, the bursa located on the extensor surface in the area of the olecranon process is most often affected. With bursitis of the knee, out of ten, only three bursae are most often affected, and the protrusion of the inflamed bursa can be not only towards the kneecap, but also into the popliteal fossa.
Inflammation of the bursa in the area of the olecranon
Otherwise, the course of the disease is practically no different from inflammation of the bursae of other joints.
Recovery and rehabilitation
Rehabilitation in order to restore mobility in the joint should begin from the first days after pain relief. The rest time for the joint should be minimal, since immobility leads to wasting of the surrounding muscles and changes in the tendons. In the first day after severe pain occurs, it is imperative to suspend the limb from the neck; for this there are special bandages, or you can use an elastic bandage. If the patient has signs of chronic bursitis and the history of the disease is long enough, it is necessary to use a bandage for the elbow joint or an elbow orthosis during exacerbations.
The objectives of exercise therapy for bursitis of the elbow joint are to restore the mobility of the joint, improve the production of synovial fluid, reduce the production of exudate in the cavity of the bursa, improve the blood supply to the joint capsule, and improve the outflow of venous fluid containing harmful substances. Physical therapy should be performed already at the stage of subsiding exacerbation, always under the guidance of an experienced instructor. Thus, exercises with a small range of motion should be avoided, and weights should be prohibited.
Causes of the disease
There are many reasons that provoke inflammation of the bursa. The main one is various mechanical injuries: elbow bruises, abrasions, wounds, fractures, as well as microtrauma due to everyday increased stress.
- deposition of salts in the synovial cavity;
- arthritis of various types: gouty, rheumatoid, psoriatic;
- erysipelas;
- boils, bedsores, carbuncles with the introduction of infection from the lymph or bloodstream into the joint of infection.
- diabetes,
- immunodeficiency,
- old age,
- metabolic disorder,
- professional activity,
- presence of an autoimmune disease,
- allergic reactions,
- taking steroids.
Causes of the disease
Bursitis, like any inflammation, can be aseptic, that is, occurring without the participation of harmful microorganisms, and infectious. The following reasons lead to the development of aseptic bursitis:
- metabolic disorders, for example, accumulation of crystalline substances (urates) in the joint cavity and in the tissues of the joint capsules. These are gouty bursitis, arthritis and bursitis with terminal uremia (urea). Such diseases are called crystalline bursitis;
- prolonged static tension in the elbow joint, with support on the surface. This situation occurs in people of certain professions, or when they remain in a stationary position for a long time, for example, while intoxicated. In addition, there may be opposite situations associated with excessive load on the joint, for example, during certain sports. So, there is the concept of “tennis elbow”. Working at a computer with constant support on your elbows is very harmful;
- Severe trauma, such as a bruise, can also lead to aseptic inflammation. There is no violation of tissue integrity here, but reactive aseptic inflammation with exudation occurs, as a result of which inflammation of the elbow joint develops, and then bursitis. Traumatic bursitis also often develops with chronic, minor impact, but permanent damage to articular tissues. These microtraumas must occur over a long period of time for symptoms to develop. The post-traumatic process is typical for athletes;
- Sometimes the cause of inflammation of the joint capsules is an allergic reaction. This does not happen often, but it does happen if the patient has a multivalent allergy. Also, pronounced toxic swelling of allergic origin can develop from bites, for example, of wasps or bees.
Don't Miss: Bunion
Types of bursitis
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| Classification | Kinds |
| According to the process | Spicy |
| Subacute | |
| Recurrent | |
| Chronic | |
| By localization of inflammation | Bursitis of the subcutaneous ulnar bursa |
| Bursitis of the interosseous ulnar cavity | |
| Radioulnar bursitis | |
| Taking into account the pathogen | Nonspecific infected (causative agent - streptococcus, staphylococcus) |
| Specific infected (causative agent - gonococcus, pallidum spirochete, mycobacterium tuberculosis, etc.) | |
| Due to the appearance | Professional |
| Lime | |
| Valgus | |
| Brucellosis | |
| Proliferating | |
| According to the composition of joint exudate | Serous |
| Hemorrhagic | |
| Fibrinous | |
| Purulent |
- The subcutaneous bursa is most often affected with the development of the serous type of the disease.
- Nonspecific infected bursitis of the elbow is also common, and rarely - brucellosis, syphilitic or another specific type.
- Of all types of pathology, the purulent one is the most dangerous, since it gives severe complications: sepsis, osteomyelitis, the appearance of an abscess, phlegmon, fistulas, inflammation of the ulnar lymph nodes.
- The most “harmless” is serous bursitis of the elbow joint, since the joint fluid is not infected.
The primary purulent process develops when the elbow is injured, the secondary one - against the background of an existing acute or chronic process after infection of the bursa secretion.
Post-traumatic serous bursitis can eventually become purulent due to the high risk of infection through existing wounds, scratches or other violations of the integrity of the skin.
Characteristic symptoms
Symptoms of acute serous-hemorrhagic or serous process
Mild pain, swelling, redness, increased temperature in the area of inflammation.
Movement in the elbow is limited.
There may be a spherical protrusion visible to the eye, soft to the touch.
The general condition, as a rule, does not suffer; only some patients experience low body temperature, accompanied by malaise and weakness.
Acute inflammation ends with recovery or becomes chronic.
Symptoms of a chronic type of disease
Chronic bursitis of the elbow joint lasts much longer than acute bursitis, manifesting itself with the following symptoms:
- moderate pain when moving,
- discomfort in the elbow area,
- movements in the joint are preserved almost completely,
- the area of inflammation looks like a dense formation.
Purulent bursitis
Symptoms of a purulent type of disease:
- Pain with purulent is sharp, bursting or tugging.
- The more acute the inflammation, the more intense the pain syndrome.
- The elbow is hot to the touch, swollen, the skin is congested with blood (hyperemic), and sharp pain is noted on palpation.
- Movements are severely limited, regional lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Symptoms of general intoxication appear: the temperature rises to 38–39 degrees, you feel weak, tired, sweating, headache, and irritability.
Manifestations of the disease
Symptoms and treatment of pathology are closely interrelated. After all, based on the clinical picture and additional studies, the doctor makes a diagnosis and then prescribes therapy. If there are suggestions that bursitis of the elbow joint is progressing, then the symptoms should be as follows:
- Initially, a small lump, lump, or swelling may be found on the elbow, which grows over time;
- a tumor appears, when palpating the affected area it is not difficult to notice that the temperature in this place is higher than in nearby healthy tissues;
- another characteristic sign is an increase in pain as the pathology progresses (as the anomaly develops, the pain bothers the person even when stationary);
- general weakness, dizziness, increased body temperature (for some types of the disease in question, up to 40°C).
With this disease, movements are not fully limited; this fact distinguishes the pathology in question from arthritis. By the way, bursitis can also affect the knee. The clinical picture is similar. A qualified specialist will tell you how to treat bursitis of both elbows and knees.
Treatment methods
Acute bursitis of the elbow joint is treated by a rheumatologist or orthopedist, and chronic advanced bursitis is treated by a surgeon.
Acute serous inflammation is treated by applying a tight bandage to limit the range of motion, taking one of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, applying cold, lubricating the elbow with ointment, or better yet, a gel with an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. With severe inflammation, for example, with traumatic bursitis, the symptoms are relieved by the injection of corticosteroids into the bursa, which have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect.
Treatment of the purulent process is complemented by antibacterial therapy. A therapeutic puncture of the synovial bursa is indicated to remove excess fluid, rinse the cavity, and administer an antibiotic there. In severe cases, the bursa is drained. If the above methods are ineffective, an operation is performed to excise the inflamed bursa. During the period of remission, physiotherapy is indicated to prevent re-exacerbation.
Summary
Modern treatment of elbow bursitis provides a positive outcome and relief from symptoms even with severe purulent inflammation. It is only important not to let the disease progress, to consult a rheumatologist or orthopedist in time and get treatment - only then can you hope for a speedy recovery without complications.
Source sustavzdorov.ru
With inflammation of the synovial bursa, any person’s general condition worsens.
This is the first sign of bursitis. It can be found in the area of any joint: hip, shoulder, knee.
However, serous or traumatic bursitis of the elbow joint is more often diagnosed in patients of different ages: the symptoms, causes and effective treatment at home and in the hospital will be discussed further in the article.
The disease is quite serious, so it is better to stop the inflammatory process at the initial stage. The consequences and complications can be quite unpredictable.
You need to know how to properly treat bursitis of the elbow joint, which specialist you can contact, what to do if your arm hurts unbearably in the bend.
Prevention
Prevention of elbow bursitis includes:
- normalization of lifestyle (dosed physical activity and proper nutrition high in fiber and nutrients);
- periodic warm-ups for people at risk: jewelers, writers, journalists, office workers;
- gentle physical activity and mandatory medical examinations for miners, loaders, athletes, etc.;
- treatment and control of elbow joint injuries;
- prevention and timely treatment of inflammatory diseases (arthritis, gout);
- periodic examinations for infectious and sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, tuberculosis, syphilis);
- control of allergic and autoimmune conditions;
- treatment of all wound surfaces with antiseptics (especially in the joint area);
- getting rid of bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol.
To prevent complications of elbow bursitis - the formation of adhesions, calcification, arthritis, osteomyelitis, necrosis of sepsis and even death - a proper examination and a clear treatment plan are necessary.
Remember, only a specialist can prescribe effective and safe therapy!
Causes of elbow bursitis
Elbow injuries are quite common. It happens in adults and children. Some do not pay attention until pain occurs, others experience traumatic shock and cannot recover for a long time.
Minor damage, accidental movements, sharp impacts can lead to injury. As a result, bursitis of the elbow joint develops; the article offers the main symptoms and treatment methods for you to get acquainted with.
Bursitis of the right and left elbows appears for different reasons. Inflammation of the joint capsule, nerves, tendons and muscles located nearby occurs from impact, bruises, microtraumas, abrasions.
Other equally common causes of post-traumatic elbow bursitis:
- finding the arm for a long period of time in a very uncomfortable position, when the elbow is tense, pinched or lowered from the working surface;
- salt deposits near the joints;
- presence of arthritis, diabetes;
- unsuccessful movement of a limb;
- drug treatment with steroids.
People who receive increased loads on the elbow area are at risk: athletes, draftsmen, office professionals.
Mechanism of disease development
The disease, called bursitis of the elbow joint, has its own characteristics of occurrence and course.
Inflammation of the joint or ulnar bursa occurs, which is a small capsule filled with synovial fluid.
It plays the role of a shock absorber, protecting periarticular tissues and bones from friction.
Once the infection gets into the bursa, the process of inflammation begins. The amount of synovial fluid immediately increases, and its composition gradually changes.
It is noticeable that the elbow is swollen. There is pain and the joint becomes inflamed. The bag continues to expand and swell.
Swelling becomes noticeable. Very soon, in addition to synovial fluid, purulent mucus or blood clots will appear in the inflamed bursa.
With such symptoms, the presence of bursitis of the hemorrhagic elbow joint is usually stated.
Infection accompanies a purulent process. It is localized not only in the area of the left or right elbow, but also spreads to neighboring tissues. Purulent bursitis of the elbow joint is unpredictable and dangerous.
The consequences may be different:
- calcification;
- tissue necrosis;
- formation of adhesions.
Unlike other diseases, chronic bursitis of the elbow joint has distinctive features:
- There is no fat layer on the elbows, so the muscles are not protected. Knees hurt in much the same way when the bursa becomes inflamed.
- Three synovial bursae are affected at once, but the bursa located in the area of the olecranon on the extensor surface suffers more.
Otherwise, elbow bursitis has symptoms similar to other diseases.
Symptoms of elbow bursitis
Having found out why elbow bursitis occurs, it is necessary to identify its symptoms, by which the disease is determined. Symptoms directly depend on the type of disease.
Serous bursitis can be acute or chronic. It differs in that the fluid in the bursa resembles serum, but the exudate is not infected.
Its symptoms are pronounced, but attract little attention:
- the elbow is slightly swollen, it hurts when making any movements;
- swelling appears in the area where the pain is located;
- the temperature rises slightly (up to 37.5º), but a rush of heat is felt at the site of the joint lesion;
- The skin around the bursa turns red.
X-ray shows that there is no internal damage to the joints, but the cavity of the synovial bursa is significantly enlarged (up to 10 cm), which means that motor function will be impaired.
If left untreated, elbow bursitis will change from acute serous to chronic, and the symptoms will become less noticeable.
Let's look at what acute purulent infected bursitis of the elbow joint looks like. His signs are different. The key point is the pain felt even with a light touch.
- the presence of significant edema due to the accumulation of synovial fluid;
- the swelling sharply increases in size (up to a chicken egg);
- spreading of swelling to adjacent tissues;
- redness of the skin in the elbow area;
- movement is limited;
- temperature rises to 39º;
- On palpation, pulsation is felt at the site of the lesion.
You may notice pus on the skin if there are wounds from injuries.
If the elbow is swollen and inflammation of the elbow joint continues due to bursitis, treatment must be started immediately.
Otherwise, new symptoms will appear: open fistulas, phlegmon, deterioration of general condition. Only a surgeon can completely cure such a pathology.
There will be a puncture, surgery and long-term rehabilitation after a course of therapy.
Acute hemorrhagic bursitis is characterized by the presence of blood cells in the fluid. The cavity of the bag increases and becomes inflamed. Tissue swelling appears.
To stop the spread, you have to apply a tight bandage to fix the joint. Sometimes surgical removal of the bag is required.
Forms of the disease and characteristic symptoms
The acute form of bursitis is characterized by a sudden onset of the inflammatory process, which manifests itself the next day after the injury. There is a slight swelling in the area of the apex of the elbow, the consistency is soft to the touch. The swelling is painful, which manifests itself both upon palpation of the affected area and at rest. Inflammation is accompanied by general poor health, weakness and fever. Day after day, over the course of one week, the swelling grows, causing the person significant discomfort and hindering movement in the joint. Such a patient must immediately seek medical help and undergo the course of treatment prescribed by the doctor in order to avoid the disease becoming recurrent, when even a minor factor leads to a new round of inflammation after an apparent recovery.
Bursitis is more often unilateral, less often it occurs symmetrically on both elbow joints.
A feature of the chronic form is not a sudden, but a gradual development of small edema. A person does not immediately pay attention to the unusual condition of the elbow, so the disease can last for years in a sluggish form. The prolonged course of the inflammatory process negatively affects the joint itself, causing pathological changes in it.
Chronic bursitis is dangerous for joint health
Unlike joint disease (osteoarthritis or arthritis), which hurts mainly when moving, bursitis hurts both at rest and when pressure is applied, as well as during movement.
If an infection has been introduced into the synovial bursa (most often from the outside as a result of a bite or cut), then the pathogen begins to multiply inside the periarticular pocket, causing first serous and later purulent inflammation. It is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature, even fever. The swelling site is hot to the touch. Septic, or infectious, bursitis is dangerous due to the possible development of necrosis of the walls of the joint capsule and the entry of infection into the general bloodstream.
Purulent bursitis is an advanced case of septic inflammation of the synovial bursa
In summary, common symptoms of bursitis include:
- Swelling: This is usually the first sign that the patient notices. The skin on the back of the elbow may be loose, so swelling may not be noticed at first. In some cases, swelling increases rapidly and is immediately visible. The tumor may be the size of a golf ball at the tip of the elbow.
- Pain: As the bursa stretches, the pain in the elbow increases, especially when flexing. As a rule, with extension the pain decreases or disappears. But there is a category of people with elbow bursitis who do not experience pain in principle, regardless of whether their arm is bent or straightened.
- Redness or marked warmth on the back of the elbow: may indicate an infection.
- Tenderness in and around the elbow.
- Pus: In advanced cases of infectious inflammation, the presence of yellow or white, thick, cloudy exudate in the infected elbow is typical.