Often in therapeutic practice, a disease such as segmental pneumonia occurs. The human lungs are made up of lobes, and the lobes are made up of segments. A segment is a collection of primary lung lobules (acini) that have a common blood supply and innervation. Segmental pneumonia often occurs in an erased form, which makes diagnosis difficult. To identify this pathology, an x-ray examination in two projections is required. What are the causes, symptoms and treatment of this disease?
Reasons for development
Segments are the morpho-functional parts that make up the lobes of the lungs. The left lung consists of 2 lobes and 8 segments, and the right lung is formed of 3 lobes and 10 segments. Each segment is ventilated by a separate bronchus and fed by its own part of the pulmonary artery. The defeat of one of these areas is called segmental pneumonia. If two or more segments are involved in the process, the disease is called polysegmental inflammation.
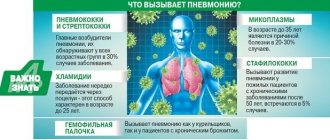
Most often, the causative agents are bacteria (Haemophilus influenzae, pneumococci, streptococci) and viruses (influenza, adenoviruses, viral respiratory infections). Inflammation in the lung segment may develop under the influence of fungi or protozoa.
Most often, pathogenic microflora enters the child’s body through inhalation. An aspiration route of infection is also possible, when microorganisms enter the respiratory tract from the nasopharynx. In some cases, infectious agents penetrate the lung tissue from distant foci through the bloodstream.
The development of inflammation of the lung segment is facilitated by a decrease in immune status and hypothermia. This form of pneumonia is often diagnosed in children prone to allergic reactions.
Causes of segmental pneumonia
Segmental pneumonia is an infectious disease that can be caused by:
- Viruses - cause inflammation on their own or contribute to the addition of secondary bacterial flora;
- Bacteria;
- Mushrooms.
Typically, infection occurs outside the walls of a medical institution, which is why such segmental pneumonia is also called community-acquired pneumonia.
Segmental pneumonia on the right or left is more often caused by microbes. The most common pathogens are pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, staphylococci and streptococci, Klebsiella. Atypical pneumonia is caused by chlamydia, mycoplasma, and legionella. Viruses can also cause inflammation (adenovirus, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus). In some cases, it is possible to detect several types of microorganisms at once.
Pneumonia does not necessarily occur due to the introduction of an infectious agent through the respiratory tract (aerogenously). There are other possible ways of its penetration into the pulmonary parenchyma:
- Aspiration - inhalation of infected mucus from the nasopharynx, stomach contents in bedridden patients, comatose patients, etc.;
- With blood flowing into the lung from other organs and tissues that have foci of infection.
The causative agents of segmental pneumonia are widespread, they can be found anywhere, however, not all people in contact with sources of infection develop pneumonia. The reason for this is a special tendency to the disease, which arises due to the presence of predisposing factors:
- Pathology of immunity, tendency to hyperergic immune reactions;
- Immunodeficiency syndromes;
- Exudative-catarrhal diathesis in children;
- Smoking;
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system (bronchitis, for example);
- Hypothermia.
Symptoms
The disease begins acutely, and symptoms rapidly increase. The temperature rises to febrile levels (38-39 degrees), intoxication of the body quickly develops. Toxic waste products of pathogenic microflora spread to all tissues, resulting in the following symptoms:
- weakness,
- general malaise,
- headache,
- increased sweating,
- Sometimes seizures begin, and the child may experience some confusion.
The cough usually starts on the second or third day. The child may complain of pain behind the sternum or in the stomach area. The baby has no appetite, he becomes lethargic, does not show activity, refuses to play and run. The skin becomes pale and may have a blue tint in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
Causes of polysegmental pneumonia
Polysegmental pneumonia (especially bilateral) is one of the most severe illnesses and requires prompt treatment. The fact is that bilateral polysegmental pneumonia always develops rapidly, leading to breathing complications and even death.
With this disease of any type (bilateral, right-sided or left-sided), an inflammatory effect occurs on the epithelium of the lungs. This inflammation disrupts work in several functional segments (they are called areas of the lungs containing large numbers of alveoli). The disease progresses rapidly, which eventually causes respiratory failure.
Polysegmental pneumonia: causes of occurrence
Experts establish an X-ray conclusion about polysegmental pneumonia when foci of inflammation occur in the patient’s lung tissue, which can be located in different segments on either side or on both sides simultaneously.
When this disease occurs, children experience painful sensations, because in their lungs throughout the illness the pleura is irritated (it acts as a protective membrane), which is located on top of the lung fields.
The pleura contains many nerve endings, which causes irritation and pain. The lungs themselves do not have pain receptors, so severe bilateral inflammation is not always immediately detected until the patient undergoes an x-ray procedure or notices the first signs.
The causes of polysegmental disease can be different, the main ones are:
- the occurrence of bacterial infections such as staphylococcus, pneumococcus, chlamydia or mycoplasma;
- lung damage by viruses;
- defeat by diseases from a number of parasitic and fungal ones.
One of the serious features of polysegmental pneumonia in children is considered immediate hypersensitivity (health workers use the abbreviation GNT). It occurs in the area of the pulmonary affected areas in the form of tissue edema, which develops quickly.
Most often, immediate hypersensitivity occurs with pneumococcal infection, since its antigens are most similar to body proteins, which is why the immune system works unstable, not recognizing HNT antigens. In this case, the immune system perceives its proteins as bacterial antigens and subsequently begins to destroy them. In adults, this reaction occurs when there is right-sided lower lobe polysegmental pneumonia in the body. Immediate hypersensitivity contributes to the deterioration of the patient's condition due to increased inflammatory effects on the body.
Signs of emerging polysegmental inflammation
The polysegmental type of inflammation in patients of any age includes symptoms of intoxication or bronchopulmonary categories. The former aggravate the course of the disease in the patient and are detected by muscle weakness, dizziness, headaches, chills, fever and painful sensations in the joints.
Signs of intoxication syndrome:
- Polysegmental inflammation with intoxication syndrome is always accompanied by elevated temperature, reaching 39-40°C. The development of the disease is lightning fast and is most often provoked by pneumococcal pneumonia. Pneumonia itself is characterized by a constantly elevated temperature (it hardly subsides even over several days); a gradual decrease in temperature is facilitated by adequate treatment.
- Significant chills in some cases are a precursor to feverish sensations that last for several hours, during which time the patient sweats profusely. When the epithelium of the lungs is damaged, the concentration of pathogens increases, which contributes to a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain due to an increase in blood viscosity. This causes dizziness and headaches.
- Violation of the pulmonary epithelium in children occurs due to staphylococcal or streptococcal disease and contributes to a stable elevated temperature of up to 40°C. Medical workers gave this fever the name febris continua, the translation of which means “constant fever.” Pneumococcal pneumonia in children can cause fulminant fever, accompanied by a clear intoxication syndrome. This type of fever may not go away for several days.
- Croupous childhood pneumonia is accompanied by intoxication syndrome. This type of pneumonia is very rare. Clinical signs of polysegmental pneumonia are similar to those of segmental pneumonia. It manifests itself in children in the form of shortness of breath, wheezing and weakened breathing, and the localization of foci occurs mainly in the upper parts of the lungs. To clarify the damage to the segments, x-rays are taken in 2 projections. In this case, the infiltration shadow is uniform and intense.
- Polysegmental pneumonia contributes to the formation of muscle weakness in patients. The reason for this is reduced blood fluidity, which further impairs the oxygen saturation of the body.
- A similar pathogenesis occurs in the joints and is accompanied by painful sensations in them. This happens due to deterioration of microcirculation in the periosteum.
Signs of bronchopulmonary syndrome
When infiltrate accumulates in the body and pathogens multiply in the respiratory tract, bronchopulmonary syndrome occurs. The following main symptoms are distinguished:
- the occurrence of hoarseness when breathing and speaking, which appears due to swelling of the walls of the bronchi;
- cough with sputum production;
- When inflammatory processes occur in the pleural layers, painful sensations occur in the chest.
A normal body uses the cilia of the epithelium of the upper respiratory tract to remove pathogens. If the cilia do not work properly or infectious bacteria enter the underlying sections, the bacteria are eliminated through bronchial contractions in the form of a cough.
Polysegmental pneumonia promotes large accumulation of fluid, the body removes it through a prolonged cough. With pneumonia, the cough lasts until the airways are completely cleared.
Pain in places where the lungs are affected occurs due to inflammation of the pleura, which is irritated by lesions in any form of the pleural layer. With pleurisy, polysegmental pneumonia aggravates pain or causes severe chest pain with sudden body movements.
All of the above symptoms are factors of pneumonia. To confirm them, an x-ray must be taken. All these signs are reason to visit a pulmonologist as soon as possible to avoid serious complications.
How is polysegmental pneumonia treated?
Treatment of unilateral or bilateral pneumonia is possible through the use of antibacterial agents and drugs.
The etiology of pathogens in children and adults is different, so therapy involves the use of different antibiotics.
The best will be timely treatment, when medical specialists will be able to quickly sow cultures of bacteria resulting from the disease on a special medium and determine the sensitivity of the disease to antibiotics. During 2 weeks of therapy, the doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs to the patient. Treatment also includes eliminating existing complications or preventing them.
Bilateral, right-sided or left-sided polysegmental pneumonia is a disease that should never be neglected. Its development can lead to respiratory failure and death.
respiratoria.ru>
Possible complications
If pneumonia does not end with recovery, it takes a protracted course, this can lead to the development of bronchiectasis, the proliferation of connective tissue at the site of the inflammatory process (sclerosis).
This form of pneumonia can be complicated by the following pathologies:
- development of pleurisy,
- abscess formation,
- pleural empyema,
- obstructive syndrome,
- cardiopulmonary failure.
The cause of complications in segmental pneumonia is untimely treatment of the disease and attempts at self-medication. Also, a complicated course of pneumonia can be observed in children suffering from serious concomitant pathologies and immunodeficiency.
What is the pulmonary segment
The pulmonary segment is anatomically represented by a cluster of alveolar acini, which have a common blood supply and innervation, separated from the surrounding tissues by layers of connective tissue.
X-ray, each pulmonary segment has a specific location on frontal and lateral images. To accurately localize segmental pneumonia, it is necessary to perform a chest x-ray in two projections.
When diagnosing the disease, it is also necessary to assume whether the patient has right-sided or left-sided pneumonia, which is noted by general practitioners or pulmonologists in the conclusion of a chest X-ray examination.
Diagnostics
If a child shows signs of pneumonia, he should be immediately shown to a pediatric pulmonologist or pediatrician. The doctor will analyze the clinical symptoms, collect anamnesis, and conduct a physical examination, including auscultation and percussion. After this, the following studies are prescribed:
- general clinical examinations of urine and blood,
- blood biochemistry,
- culture of sputum,
- serological tests (PCR, ELISA),
- X-rays of light.
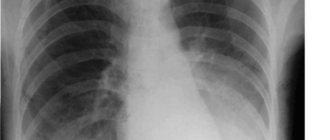
The most informative method for making a diagnosis is radiography. In the photographs you can see darkened areas with clearly defined boundaries. These are the affected segments. If X-ray data is insufficient, the doctor may prescribe a CT scan of the lungs.
Differential diagnosis is carried out in relation to other forms of the disease, as well as tuberculosis, cancer, bronchiolitis obliterans, and pulmonary infarction.
Features of the course of segmental pneumonia
Segmental pneumonia is a fairly serious problem that requires immediate treatment. Otherwise, it can cause dangerous complications that will not be so easy to cure.
Segmental pneumonia - what is it?
This disease is nothing more than a very serious lesion of the human respiratory tract, which never spreads beyond a specific pulmonary segment. This form of pneumonia is the second most common form of pneumonia in humans. In the first place is inflammation of the lungs of focal type.
Most often you can find pneumonia, which occurs in the lower lobe of the right lung; in most cases it develops in adults. It is interesting that in children this causes an inflammatory process on the opposite side - left-sided pneumonia. This difference is caused by a certain difference in the structure of the chest.
In addition, a distinction is made between subsegmental inflammation and ordinary segmental inflammation. The difference is that with a normal inflammatory process, much fewer alveoli are affected, and the inflammatory process takes place over a smaller area of the lung. It is worth noting separately that using an x-ray it is very difficult to determine what type of disease is in an adult or a child. To do this, it is necessary to do additional tests and examinations.
What is the pulmonary segment in humans?
In order to understand the causes of this complex disease, it is worth taking a little look at human anatomy and finding out what exactly the segments of the human lungs are.
The lung segment is a small collection of alveoli. Moreover, this accumulation has a common blood supply with the body, as well as innervation. It is separated from other segments by thin layers formed from connective tissue.
If we examine each segment of a person’s lungs in an X-ray image, they are characterized by a special localization both in the direct image and in the lateral image. Therefore, in order to determine quite accurately the location where the source of inflammation is located, it is necessary to take photographs of the chest in two projections.
In addition, during diagnosis it is very important to first determine in which lung segmental pneumonia is observed. This can be done by a therapist or a pulmonologist after carefully examining and studying the x-rays.
Causes of the disease
This type of pneumonia occurs due to the fact that the body’s local defenses are sharply reduced. Such a change may occur as a result of the development of a cold or after severe hypothermia. In addition, the cause of the development of the disease may well be pneumonia pathogens, which begin to multiply very actively only in a separate area of the lungs.
So, right-sided segmental pneumonia in adults develops due to the following reasons:
- there is significant deformation of the bronchial system;
- quite often the wall of the lower respiratory tract becomes inflamed, which results in defects, for example, the amount of connective tissue increases;
- immunity in this part of the body is greatly reduced due to the fact that blood supply processes are disrupted;
- Under the influence of nicotine, a fairly strong spasm of the blood vessels in the lungs occurs, which becomes the cause of further development of the disease.
If we talk about the occurrence of pneumonia in children and the elderly, then the reasons are somewhat different. First of all, it may be too weak immunity. The disease can be caused by a pathogen that enters directly into the respiratory system. Even if it is the most common streptococcus, it can become an impetus for the development of an inflammatory process in the lower part of the lungs.
Types of segmental pneumonia
Today, experts distinguish several types of segmental pneumonia and, depending on this, prescribe treatment to the patient:
- typical appearance;
- atypical;
- viral;
- toxic;
- fungal;
- drug.
Symptoms of the disease
About two days after the inflammatory process begins to develop in a person’s lungs, the first signs of the disease begin to appear. Symptoms of segmental pneumonia include the following:
- if the cause is a bacterial infection, then there is a sharp increase in temperature to 39 degrees or higher;
- as a result of intoxication of the body, a person feels constant and severe fatigue, a headache appears, and in especially severe cases, delirium or even hallucinations may occur;
- you can feel pain under the ribs, which occurs due to damage not only to the lungs, but also to the stomach;
- tachycardia begins to develop: this indicates that there are large quantities of toxins or even breakdown products of cells and tissues in the blood;
- if adynamia is observed in a patient, this indicates a very severe course of the disease (in this case, experts are guided by temperature: the higher it is, the faster the inflammatory process begins to progress);
- the general intoxication of the whole body can be understood by the fact that a very large amount of sweat begins to be released every time a person changes body position;
- after a few days a fairly strong cough appears and a lot of sputum is produced;
- shortness of breath occurs.
Each specialist, in order to prescribe the correct treatment for the patient, will pay attention to the patient’s sweating. Thanks to sweating, you can understand how well metabolic processes occur in the human body. In addition, the degree of sweating warns of the possible occurrence of fever in a person. For example, if a person suddenly begins to sweat in large quantities, this means that literally in a few minutes the body temperature will rise quite significantly. In this regard, it is necessary to take medicine against fever as soon as possible.
If all the symptoms of the disease have disappeared and nothing is visible on the X-ray images, but sweating and general malaise are present, this indicates that the disease has not been completely cured.
In such situations, doctors may prescribe additional antibacterial and vitamin medications to maintain the patient’s body.
Treatment of allergies in connection with segmental pneumonia in an adult
Quite rarely, but still in the presence of segmental pneumonia, an allergic reaction can occur. In this regard, a person may experience suffocation and even anaphylactic shock. If this happens, then you need to administer a dose of adrenaline to the sick person as quickly as possible and immediately take him to the pulmonology department.
Shortness of breath in people who suffer from segmental pneumonia occurs due to the fact that a small area of the lungs does not take part in breathing. Other segments become larger due to the fact that the usual amount of air fits in fewer alveoli. This occurs due to the fact that the body is trying in every possible way to eliminate the lack of oxygen. If a similar problem arises during illness, then the patient must be taken to the hospital and given artificial ventilation. In this way, it will be possible to very quickly restore the amount of oxygen necessary for the body.
Inflammatory processes in the lungs are a very serious problem that requires immediate treatment. The recovery process can take a very long time, and even if the X-ray images do not show the affected areas, the disease may not leave the sick person for quite a long time.
With children the situation is even more difficult than with adults. The fact is that the child’s immunity is of a reactive type. This means that literally a few days after all the symptoms of segmental pneumonia have disappeared, they can arise again and in an even more severe and dangerous form for the child.
As practice shows, treatment in most cases ends without complications and is quite successful. The main thing is to take all necessary measures in time and not to start the disease.
respiratoria.ru>
Treatment methods
Children whose pneumonia is severe, with complications, as well as those who have serious concomitant diseases, are admitted to a hospital for treatment. In other cases, it is possible to carry out therapy at home with outpatient monitoring.
Treatment of this disease includes measures aimed at suppressing the activity of the infectious agent, detoxifying the body, stopping foci of the inflammatory process, as well as preventing or eliminating respiratory failure.
The main therapy is carried out with the use of antibiotics. The choice of drug is made by a doctor based on bacteriological analysis data. Sometimes you have to wait several days for test results, but treatment must begin immediately. In such cases, the doctor prescribes one or two types of broad-spectrum antibiotics (penicillins, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins). If there is no improvement within 1.5-2 days, then the drugs are replaced. A course of antibiotics is prescribed for a period of about two weeks.
Additionally, the following medications are prescribed:
- bronchodilators,
- mucolytics,
- glucose solution, saline solutions administered by infusion to eliminate intoxication,
- antipyretic.
Therapy is also carried out aimed at eliminating disorders resulting from inflammation of the segmental lungs. According to indications, drugs to improve the cardiovascular system, antihistamines, corticosteroids, and sedatives are prescribed.
If a child develops respiratory failure, he is prescribed oxygen therapy. Also indicated are bronchial lavages with special solutions (bronchoscopy) and inhalations.
After acute symptoms are relieved, physiotherapy is used. It is recommended to perform massage and breathing exercises.
Typically, the affected segment collapses because its alveoli collapse. This condition is called atelectasis, and if it is present, pneumonia can take a protracted course. With adequate treatment of uncomplicated forms of the disease, the main symptoms disappear after 10-12 days. Changes can be visible on x-rays for up to a month.
Diagnosis and treatment of segmental pneumonia
Diagnosis of segmental pneumonia is based on data from an objective examination of the patient (listening to the lungs, percussion), instrumental methods, and questioning. During a conversation with the patient, the doctor finds out exactly how the disease began, what chronic diseases are present, what medications are taken constantly, whether there was hypothermia the day before, etc.
Auscultation in the first days from the onset of pneumonia may not provide significant information, as well as percussion. Breathing may become harsh or weakened, but there is usually no wheezing. As the area of the lung thickens and inflammatory effusion accumulates in it, moist fine rales and crepitus appear. When tapping on the chest over the affected area of the lung, there is a dullness of the percussion sound associated with compaction of the lung tissue.
Of the general clinical tests, the most important are general and biochemical blood tests, which will show signs of inflammation:
- significant increase in ESR;
- leukocytosis with a shift of the formula to the left;
- increase in acute phase parameters (C-reactive protein, seromucoid, sialic acids, etc.);
- a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells is possible.
Thus, in the initial phase of the disease, segmental pneumonia can be suspected only by comparing the clinical manifestations with the data of the initial examination. X-ray and computed tomography of the lungs can confirm the diagnosis of segmental pneumonia.
The x-ray reveals homogeneous triangular shadows corresponding to the affected segment. The boundaries of these shadows are clear, the roots of the lung lose their structure, and the pulmonary pattern may become stronger due to the inflammatory reaction. When evaluating images, it is important to distinguish segmental pneumonia from tuberculous lesions, malignant tumors and their metastases, foreign bodies in the bronchi, and other forms of inflammation of the lung tissue. Additional computed tomography helps with this.
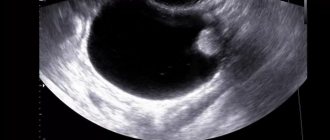
Segmental consolidation of the upper lobe: a) Chest X-ray reveals opacity in the right upper lobe of the lung b) Ultrasound performed at the level of the axilla shows a “tissue” pattern of the consolidated segment with vessels inside. In depth there is an irregular border (flap sign), a transition between consolidation and normal aerated lung
Another important laboratory test is sputum culture on nutrient media. Bacterioscopy and sputum culture are indicated for all patients with suspected bacterial pneumonia, as they make it possible to accurately determine the type of pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics. Sputum is taken in the morning, when it is easier to cough it up in sufficient quantity, into a sterile container.
Treatment of segmental pneumonia should be started as soon as its signs are recorded on an image of the lungs. Treatment goals:
- Eliminate the infection that caused the inflammation;
- Eliminate symptoms of respiratory failure;
- Neutralize toxins;
- Create conditions for the resorption of inflammatory infiltration in the lung.
In cases of mild to moderate severity of the pathology in adults, treatment can be carried out at home under the supervision of a local doctor. In children, severe, complicated, protracted pneumonia, the presence of aggravating diseases require hospitalization.
Etiotropic treatment includes the use of antibacterial drugs in accordance with the expected or established sensitivity of the microbe to the antibiotic. Until the results of bacterial culture are obtained, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used (penicillins, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, cephalosporins - cefaclor, azithromycin, amoxicillin, etc.), then they are changed to others if necessary. If there is no effect in the first 2-3 days (decrease in fever, improvement in well-being), the antibiotic is changed earlier.
To ensure airway patency, use:
- Bronchodilators (berodual in the form of inhalations);
- Expectorants and mucolytics (ACC, ambrohexal in inhalation or solution, ambroxol in tablets);
- Therapeutic bronchoscopy with irrigation of the bronchi with medications;
- Ultrasonic inhalations with alkaline solutions, antiseptics.
Symptomatic treatment includes:
- Antipyretics (paracetamol, ibuprofen);
- Antihistamines (fenkarol, loratadine, glucocorticosteroids in severe cases);
- Sedatives (valerian, motherwort, etc.).
To reduce intoxication, plenty of warm alkaline drinks are prescribed; if necessary, glucose and sodium chloride solution are administered intravenously. Intravenous infusions of calcium chloride help reduce inflammation. The presence of signs of respiratory failure requires inhalation of an oxygen mixture (oxygen therapy).
During the recovery period, the patient is prescribed physical therapy - UHF, electrophoresis of drugs, ultraviolet light on the chest, vibration massage, manual chest massage. Be sure to perform breathing exercises to help improve the flow of mucus through the bronchi.
The prognosis for segmental pneumonia is always serious. With adequate and timely treatment, it is favorable if there is no aggravating background. Otherwise, the risk of complications is high, and in the case of sepsis, most often the disease ends in the death of the patient. In mild to moderately severe cases, segmental pneumonia usually ends in recovery after about three weeks from the onset of the disease. Protracted, complicated pneumonia is characteristic of viral inflammation, late initiation of treatment, develops in patients with severe concomitant diseases and has an unfavorable prognosis.
Prevention of segmental pneumonia includes general health measures, such as hardening, systematic physical activity, and good nutrition. Children at risk, as well as people working in children's groups, are recommended to be vaccinated against pneumococcal infection. During epidemics of respiratory diseases, contact with sick people should be minimized if possible, crowds of people should be avoided, and if signs of respiratory pathology appear, it should be treated in a timely manner.
In light of the latest events with the coronavirus infection, which has gripped the entire world as a pandemic, the observance of simple but quite effective protective measures to prevent segmental pneumonia is of particular relevance:
- Thorough and frequent hand washing with soap, treating them with antiseptics, especially after visiting stores and pharmacies;
- When coughing and sneezing, you should cover your mouth and nose not with your hand, but with a napkin or handkerchief;
- You should not only not smoke, but also avoid rooms in which they smoke;
- In summer it is important to avoid drafts, in winter and in the off-season - hypothermia;
- In crowded places, during a seasonal epidemic of respiratory diseases, it is recommended to wear a mask;
- As prescribed by a doctor - immunotherapy, flu vaccination;
- The house needs to be ventilated and wet cleaned regularly.
If you suspect pneumonia, you should stay home and call a doctor; your child should not be taken to kindergarten or school. Only qualified assistance from specialists will help in a speedy recovery, while self-medication and abuse of traditional medicine can cause negative consequences.
Prevention
For prevention purposes, a child needs to be hardened from an early age and his immunity strengthened. This requires a balanced and nutritious diet, regular physical activity, and adherence to a daily routine. An effective preventive measure is to vaccinate a child against pneumococcal infection and influenza.
To prevent the development of this disease in a child, it is necessary to promptly and correctly treat respiratory infections and sanitize chronic infectious foci.
Segmental pneumonia is dangerous, like other forms of this disease. To prevent severe consequences of pneumonia, you need to consult a doctor when the first symptoms appear, undergo an examination and strictly follow the recommendations of a specialist.
Restoration of the body
Treatment of such a phenomenon as segmental pneumonia in children should pursue the following goals: 100% elimination of focal inflammation and the fight against all symptoms of pneumonia. We are talking about the symptomatic nature of therapy.
In order to eliminate the inflammatory focus, specialists use treatment with gentle antibiotic drugs.
This is not the best option for a child’s body, but in case of pneumonia it will not be possible to do without antibiotic components. Exactly what medications are required for the childhood form of segmental pneumonia and in what quantity they are needed can only be determined by a general practitioner or family doctor.
Speaking about symptomatic treatment, it should be noted mucaltic components that facilitate the process of sputum discharge. You cannot do without antipyretic drugs; they should be used no more than 50% of the amount usual for adults.
The next stage, which makes the treatment of the disease complete, is strengthening the immune system. For this purpose, multivitamin complexes are used, as well as vitamins of groups A, B and C. Additionally, you can consume ascorbic and folic acid, fresh vegetables and fruits. Interstitial pneumonia in children can be defeated with the same methods.
Treatment of pneumonia with folk remedies
Traditional medicine knows many time-tested recipes. Pneumonia is no exception. In addition to traditional medicine, folk medicine is an effective treatment and acceleration of the recovery process in both children and adults.
Milk is considered an effective remedy in the fight against pneumonia. Based on it, you can prepare a medicinal infusion of fig fruits.
To do this, pour two dried figs into a glass of milk and cook over low heat for about fifteen minutes. The figs should soften during this time. The resulting infusion must be drunk throughout the day. During illness, you need to drink a glass of drink every day.
For severe forms of pneumonia, badger fat is recommended. For one month, you need to take one tablespoon of fat on an empty stomach, three times a day. To soften the taste of badger fat, it can be dissolved in hot milk (a tablespoon per glass of milk), thereby doubling the healing effect.
Onions and garlic are well-known folk remedies for many colds. Chopped onion into a pulp, mixed with honey 1:1. The resulting mixture is taken one teaspoon, three times a day, on an empty stomach.
You can also take chopped garlic (300 grams) and infuse it with one liter of Cahors. Infuse for fourteen days. Take the infusion pre-heated, one tablespoon every hour. This treatment is contraindicated for children, pregnant women, as well as persons suffering from liver disease and alcohol addiction.
Herbal infusions have also proven themselves in the fight against diseases of the lungs and respiratory tract. You can try, for example, this recipe: take one teaspoon each of pine buds, anise, fennel fruit and licorice root. Pour boiling water over the herbs and leave for twenty minutes. Strain the infusion and take three times a day.
It is worth noting once again that all the methods described here are strictly individual. Although they can be effective, they should still be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional. Traditional medicine should in no case act as a replacement for traditional medicine, only complement it.
Classification
Inflammation can occur in one or two lungs at the same time. Depending on this, they distinguish:
- Left-handed.
- Right-handed.
- Double-sided.
When the process affects several segments at the same time, they speak of the development of polysegmental pneumonia.
According to the nature of the disease, it can be:
- Spicy.
- Subacute.
- Chronic.
Most often, right-sided segmental pneumonia occurs. This is due to the fact that there are more shares on this side. Usually the pathology occurs acutely, so patients quickly consult a doctor.
When the first signs appear, you should immediately seek medical help. Pneumonia requires proper and timely treatment, as the risk of complications is high. In some cases, this pathology can cause death.