What is Bartholin's gland?
The main function of the Bartholin gland is the secretion of secretion, which contributes to the normal, physiological conduct of sexual intercourse.
This is due to the ability of the secretion to provide the role of a lubricant, which is secreted into the vestibule of the genital organs. The Bartholin gland is located in the thickness of the labia. It has a paired arrangement, its diameter does not exceed 2 cm. The excretory ducts are located on the inside of the labia minora. It is when the secretory function cannot be carried out, due to a violation of the outflow of viscous secretions, that the disease bartholinitis develops.
In most cases, the root cause of cystic formation of the gland is an infectious-inflammatory process of the external genital organs. A number of factors contribute to the spread of infection and damage to the excretory canal of the Bartholin gland:
- A decrease in the body's defenses, provoked by the presence of chronic diseases, vitamin deficiencies, long-term use of medications, acute viral infections, psycho-emotional disorders (stress, nervous breakdowns, depression), hormonal imbalances;
- Infectious and inflammatory lesions of the vagina: dysbiosis, vulvovaginitis, colpitis. From the area of the external labia, the infection spreads further, and under its influence the outlet of the gland canal closes. As a result, secretion accumulates in the duct and a cyst forms;
- Violations of intimate hygiene rules. Lack of cleanliness of intimate areas contributes to the development of pathogenic microorganisms and their further spread. Carrying out hygiene measures in the genital area allows you to mechanically remove excess amounts of pathogenic bacteria, which prevents the occurrence of infectious and inflammatory processes. Hygiene is especially important during menstruation: a woman needs to change pads, tampons, and clean the intimate area on time;
- Wearing poor quality underwear. Artificial, non-natural fabrics, caustic dyes used in the manufacture of panties, disrupt air and heat regulation, can provoke allergic reactions, excessive accumulation of mucus;
- Injuries, mechanical damage to the vaginal vestibule during surgery, sexual intercourse, deep hair removal. Mechanical injury promotes the active penetration of infectious agents. Improper healing of damage to the vulva provokes the appearance of scars and tissue growths of the mucous membrane, which can disrupt the normal outflow of mucous secretions;
- Promiscuous, unprotected sexual intercourse. Such sexual behavior not only greatly increases the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases, but also contributes to the rapid development of pathogenic microflora.
Features of the disease
The Bartholin gland is located between the labia majora and minora, at their base. The excretory ducts open in the upper part of the labia minora. The main task of this gland is to secrete a special grayish substance. Due to its composition, mucus provides high-quality hydration of the vaginal opening, which will allow you to have painless sex.
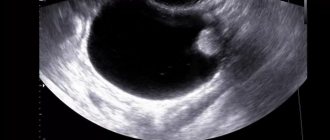
A Bartholin gland cyst is a small tumor located inside the gland. It has a round shape, and inside there is a secret. It is separated from other tissues by a dense capsule. The cyst is formed due to the closure of the excretory duct of the gland. This violation does not allow sufficient lubricant to be released into the vagina, which causes discomfort during sexual intercourse. If not treated in a timely manner, the cyst increases in size, which does not allow full movement. In addition, a purulent neoplasm appears on it, which leads to the development of infection. A photo of a cyst in women is located below.
What is pathology
Bartholin's glands are paired organs located on both sides of the vestibule of the vagina in the area of the labia majora. The work of the glands is to produce secretion, which is excreted through the excretory duct. The secreted mucus prevents the penetration of infections, moisturizes the mucous membrane, prevents its dryness and pain during sexual intercourse.
The work of the glands is controlled by the central nervous system and is directly related to cyclical changes in the hormonal system. The paired organs are small (no more than 2 cm in diameter) and are not visible or palpable.
As a result of blockage of the excretory duct (full or partial), the removal of secretions is disrupted. This leads to the accumulation of mucus inside the canal, the increasing volume of which stretches its walls, which leads to the formation of a hollow node filled with secretion or a cyst.
In most cases, a violation of the outflow of mucus and the formation of a cystic node is provoked by an infection. When it penetrates the cavity of the gland, an acute inflammatory process begins, the contents of the cavity become purulent.
Often the occurrence of cystic formation is caused by mechanical blockage of the gland canal. This situation occurs with tissue proliferation or fibrosis.
The prognosis for Bartholin's cyst is generally favorable. Timely treatment and preventive measures will prevent complications and relapses.
Characteristic features of cystic formation:
- Education has no hereditary predisposition;
- The cyst in expectant mothers does not affect the hormonal composition, the course of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus,
- Relapses are possible;
- An inflamed cyst of the labia can reach 8 cm in size;
- Uncomplicated formations go away on their own;
- Cystic formation is not prone to degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
Causes of bartholinitis:
Bartholinitis occurs due to infection in the Bartholin gland through a narrow opening of the excretory duct on the inner surface of the labia minora. Once deep into the gland, microorganisms actively multiply. This leads to inflammation and suppuration of the Bartholin gland.
Not all genitourinary infections cause bartholinitis. In the vast majority of cases, bartholinitis is provoked by sexually transmitted infections. Most often it is gonorrhea, less often - trichomoniasis and chlamydia.
Bartholinitis of nonspecific etiology is extremely rare - in this case, the causative agent is bacteria - staphylococci, Escherichia coli, streptococci, and so on. This is possible if personal hygiene rules are not followed. It should also be taken into account that even in the presence of sexually transmitted infections, bartholinitis does not develop in everyone and not always.
Immunity plays an important role in the development of the disease: if it is weakened, the chances of developing bartholinitis increase.
Depending on the clinical course of the disease, bartholinitis can be acute or chronic. Acute bartholinitis is characterized by the formation of a true or false abscess of the Bartholin gland (a limited focus with pus).
When a false abscess forms, the excretory duct of the gland first becomes inflamed (“canaliculitis”, in scientific terms). The skin over the site of inflammation turns red and swells. If you press on the inflamed area, pus will come out. Next, a blockage of the excretory duct of the gland occurs and pus is no longer released, but accumulates in the Bartholin gland. Because of this, the gland is greatly stretched and protrudes, forming a painful “bump”-shaped formation. During movements - when walking, running, during sexual intercourse - the pain intensifies, and a burning sensation appears in the perineum. Sometimes body temperature rises slightly. If you do not contact a gynecologist for a long time, the disease becomes chronic.
With a true abscess, the infection penetrates directly into the Bartholin gland, and the parenchyma of the gland melts. In this case, the symptoms of the disease are more pronounced than with a false abscess. The labia majora and minora become very swollen. The body temperature rises to more than 38 degrees, the inguinal lymph nodes enlarge, chills, weakness, and “pulsating” sharp pain in the labia majora appear. Spontaneous opening of the abscess with the release of yellow-green pus is possible, which leads to a weakening of the symptoms of the disease. But if left untreated, the inflammation recurs again and gives complications, or, like a false abscess, becomes chronic.
In the chronic form of bartholinitis, the symptoms of the disease temporarily subside and worsen again. Instead of an abscess, a cyst (liquid formation with inflammatory exudate) forms in the gland.
With any form of bartholinitis, you should never self-medicate or try to squeeze out an abscess or cyst - this can lead to blood poisoning . If such symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a gynecologist.
Development mechanism
The formation of Bartholin gland cysts, resulting from an infectious lesion, is provoked by the ingress of pathogenic organisms. Pathological vaginal discharge that enters the vulva area transmits infection to the Bartholin glands. Penetrating into the excretory canal, infectious agents provoke pathological changes, inflammation, tissue swelling, as a result of which the duct is blocked and the outflow of mucous secretion is disrupted. Accumulating mucus, its increasing volume, stretches the walls of the canal, forming a cavity filled with a thick substance.
Inflammatory processes are provoked by penetrating pathogenic bacteria and organisms: Trichomonas, gonococci, streptococci, staphylococci.
A Bartholin gland cyst can develop for two reasons: as a result of infection or mechanical blockage of the excretory duct of the gland. Infection of the gland can occur as a result of specific pathogens entering it (chlamydia, gonococci, ureaplasmas or trichomonas), or when it is affected by nonspecific pathogens (streptococci or staphylococci, E. coli or Proteus).
Here it must be said that a key role in the formation of a cyst is played by predisposing factors that create conditions for infection and blockage of this organ. These include:
- weakened immune system;
- the use of lubricants that can clog the ducts of the sebaceous glands;
- neglect of the rules of hygienic care of the genitals;
- promiscuity;
- wearing tight synthetic underwear;
- wearing tight clothing (trousers or jeans);
- epilation of the bikini area, which can damage the skin;
- presence of bacterial vaginosis;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus);
- immunodeficiency states;
- stressful conditions;
- gynecological diseases (endometritis, adnexitis or cervicitis);
- general diseases (pyelonephritis, tonsillitis or caries);
- gynecological manipulations that can cause damage to the vulva and vaginal mucosa (hysteroscopy, abortion);
- rough sex.
When infectious agents enter the vaginal mucosa, they cause inflammation, which also spreads to the excretory canals of the Bartholin glands. This provokes canaliculitis, i.e. blockage of the canal, as a result of which the secretion produced by the gland accumulates in its cavity, forming a cyst. If the blockage is not removed in a timely manner and the fluid is not allowed to escape, it will begin to fester and cause an abscess.
In some cases, a cyst may appear without the participation of infectious agents. For example, the duct may become clogged due to greatly overgrown surrounding tissue or, more likely, due to damage to the mucosa with subsequent overgrowth.
The causes leading to this pathological condition may have different etiologies. But it is customary to identify the main causes and factors that increase the chance of developing a Bartholin gland cyst.
Main reasons:
- Venereal diseases of the genital organs. Most often caused by chlamydia, trichomonas, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, toxoplasma.
- Violation of the rules of personal intimate hygiene.
- Fungal diseases caused by mycelium of the genus candida.
- Infection of gland tissue with E. coli, streptococcal or staphylococcal bacteria.
- Gynecological procedures that resulted in mechanical damage to the genital organs.
- Hysteroscopy, frequent abortions.
In addition to the main causes, this disease can occur under the influence of negative factors:
- Decreased immunity (due to chronic diseases).
- Injury to the skin (often occurs when visiting beauty salons for the purpose of hair removal).
- Wearing uncomfortable, synthetic underwear.
- The use of hormonal and antibacterial drugs for a long time, or in a dosage significantly exceeding the therapeutic one.
It should be especially noted that promiscuous sex life and non-use of barrier contraception methods lead to the development of this pathology.
Sometimes the appearance of a Bartholin gland cyst can be caused by:
- Seasonal influenza epidemics.
- Tonsillitis.
- ARVI.
- Sinusitis.
- Dental diseases (gingivitis, caries, periodontitis).
- HIV infection.
As a rule, a cyst is formed due to a violation of the secretion of mucous secretion from the glands, which has a detrimental effect on a woman’s health. The accumulated discharge is enclosed in a dense capsule, forming a cyst. Its dimensions can reach up to 8 cm. Such a violation is provoked by various factors, the main ones being the following:
- sexually transmitted infections (ureaplasma, trichomonas, gonorrhea, mycoplasma, chlamydia);
- candidiasis (thrush);
- a violation of the consistency of the secretion, an increase in its viscosity, this creates difficulties in evacuating it to the vestibule of the vagina.
The development of a Bartholin gland cyst is facilitated by the following unfavorable factors:
- failure to maintain personal hygiene of the genitals, especially during menstrual periods;
- mechanical damage to the skin during depilation;
- regularly wearing tight underwear. It does not allow the secretion to be fully released, so stagnation occurs, which is why a cyst forms;
- promiscuity;
- irregular sexual intercourse;
- the presence of a chronic infection in the body.
Reasons for development
The causes leading to this pathological condition may have different etiologies. But it is customary to identify the main causes and factors that increase the chance of developing a Bartholin gland cyst.
Main reasons:
- Venereal diseases of the genital organs. Most often caused by chlamydia, trichomonas, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, toxoplasma.
- Violation of the rules of personal intimate hygiene.
- Fungal diseases caused by mycelium of the genus candida.
- Infection of gland tissue with E. coli, streptococcal or staphylococcal bacteria.
- Gynecological procedures that resulted in mechanical damage to the genital organs.
- Hysteroscopy, frequent abortions.
In addition to the main causes, this disease can occur under the influence of negative factors:
- Decreased immunity (due to chronic diseases).
- Injury to the skin (often occurs when visiting beauty salons for the purpose of hair removal).
- Wearing uncomfortable, synthetic underwear.
- The use of hormonal and antibacterial drugs for a long time, or in a dosage significantly exceeding the therapeutic one.
It should be especially noted that promiscuous sex life and non-use of barrier contraception methods lead to the development of this pathology.
Sometimes the appearance of a Bartholin gland cyst can be caused by:
- Seasonal influenza epidemics.
- Tonsillitis.
- ARVI.
- Sinusitis.
- Dental diseases (gingivitis, caries, periodontitis).
- HIV infection.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of this disease largely depend on the size of the cyst, which can be either miniature or quite impressive. If a small cyst remains unnoticed, a large formation seriously impairs the quality of life.
A large tumor causes pain during movement, especially when walking or trying to sit down, and also causes discomfort during intimacy.
Visually, the gynecologist can notice asymmetry of the labia, as well as a round hyperemic elevation above the skin due to the formed cyst. When pressed, such a formation does not cause pain or is barely noticeable, and also slightly rolls under the skin, which means it is not fused to it. True, all the above symptoms are characteristic only of a cyst that is not associated with inflammation.
In the case of an infectious process in the cyst, the symptoms of the disease change dramatically. Inflammation takes over the Bartholin gland canal, causing it to become swollen and clogged. True, it is not completely clogged, which means that when pressure is applied to the inflamed area, purulent contents are released through the duct. A woman in this state complains of constant bursting pain, observes redness of the labia, and when palpating it feels a dense sphere.
If you do not start treating the inflammatory process in a timely manner, the gland duct is completely closed, and the purulent contents remain inside, with no way out. In this case, when walking, the woman feels a sharp pain, and when examining the genitals, she notices swelling in the affected area, redness and swelling.
Touching the cyst also causes pain. Doctors call this condition a false abscess. Very often, such abscesses open spontaneously, and patients no longer need to see a doctor. The truth is that the insidiousness of the Bartholin gland cyst manifests itself here, because spontaneous opening of the abscess ultimately clogs the duct and leads to the formation of a new cyst.
When the infectious process affects the tissues of the Bartholin gland, and purulent melting of these tissues occurs, a true abscess occurs. This process is accompanied by a huge size of the cyst (10–15 cm), severe throbbing pain, severe swelling and all the symptoms of intoxication of the body, including high fever, weakness and lethargy, headache and dizziness.
At the beginning of this disease, the cyst has a small diameter (up to 2 mm), it is painless and does not cause any unpleasant sensations of discomfort. This pathological process can occur over a long period of time.
Routine medical examinations help identify this cystic change. Or when its growth becomes noticeable, and its size may exceed 10 centimeters in diameter.
During the development of a Bartholin gland cyst, a clinical picture develops, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Dryness of the mucous walls of the vagina, accompanied by unbearable vaginal itching.
- Throbbing pain that intensifies as a result of sudden movements or when walking quickly.
- Rapid fatigue, a feeling of weakness, and daytime drowsiness appear.
- The psycho-emotional state is disturbed, there is a sharp change in mood.
- Sometimes symptoms of hyperthermia (up to 39 degrees) are observed.
- The digestive system can react to this disease with the appearance of nausea and uncontrollable vomiting, and the development of symptoms of anorexia.
If no therapeutic action has been taken for this disease, the cyst may fester, which leads to the development of an abscess.
This condition is accompanied by:
- A sharp rise in temperature, to critical numbers.
- Severe symptoms of general intoxication of the body (nausea, vomiting, defecation disorder, diarrhea or constipation).
The cyst can open on its own, and its contents penetrate into the bloodstream. This leads to the development of sepsis, and is an alarming sign and a reason for urgently contacting a doctor.
Manifestations of cyst formation are determined by the stage of the developing pathoprocess (in some cases, cyst formation is not accompanied by inflammation or suppuration). Symptoms are also determined by the degree of damage, affecting the excretory duct or spreading to glandular tissue.
1. Canalicutitis. In this case, the inflammatory focus is localized in the excretory duct, without spreading further. Main manifestations:
- The walls of the canal are partially narrowed without disturbing the outflow of secretions;
- The cystic node is not formed;
- The patient's condition is not serious;
- The labia or one of them becomes swollen and painful;
- During walking, in a sitting position, or during sexual intercourse, unpleasant, uncomfortable sensations arise;
2. Adhesion of the walls of the duct, without disrupting the functioning of the gland (false abscess). Infectious agents that have penetrated the tissue of the canal walls cause inflammation and swelling, which significantly narrows the ductal lumen, aggravating the course of the condition. As a result, more pronounced symptoms are observed than with canaliculitis:
- The pain of swollen labia is more noticeable;
- Unexpressed pain syndrome is observed not only during walking, sex, but also at rest;
3. Purulent bartholinitis (acute suppuration). The condition is characterized by the spread of infectious and inflammatory lesions to glandular tissues and their destruction. Symptoms of purulent bartholinitis:
- The cystic formation takes on maximum dimensions (in some cases, up to 8 cm), and is filled with purulent contents;
- An acute pain syndrome of a pulsating nature occurs. Pain occurs even with a light touch to the seal;
- There is an increase in lymph nodes in the groin area;
- Body temperature reaches 38.5-40C;
- A state of intoxication occurs (severe weakness, nausea, headaches, chills).
Spontaneous opening of the cyst may occur, and a large volume of purulent secretion flows out of the burst cavity. The wound bed that occurs at the site of a ruptured formation is characterized by a long period of healing, overgrowth of tissue with the appearance of a scar.
The uncontrolled course of the pathology, a frivolous attitude towards the occurrence of a cystic node, can lead to serious complications:
- The suppuration spreads further, affecting fatty tissue, entering the bloodstream and causing blood poisoning;
- A chronic condition of a sluggish nature will provoke periodic suppuration in the area of the duct and glandular tissues.
At the initial stage, the neoplasm is practically invisible, it does not have pronounced symptoms, its size is small, so only a doctor can notice it during an examination. The only thing that can signal an illness is a slight swelling at the base of the labia majora, closer to the anus. In an advanced state, the cyst manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- the labia is swollen;
- a round tumor appears under the skin;
- there is discomfort and pain when walking, palpating and sexual intercourse.
The cyst may become inflamed, in which case its contents suppurate and the following symptoms occur;
- pulsation is felt at the site of the lesion;
- general malaise, accompanied by weakness and apathy;
- nausea and vomiting appears;
- the temperature rises above 37.5°.
Symptoms of the disease
Micropapillomatosis.
A Bartholin gland cyst can start from a small pea and reach 8 cm. If the cyst is small, a woman discovers it completely by accident; high immunity copes with the disease on its own. The cyst should not be confused with micropapillomatosis of the vaginal vestibule, which is characterized by a pinkish rash on the external genitalia on both sides. Diagnosis begins with an examination by a gynecologist of the external genitalia and vagina.
In case of bartholinitis, the cyst has a round shape and varies in size. It is located under the labia, so one side is much larger due to the ongoing inflammation and swelling of the tissue. Upon palpation, a round, mobile, elastic formation is determined, with minor pain. Can only be located on one side. The clinical manifestation of purulent bartholinitis differs from the resulting cyst.
The inflammatory process provokes swelling and narrowing of the excretory duct. When you press on the cyst, a small amount of pus is released. The main symptoms of bartholinitis are a feeling of discomfort and slight pain.
It is not recommended to heat the cyst or squeeze out the pus, since the area has a large number of lymphatic vessels and good blood supply. When heated, the infection quickly spreads throughout the body and sepsis can begin. Timely help from a doctor will help relieve inflammation, destroy the infection and prevent its growth.
Complications of the disease
Without treatment, the cyst gradually grows and completely closes the excretory duct. The outflow for pus is closed, the walls stretch, and the woman is diagnosed with an abscess. Symptoms of bartholinitis become pronounced, pain and intoxication appear. On examination, the labia is swollen, bright red, pressure is accompanied by acute pain. The abscess can open on its own, releasing a large amount of pus.
The woman thinks that the disease has gone away on its own and does not seek help, although treatment for bartholinitis is needed right now. The infection that provoked its formation remains, which can lead to relapse and a sluggish inflammatory process. Constant inflammation contributes to the narrowing of the duct, the secretion accumulates, and over time a Bartholin gland cyst is formed.
When the infection penetrates into the gland itself, it begins to collapse and a capsule with pus appears. The woman begins to develop a fever, a sign of intoxication, the temperature rises, the skin near the abscess is crimson, hot, throbbing pain, acute bartholinitis is diagnosed. To determine the cause of the disease, it is necessary to take a smear and bacteriological culture from the vagina. Complications of bartholinitis are the development of inflammatory processes and relapses.
Diagnosis of the disease
When contacting the antenatal clinic, the gynecologist initially pays attention to the patient’s complaints. After their systematization, a visual examination of the external genitalia is performed. Usually there is slight swelling and enlargement of the labia, their asymmetry, and slight pain.
During palpation examination, a round, movable compaction is felt. Pressing causes slight pain.
If a woman seeks advice in the stage of suppuration of the Bartholin gland, then diagnosis does not cause any particular difficulties. This is facilitated by a clear clinical picture.
After palpation and visual examination, the following is prescribed:
- Biochemical and clinical blood analysis.
- Examination of a smear using PCR methods.
- Bacterial culture to establish sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
The best solution in such a situation would be to consult a gynecologist. For a specialist, a Bartholin gland cyst does not pose a big problem. After conducting a gynecological examination and noticing a round elastic bubble under the skin of the labia, the doctor prescribes a number of laboratory tests for the patient, in particular:
- complete blood count and urine test;
- blood chemistry;
- vaginal smear;
- PCR diagnostics to detect hidden sexually transmitted infections;
- bacterial culture for the presence of a specific infectious agent, and identification of antibiotic sensitivity to it.
In what situations is cyst removal necessary?
Of course, not all cases require removal. If the cyst is small and no more than 2 centimeters, then such cysts do not require emergency surgery. As a rule, in such cases, regular diagnostics are carried out so that the development of the formation can be monitored. Quite often, such cysts can resolve on their own. If a woman feels discomfort, then small formations are removed.
Large and large cysts that interfere with daily life are removed surgically. It is worth remembering that if pathologies are detected in time, then surgery can be avoided and the cyst can be cured with the help of complex drug therapy.
Removal of a Bartholin gland cyst is necessary for the following indications:
- if the tumor on the labia rapidly progresses;
- the development of inflammation, which is accompanied by a purulent process;
- painful sensations in the area of the external genitalia.
The operation is performed on the day the woman applies, without prior preparation. If the cyst bursts, severe pain appears. Then complete removal of the Bartholin gland with further antibiotic therapy is recommended.
Many women are interested in the question: why is drainage with a web catheter rarely performed? This procedure is ineffective, as frequent relapses occur, which can aggravate the situation. It may also be necessary to remove the entire organ. The procedure is required when, along with the Bartholin gland, its duct is also removed. Excision is used in extreme cases. To begin with, doctors try to achieve the desired result using gentle treatment methods.
Treatment without surgery
The choice of tactics and treatment regimen is made by a gynecologist. In this case, the condition of the sick woman and how long the disease lasts are taken into account. The most important factor in the treatment of this pathology is the size of the cystic compaction.
If the cyst does not exceed 2 mm in diameter, then treatment is carried out without surgical intervention. Medicines are prescribed for local use and oral use. Traditional healing recipes are used as additional remedies.
The main goals of conservative treatment:
- Prevent further inflammation, eliminate symptoms of swelling and painful manifestations.
- In case of suppuration, exclude the development of an abscess.
- The cystic capsule is opened to enhance the outflow of its contents (when suppuration cannot be eliminated).
In the postoperative period, the following medications are prescribed:
- Medicines belonging to the pharmacological group of antibiotics.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Non-narcotic analgesics.
- To reduce pain and eliminate swelling, you can use a cold heating pad.
- Be sure to treat the seams with antiseptic solutions.
- Use Levomekol for dressings.
- Use physical therapy 10 days after surgery.
- Avoid sexual activity for a month.
- Complete refusal of baths, swimming pools, solariums, hot baths.
- Underwear should be loose and not made of synthetic fabric.
- Maintain intimate cleanliness of the genitals.
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnostic measures include:
- Examination by a gynecologist. The doctor examines the external genital area and the vagina. The specialist pays attention to the presence of asymmetry of the labia, the presence of a formation (a large cyst of the labia majora is determined visually, a medium, small cyst is determined by palpation);
- Laboratory and instrumental methods:
- A general blood test is taken to determine the extent of the damage. In acute suppuration, an increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and a shift of neutrophils to the left are detected;
- A general urine test is performed, which determines the presence and number of leukocytes;
- Bacterial seeding, where the presence of microorganisms, their viability and quantity are determined;
- PCR analysis. The study, in the presence of an inflammatory process, makes it possible to identify sexually transmitted infections;
- Examination of a vaginal smear to determine the type of microorganisms present.
Surgery
Currently, there are many methods of surgical treatment of Bartholin gland cysts.
This is due to the emergence of new scientific developments that are applied using the latest advances:
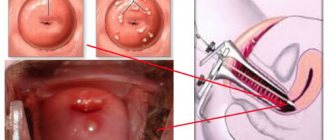
- Marsupialization of the cyst. This is a type of surgical treatment for cysts. This operation does not require the patient to be hospitalized and is performed on an outpatient basis using general anesthesia. The operation takes no more than 30 minutes. After anesthesia, the vaginal mucosa is dissected, resembling an oval shape. After this, the cyst is removed using the same oval cut. The cyst is removed, along with its contents, the cavity is thoroughly washed and sutured. After this type of surgery, the patient leaves the hospital after 1 or 2 hours. Sometimes she may be in the hospital for 24 hours, depending on her condition. This type of operation makes it possible to preserve the gland and its normal functioning. The negative side of this surgical effect is that in 10% of cases a relapse may develop. Before it is carried out, the following is prescribed: Clinical and biochemical blood test.
- Blood for Rh factor.
- Clinical examination of urine.
- Blood test for sugar content.
- Coagulogram.
- Vaginal smear.
- Fluorography.
- The precision of the impact, adjacent areas and healthy tissues are not affected and are not subject to trauma.
- Requires mandatory placement of the patient in a hospital.
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment of bartholinitis will depend on the presence of inflammation, how long it bothers the woman and its size. A cyst that does not exceed two centimeters and is not accompanied by pain does not require emergency treatment. It is necessary to monitor it, sometimes they tend to resolve on their own. A large cyst prevents you from living a full life. Removal of a Bartholin gland cyst occurs through surgery.
In case of relapse, it is necessary to identify the causes and begin treatment at an early stage in order to avoid surgery. To do this, you must adhere to the following rules:
- maintain physical peace. Active walking and running lead to the fact that the inflamed area is even more injured, and the inflammation increases;
- apply cold to the genitals, relieves inflammation, swelling, pain, prevents further spread of infection;
- use warm sitz baths with potassium permanganate or chlorhexidine. Applications with Vishnevsky or Levomekolev ointment, how many times to do them, you need to ask your gynecologist;
- to quickly cure acute bartholinitis, you need to start taking broad-spectrum antibacterial medications;
- antihistamines, pain-relieving drugs and a multivitamin complex.
Surgery
When a Bartholin gland cyst occurs, treatment must begin immediately, and in severe cases, surgical intervention is necessary. But before that, you need to find out the reason for its appearance. If an infection is triggered, antibacterial therapy is necessary, which sometimes helps relieve inflammation and restore patency of the duct.
The purpose of the operation is to restore the patency of the gland after removal of the cyst.
There are contraindications to the operation; this is during pregnancy and when a woman’s child is breastfed. What to do then? The operation is replaced by puncture, when a puncture is made with a long needle and its contents are removed.
Progress of the operation
During the treatment of an abscess and purulent cyst, an incision is made and the bartholinitis is opened and its contents are drained. The surgeon removes the cyst and then treats the cavity with an antibacterial solution. After the pus is released, a duct is formed in the gland, and the edges of the wound are sutured to the mucous membrane of the labia. The main goal in the treatment of chronic bartholinitis is to preserve and form the excretory duct, since cleansing the vagina from harmful microorganisms depends on its presence.
After removal of the cyst, the Bartholin gland may stick together again, forming an abscess. To prevent this, you need to restore the normal duct in the gland. To do this, an incision is made in the cyst and a catheter is inserted, and the contents flow out through the opened duct. When the wound heals, the catheter is removed, and a formed duct remains in its place.
Surgical treatment does not always help to forget about the problem, and the Bartholin gland cyst appears again. After repeated relapse, removal of the Bartholin gland is recommended.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis using local anesthesia. The greatest result from the operation can be obtained only when it is performed by a highly qualified surgeon. How long the operation will last depends on the amount of pus contained in it, generally no more than 30 minutes. There may be some minor bleeding after surgery.
Regardless of the type of treatment, it is necessary to take immunostimulants and perform physical procedures to help speed up wound healing.
Rehabilitation period
The healing incision must be treated with an antiseptic twice a day to prevent re-infection. Then a wound healing ointment is applied to a sterile bandage and applied to the wound. These procedures must be carried out until complete healing, usually 7-10 days are enough. During the postoperative period, carefully monitor the hygiene of the genital organs and maintain bed rest.
Many people ask whether it is possible to resume sexual activity two to three weeks after surgery. Doctors do not recommend doing this; in order for the incision to heal completely, a whole month must pass, otherwise bleeding may begin.
Bartholinitis cyst in a woman, its symptoms and treatment will be the same for everyone, the most important thing is to contact a gynecologist in a timely manner to prevent the spread of infection throughout the body and preserve the Bartholin gland.
Removal of Bartholin's cyst
Surgical removal of a cystic formation of the Bartholin gland is indicated in the following cases:
- Large cyst sizes;
- Growth of the formation, severe pain syndrome;
- The presence of suppuration of the gland;
- Relapses.
The goal of surgical intervention is to remove the cyst on the Bartholin gland, restore the patency of the ducts, the function of the gland, prevent abscess and spread of the inflammatory-purulent process to neighboring tissues.
Surgical methods:
- Marsupialization of Bartholin's cyst. During this procedure, the surgeon excises the cystic capsule with a scalpel and treats the cavity with antiseptic drugs. Initially, a preliminary incision is made to drain the contents of the capsule. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The method is applicable for frequent relapses;
- Vaporization of the formation (vaporization of the Bartholin gland cyst). For this operation, a laser is used to remove the formation by gradually evaporating the contents of the cystic cavity. The targeted effect ensures the safety of nearby tissues. The method is absolutely bloodless and painless (unlike marsupialization of a Bartholin gland cyst, enucleation, resection of the formation), the risk of relapse is minimal;
- Husking. This method involves removing the node along with the shell. General anesthesia is used. Only a highly qualified, experienced specialist can perform the operation: since bleeding may occur, there is a possibility of deformation and scarring of the tissue. The recovery period lasts about a month;
- Radical excision of a cystic formation (extirpation). During the operation, the formation of an external fold, the cyst of the labia minora is removed along with the gland. The method is used for frequent relapses, severe abscesses, and the lack of effectiveness of other removal methods. There are no relapses after the operation.
Recommendations for women after surgery to remove a Bartholin gland or a cyst in it
To minimize the risk of relapse after removal of a cystic formation in the Bartholin gland, the patient should carefully monitor her health and adhere to the following tips:
- at night, insert gauze swabs soaked in Miramistin or Chlorhexidine into the vagina;
- wash the wound daily with antiseptic solutions (for example, Betadine);
- use ointments with a healing effect only after all the pus has come out of the opened cystic cavity (otherwise the thick gel will clog the outlet and a purulent abscess will form again);
- carry out disease prevention, take measures to prevent relapses (wash yourself thoroughly and correctly, performing the procedure in such a way that the flow of water from the shower is directed from the external genitalia to the anus, and not vice versa);
- for preventive purposes, wash with antibacterial decoctions of medicinal herbs, use condoms during sexual intercourse, wear loose underwear;
- contact a doctor immediately after the onset of inflammation (this will help to identify the pathology at an early stage and treat it without surgery).
Bartholin gland cyst during pregnancy
The occurrence of a cystic node during pregnancy is not uncommon, since the immune system is weakened. In cases where the formation is not inflamed, the cyst does not have any effect on the course of pregnancy. If inflammation occurs, the doctor will make every effort to carry out treatment without surgery or postpone it until the postpartum period.
A woman may develop a Bartholin gland cyst during pregnancy. If the neoplasm does not show signs of inflammation, it does not affect the course of pregnancy in any way. In this case, treatment of the cyst is postponed until the postpartum period. If the cyst is inflamed, then, according to indications, an operation is performed to remove the festering cyst.
The expectant mother's immunity is weakened, so the body is more susceptible to infections of the vagina and genitourinary system. This explains the frequent occurrence of inflammation of the Bartholin gland.
Complications of a chronic disease can appear in the 1st and 3rd trimesters.
A cyst on the labia is treated after childbirth, if possible. Antibiotics are not recommended here; most doctors recommend surgery: opening the abscess and draining it (pulling out the fluid). Treatment methods:
- Local treatment of the cyst with antibacterial compounds (Levomekol, Ichthyol ointment).
- Rinsing and lotions with antiseptic agents (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine).
- Taking antibiotics (not recommended in the 1st trimester) - Erythromycin, Ceftriaxone, Macrobid (up to 36 weeks), Amoxicillin.
- Restoration of vaginal microflora in the chronic form of the disease (Lactonorm).
- Warm baths, lotions (in all trimesters, but 3 baths are not recommended).
Treatment after surgery for Bartholin gland cysts, its features and nuances
After enucleation of the Bartholin gland cyst, the postoperative period involves a course of antibacterial treatment. The general treatment regimen includes the following points:
- taking antibiotics (they kill the infection that led to inflammation of the Bartholin gland duct and the formation of a cystic capsule);
- a course of anti-inflammatory drugs;
- applying gauze bandages with anti-inflammatory and wound-healing ointment (Levomekol) to the surgical wound;
- applying cold (ice in a bag wrapped in cloth) during the first hours or days after surgery (this method helps relieve pain and reduce swelling at the wound site);
- treatment of postoperative sutures with antiseptic solutions 2-4 times a day (brilliant green, iodine, chlorhexidine are used for this purpose);
- 1-2 weeks after surgery, the woman should undergo a course of physiotherapeutic procedures (they are prescribed by a gynecologist).
The patient should remember that an excised Bartholin gland cyst (photo) may recur after surgery. This happens due to non-compliance with medical requirements during rehabilitation. If relapses occur constantly, the gynecologist decides to remove the gland completely. This option is undesirable for young girls, as it subsequently leads to difficulties in their sex life. Therefore, compliance with medical recommendations, monitoring personal hygiene and a healthy lifestyle should become integral components for patients with pathologies of the Bartholin gland.
Complications of Bartholin gland cyst
Possible complications:
- If a sick woman does not see a doctor on time, this means that the acute form will turn into chronic. This will significantly worsen the course of the disease, and only surgical intervention will be necessary to treat it.
- The second type of complication can be considered the development of an abscess. This course of the disease forces the doctor to use surgical treatment methods. Recently, although they are safe, they are expensive.
- If a woman is negligent about her health, has not consulted a doctor, and is not treated correctly for an abscess, the most dangerous pathology, blood sepsis, can develop, which is accompanied by violent clinical manifestations, symptoms of general intoxication, and malfunction of various organs and systems.
Preventive measures
Preventing a Bartholin gland cyst is much easier than treating it later, and in severe cases you can lose the organ altogether.
The following recommendations must be followed:
- adhere to the rules of personal and intimate hygiene;
- have one sexual partner;
- promptly treat infections and inflammation of the reproductive organs;
- visit a gynecologist once every six months;
- lead an active and healthy lifestyle;
- strengthen your immune system and eat right.
There is nothing complicated in the rules of prevention, therefore, dear women, be more attentive to your health in order to avoid irreparable consequences. Often the situation is left to chance, because women hope that the body will cope with the illness itself. And when you have to turn to specialists for help, they are forced to shrug their shoulders, because the disease is already in an advanced stage. To prevent this, at the first alarming symptoms, immediately seek medical help!