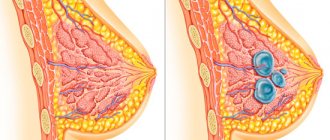
The development of a malignant breast tumor is considered the most common form of cancer in women. Every woman should know the signs of breast cancer. The sooner they can be recognized at a certain moment, the sooner it will be possible to see a doctor and begin effective timely therapy.
The development of a malignant breast tumor is considered the most common form of cancer in women.
Symptoms of breast cancer
The first signs of breast cancer often go unnoticed, since not all women undergo regular breast examinations and examinations. Symptoms of breast cancer appear as follows:
- The contours and shape of the mammary glands are noticeably changed.
- Changes the appearance and shape of the nipple (in some cases, nipple retraction appears, peeling occurs, and color change is possible).
- The skin of the breast changes its color (the affected area may be red, blue or yellow).
- Ulcers, wrinkled skin, and swelling sometimes appear on the mammary gland.
- When palpating the breast, compactions are detected, usually inactive.
- Discharge appears from the nipple when pressed.
- The lymph nodes become sore and usually enlarge.
- Unpleasant sensations and pain occur in the mammary gland.
Signs of breast cancer may vary depending on its form:
- With the nodular form, a dense nodule is detected that does not have clear contours. The skin on the gland area may become wrinkled.
- With a diffuse form, compaction can be determined. If the cancer is mastitis-like (inflammatory), the skin becomes red, and women experience a fever. If the cancer is armored, the compaction looks like a crust, the breast shrinks and becomes smaller.
- With Paget's cancer, the configuration of the nipple changes, ulcers, crusts, rashes, and discharge form.
- In the edematous form, the cancer tumor grows rapidly, the skin thickens and turns red, and swelling of the gland appears.
With small breasts, the tumor is much easier to notice, but if the breasts are large, this is more difficult to do, as a result of which the first signs of breast cancer simply go unnoticed.
A malignant tumor, when compared with a benign one, is denser, immobile, has uneven contours, and is painful.
Breast cancer: photos, first symptoms and signs, types, causes, stages, treatment, diagnosis
Free consultation on treatment in Moscow.
Call or fill out the form below: Breast cancer is a general name for a group of low-quality tumors that are localized in the mammary glands and differ in their course.
This pathology ranks second after lung cancer and is the most common cancer in women. According to global statistics, about 1.5 million cases of breast cancer (BC) are registered annually.
At the same time, in Russia, up to 54 thousand new cases of breast cancer are recorded every year.
As you age, your risk of cancer increases. In 75% of cases, the disease is detected in women over 60 years of age; in girls under 30 years of age, malignant tumors are diagnosed 150 times less often.
In men, breast cancer also occurs in 1% of the total incidence rate. Every year, in approximately 400 thousand cancer patients, the disease leads to death.
In recent years, there has been an increase in the mortality rate.
In fact, cancer is not a death sentence. It is quite possible to be cured of breast cancer; the main thing is to approach the choice of the attending physician and oncology clinic responsibly, and also not to neglect preventive diagnostics.
If you or your loved ones need medical assistance, contact us. The site’s specialists will recommend a clinic where you can get effective treatment:
What is breast cancer
The mechanism of the cancer process is based on mutation and accumulation of abnormal cells, which leads to rapid growth of the tumor and its spread to the lymph nodes and nearby organs.
In this case, some cancer cells break away from the cancer focus and spread through the bloodstream and lymphatic system, resulting in the formation of distant metastases in the brain, liver and other organs.
In such cases, treatment for breast cancer is a longer and more complex process.
Cancer is divided into several dozen forms, among which the most common are diffuse and nodular forms of cancer.
Symptoms of breast cancer
At an early stage, breast cancer does not cause women discomfort or pain. At the beginning of the development of the disease, it can only be detected through self-diagnosis or during mammography. The first clinical signs often appear closer to the 3-4 stages of development of a malignant tumor.
Breast cancer can be suspected based on the following signs:
- Seals. In the vast majority of cases, breast cancer is discovered after a woman or her partner notices a lump in the mammary gland, which prompts an early visit to a specialist.
- Nipple retraction. A pathological process is often indicated by a change in the natural shape of the nipple. If the tumor is localized near the nipple and grows into the skin, this causes retraction of the areola or deformation of the nipple.
- Discharge from the nipple. Discharge is normal during pregnancy or breastfeeding. In other cases, the presence of fluid from the nipples indicates a pathological process. Depending on the course of the disease, the discharge may be yellow, purulent, or bloody.
- Enlarged lymph nodes. Regional lymph nodes enlarge during the pathological process. At the same time, pain and discomfort are felt.
- Asymmetry of the mammary glands. Since cancer attracts healthy tissue, when you lift your arm up, a depression forms in the cancer-affected areas of the chest.
Oncopathology may be indicated by the occurrence of redness, peeling of the skin on the chest, pain in the armpit, as well as visible asymmetry and causeless soreness of the mammary glands.
Some clinical signs may indicate benign neoplasms, mastopathy, mastitis, mastodynia.
In any case, each of the listed symptoms is a serious reason to contact a mammologist for differentiated diagnosis.
Diagnosis of breast cancer
The first signs of breast cancer can be detected independently at an early stage, significantly improving the prognosis. Self-examination should be performed monthly on the 10th day of the menstrual cycle.
To do this, you need to prepare a mirror and first of all evaluate visual changes in the breast: the condition of the nipples, skin, symmetry and shape of the mammary glands.
Then you need to conduct a palpation examination, palpate the chest with your fingertips using circular movements for the presence of nodules, lumps, and depressions. You should also pay attention to the condition of the lymph nodes.
If self-diagnosis reveals suspicious changes in the breasts or nipples, this serves as an alarm, after which an urgent visit to a specialist is necessary.
In the clinic, after collecting an anamnesis and physical examination, doctors prescribe a set of diagnostic procedures:
- Blood test for tumor markers.
- Analysis of urine.
- X-ray examination (mammography), which allows you to accurately identify atypical neoplasms using X-rays in two projections.
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands - a detailed assessment of identified formations, allows you to differentiate a tumor from a cyst.
- Biopsy is the removal of affected tissue for cytological and histological analysis.
- PET-CT is carried out to determine tumor characteristics (location, size, extent of spread).
If metastasis is suspected, MRI, X-ray of the lungs, scenography of bones, and radioisotope study are prescribed. To draw up a treatment regimen and decide on the advisability of chemotherapy, a genetic analysis is performed for an oncogene that provokes a relapse of oncological pathology.
Causes of breast cancer
The development of the oncological process is caused by a disruption in the process of division and death of breast cells. There is no clear cause of breast cancer, but experts put forward a number of endogenous and exogenous factors that increase the risk of developing a malignant tumor.
Endogenous (internal) causes of breast cancer:
- genetic causes: breast cancer is characterized by mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes;
- long-term use of contraceptives;
- early menarche or late menopause;
- gynecological diseases of a chronic nature;
- miscarriage, abortion;
- hormonal and metabolic disorders;
- late labor or absence thereof;
- irregular sex life.
In addition, mastopathy and fibroadenoma, as well as a history of blood relatives of a similar disease, increase the risk of developing pathology. Exogenous (external) causes are still a matter of debate. According to experts, external factors can stimulate the development of a cancer focus together with other possible catalysts for cancer.
External risk factors include:
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- exposure to chemicals;
- chest injuries with damage to glandular tissue.
The trigger mechanism for carcinogenesis may be the action of ionizing radiation, after which the molecular structures of cells are destroyed.
Classification of breast cancer
The following types of breast cancer are classified according to histological type:
- Ductal invasive carcinoma is the most common form of cancer, accounting for about 80% of all breast cancer cases. The pathology develops inside the milk ducts, involving healthy tissue in the oncological process. The prognosis at the first and second stages is favorable in 80% of patients.
- Lobular infiltrating carcinoma - develops in the lobules that produce milk, occurs in 5-10% of cases. It responds effectively to hormone therapy and is characterized by slow growth.
- Inflammatory (mastitis-like) cancer is similar to the clinical manifestations of mastitis. A rare type of breast cancer that progresses rapidly.
Oncopathology is also classified according to the TNM system, which determines tumor size, the degree of tumor growth and the presence/absence of metastasis.
Stages of breast cancer
The severity of oncopathology can be determined by the volume of the malignant tumor and the degree of damage. To determine, classification is used in 4 stages:
- Stage I - tumor formation does not exceed 2 cm in size, there are no lesions of the lymph nodes.
- Stage II - tumor size no more than 2.5 to 5 cm, the lymph nodes surrounding the mammary gland are involved in the oncological process, distant metastases are possible;
- Stage III - the size of the malignant focus is +/- 5 cm, germination is detected in the lymph nodes of the armpits and nearby tissues.
- Stage IV - any size of atypical formation, the presence of nodules, ulcerations on the skin, there are multiple secondary cancer foci in distant organs and tissues.
Breast cancer prevention
To prevent breast cancer, experts recommend that you take the following preventive measures:
- If you have a significant medical history or genetic predisposition, undergo regular examinations, including mammography at least once a year. For women 35-55 years old, X-ray examination is indicated 2 times a year. It is also recommended to conduct self-diagnosis, which contributes to the early detection of pathology and a favorable prognosis.
- Control your body weight. According to statistics, obesity is one of the main predisposing factors to this cancer (up to 40%). Therefore, you should exercise more often, as well as adhere to a balanced diet, and eat more natural foods.
- Stop smoking and do not abuse alcohol. It is tobacco and the components of alcoholic beverages that contain a lot of carcinogens and harmful substances that provoke cellular mutations.
In addition, in order to prevent breast cancer, doctors recommend drinking coffee in limited quantities, avoiding stressful situations, not giving up breastfeeding, and regularly taking vitamin D, which actively suppresses the growth of cancer cells.
Breast cancer treatment methods
The leading treatment method for breast cancer is surgery. In any case, treatment tactics depend on the general condition of the patient and the stage of the disease.
Oncological treatment includes the use of the following methods:
- Surgical intervention. It involves the use of three techniques: mastectomy - removal of the gland with lymph nodes, adipose tissue, quadrantectomy - resection of a quarter of the breast and lumpectomy - organ-preserving surgery, in which only the cancer-affected area of the breast is excised, not exceeding 4 cm in size. After a mastectomy, breast volume can be restored using plastic surgery.
- Chemotherapy. Suppresses cancer with chemotherapy. Helps prevent relapses, and also allows you to reduce the size of the tumor before surgery. Sometimes used instead of surgery.
- Radiotherapy. It will also reduce the likelihood of relapse. Used to effectively kill residual cancer cells after lumpectomy or mastectomy.
- Targeted therapy. Often used in combination with chemotherapy or after surgery. The method consists of using monoclonal antibody drugs that effectively block the oncogene and slow down the growth of the lesion.
Immunotherapy is also prescribed, during which drugs are administered that activate the immune system to effectively destroy fast-growing cancer cells.
Treatment of breast cancer with folk remedies
Traditional medicine is not an alternative to officially recognized treatment in an oncology clinic.
Refusal of qualified medical care for the sake of using folk remedies, as a rule, leads to death. Therefore, you cannot waste time on “magical” healing infusions and decoctions.
After all, it is the timely detection and adequate treatment of malignant tumors that contributes to a favorable prognosis.
Today, breast cancer treatment in Moscow is carried out by world-famous oncologists and mammologists, who, thanks to their vast experience and the use of ultra-modern diagnostic and treatment equipment, achieve the best results of oncology therapy even in severe cases.
How long do you live after breast cancer treatment?
Survival depends largely on the stage of the disease and comprehensive, effective treatment. Ten-year survival rate at stages 1-2 is 50-80%. After cancer treatment, up to 30% of patients live for 10 years after diagnosis at stage 3 pathology, and no more than 5% at stage 4. Relapses occur in 22% of cases after radical excision of the mammary gland.
Source: https://med-kvota.ru/medical_articles/rak_grudi
Breast self-examination
A woman should have her breasts examined regularly, preferably after the end of menstruation. To do this, you need to stand in front of a mirror and carefully evaluate the shape and symmetry of the glands. The nipples also need to be examined: they must be the same in size, shape, color. When pressing on the nipples and areolas, make sure that there are no seals in them. Next, you need to squeeze each nipple and check if there is any discharge.
The breast should then be palpated. This is best done while lying on your back. You need to carefully feel all the lobes of the glands: there should be no compactions in them. Don't forget about the armpits. There should be no changes detected in the lymph nodes.
If changes are detected, the woman should be examined by a mammologist. The sooner diagnosis and treatment are carried out, the greater the chance of recovery. Stage 1 cancer in women is cured in 90% of cases. In stage 3, treatment is difficult, the prognosis is much worse.
Medical diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to perform several tests:
- Blood biochemistry and ESR. If there are signs of inflammation, then something is wrong in the body. This test is not proof of breast cancer.
- Ultrasound makes it possible to determine calcifications, which differ in color, as well as the location of the node and its size at this stage.
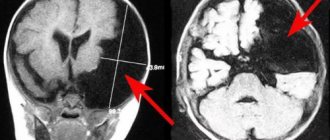
- MRI allows you to determine the presence or absence of metastasis.
- Fluorescent hybridization method to determine the breast cancer marker HER2.
- Analysis for the tumor marker CA15, which identifies breast carcinoma. An increased amount of this substance may indicate the presence of cancer in the cervix and lungs. Another marker, KI67, is also a helper marker, but it is not detected unless tumor cells are dividing. The doctor does not make a diagnosis based solely on the tumor markers found.
- Biopsy. Analysis of tissues for the presence of atypical cells.
- Scintigraphy - x-ray of bones for the presence of metastases.
In Russia, all women over 40 years of age are required to undergo mammography once a year for the prevention and early detection of cancer. Genetic analysis has no diagnostic value, but it warns a woman about possible problems in the future. If a genetic test shows the presence of mutated genes, this does not mean that the woman will definitely get sick - there must be several reasons or coincidences.
Signs of breast cancer depending on stage
1 tbsp. The tumor is up to 2 cm, located locally and is not connected to nearby tissues (for example, ductal carcinoma).
2a art. Formation up to 5 cm with germination into the area of subcutaneous tissue with the addition of changes in the skin in the form of wrinkling in the place where the tumor is located.
2b art. The appearance of a metastatic process. Metastases are single, located near the site of the lesion, for example, in the armpit area.
3a art. The formation at this stage measures from 5 cm and grows into other tissues and muscles. Women experience nipple retraction, discharge, and ulcers.
3b art. At this stage, multiple metastases form.
4 tbsp. The entire mammary gland is affected. Metastases at this stage spread to other organs and are found in the lymph nodes.
Forecast. Prevention
Of particular importance in the treatment of breast cancer is its detection in the early stages. If treatment is started at the first or second stage, the likelihood of a favorable outcome is much higher, while the fourth stage is characterized by high mortality and the impossibility of full recovery. Thus, survival prognosis directly depends on when breast cancer was diagnosed. Survival is estimated based on a ten-year period, that is, the figure indicates what percentage of patients will live for the next ten years. The prognosis for different stages of breast cancer is as follows:
The use of an integrated approach to treatment significantly improves the prognosis for all categories of patients [9].
One of the main measures to prevent breast cancer is disseminating knowledge about this disease and teaching women simple self-examination techniques, as well as regular examination by a mammogol once a year for women over 40 years of age [10]. Women with a history of breast cancer can be tested to determine hereditary predisposition (BRCA 1, BRCA-2, CHEK) and should be observed more frequently by a mammologist (once every 6 months)
A monthly examination of the mammary glands in front of a mirror will allow you to notice deviations from the norm and consult a doctor in a timely manner. Self-examination can be done regularly while washing in the shower. To do this, using circular movements, you need to palpate sequentially all sections of the right and left breast in a clockwise direction. You should also feel for any lumps in the armpit. If during this you find any lumps in the breast, changes in the skin of the breast or in the nipple area, dark or red discharge from the nipple, this is a reason to consult a mammologist. Also remember that it is advisable to perform an ultrasound of the mammary glands once a year, and starting from the age of 35, also a mammogram (once every 2 years).
In addition, it is necessary to monitor the health of the reproductive system, take hormonal medications only as prescribed by a doctor, and avoid exposure to carcinogenic factors. It is important that patients can quickly undergo the necessary examinations without having to face long waits for tests or diagnostic procedures.
The article was prepared for the website https://probolezny.ru
Causes of the disease
Heredity plays an important role in the occurrence of breast cancer. If you have breast cancer in your relatives, the risk of developing this disease increases several times.
Experts also assign an important role in the development of diseases such as ductal and other forms of breast cancer to such factors as absence of pregnancies, lactation, late childbirth, early menstruation, late menopause.
If a woman has a history of a breast tumor that has been treated, the risk of developing new tumors increases significantly.
If a woman suffers from some forms of mastopathy, for example, fibrocystic or fibroadenoma of the breast, there is also a danger of the benign tumor degenerating into a malignant one.
Experts also believe that the development of the disease is influenced by long-term use of hormonal drugs. Oral contraceptives are not one of them, but still the risk of breast cancer increases when taking such drugs in women after 36 years of age. If you have been on birth control for 10 years or more, your risk of developing the disease also increases.
Frequent X-ray examinations of the chest area, for example, in case of tuberculosis or pneumonia, also pose considerable danger.
There is evidence that patients with tumors in the mammary glands also have endocrine diseases, for example, diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction, etc.
Causes
Breast cancer is a multifactorial disease, which means that malignancy of the genetic material of cells can occur under the influence of a variety of factors, including:
There are a large number of factors contributing to the development of breast carcinoma. But almost all of them are associated with two types of disorders: increased activity of female sex hormones (estrogens) or genetic disorders.
At the moment, experts say that it is incorrect to talk about the causes of cancer, since the disease has not been fully studied. Therefore, the prerequisites for the development of oncology are usually called risk factors. There is still no exact data on why, how and to what extent these factors contribute to the development of cancer.
Breast cancer today has become one of the most common diseases of the century. Cancer cells are mutant cells that are not characteristic of normal body tissues.
A sharp increase in incidence was noted in the late 70s in post-menopausal women. Today, the age of the disease has changed, the disease has become much younger and women over the age of 25 suffer from this pathology.
Breast cancer: symptoms and signs
The female breast is a glandular organ that, during the birth of a baby, performs the important function of milk production and feeding. Young mothers do not always handle and care for their breasts skillfully enough, and it is for this reason that they often encounter problems.
- Mastopathy is characterized by the presence of many nodular seals in the tissue
- Mastitis is an inflammatory disease of glandular tissue and gland ducts (purulent, serous)
- Fibroadenoma is a benign formation in breast tissue, usually consisting of fibrous connective tissue
- During self-examination, you can detect a compaction of gland tissue, it can be of different sizes and not be single • Painful sensations may be present • Upon visual examination, you can notice a clear asymmetry and change in shape • Ulcerations, peeling or crusts may be present in the area of the areola • Feeling of pain in axillary area (regional lymph nodes) • Discharge from the nipple (provided that you are not a nursing mother) of various types, especially bloody
• Skin hyperemia and swelling - A mammogram is an X-ray examination of the breast in 2 projections. This study is carried out at a certain phase of the menstrual cycle, to avoid making an erroneous diagnosis. Ultrasound diagnostics and its varieties (Elastography) is a method for examining soft tissues, however, ultrasound does not detect calcifications and bone formations, therefore it is used in combination with other research methods. MRI or Magnetic resonance imaging is the most informative non-invasive diagnostic method, as it allows layer-by-layer examination of images of the compaction. Radioisotope research is carried out by introducing radioisotopes into the bloodstream and, using an x-ray, determining the location of their accumulation (often radioisotopes tend to accumulate in tumors, depending on its characteristics of blood supply and hormonal activity)• Puncture is an invasive diagnostic method that allows you to send part of the compaction tissue for histological examination to determine the type of cells that form this compaction• General clinical examination methods (blood tests for hormones, general blood test, etc.) d.)
- Surgery to remove tumor formation from tissues.• Hormone therapy is carried out if it is confirmed that the tumor is hormonally active and can adequately respond to treatment• Radiation therapy is carried out to slow down the growth of the tumor and transfer it to a state in which surgical intervention is possible• Targeted (targeted) radiotherapy, in this case only damaged areas of tissue are irradiated and there is practically no overall effect on the body
• Therapy with anti-cancer drugs or chemotherapy is prescribed to patients on an individual basis and with an individual selection of drugs - The size of the tumor exceeded 2 cm in diameter• The tumor is not hormonally active• The patient is of childbearing age
• Histological analysis of the tumor cells was poorly differentiated - Activity: 73k
- Gender: Woman
All these symptoms indicate the terrible disease CANCER. If you detect at least one of the listed symptoms during a self-examination, do not delay visiting a doctor.
Diagnosis of breast cancer: how to identify breast cancer?
The first stage of any diagnosis is careful attention to your body and self-examination.
The type of examination and its necessity will be determined by your consulting physician.
What are the stages of breast cancer?
Like any disease, oncology has several phases or degrees of development, which are treatable or no longer treatable.
This division is quite arbitrary and depends on the volume of the tumor, which in medical terminology is designated by the letter T (T1, T2, T3, T4), whether regional lymph nodes are involved in the disease - N (also 4 stages) and whether there are metastases to other organs and tissues (0-no, 1-present)
Stage 1 of the oncological process is characterized by the presence of a formation in the gland up to 2 cm in diameter and the absence of involvement of lymph nodes and metastases in the body. This stage is most treatable.
Stage 2 of the oncological process is characterized by tumor sizes from 2 to 5 cm in diameter with damage to up to 2 lymph nodes and the possible presence of single metastases.
Stage 3 of the oncological process is characterized by a tumor size exceeding 5 cm in diameter, involvement of almost all lymph nodes of the axillary cavity in the process, metastases may be absent.
Stage 4 of the oncological process does not take into account the size of the tumor, while the lymph nodes of both armpits are involved in the process and multiple metastases are present.
Breast cancer treatment
Oncology treatment produces the most effective results in the early stages. The sooner you start treatment, the less radical it will be. It should be noted that in the later stages, cancer cannot be completely cured and help is directed only to alleviate the patient’s condition.
Chemotherapy for breast cancer
• The skin becomes pale, itching or redness may occur, symptoms of an allergic reaction
These symptoms usually disappear after a course of therapy and a period of recovery of the body. Another unpleasant effect of the drugs is hair loss, but this will also recover over time.
Early breast cancer - treatment
With timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment, the prognosis for a complete recovery is very high. At the same time, surgical intervention will not be so radical. In the most positive cases, everything can be done even without surgery and non-invasive treatment (radiotherapy, chemotherapy)
With early treatment, not the only trace after surgery, if it is necessary, will be a small scar. Partial excision of the breast tissue is performed, along with the tumor, and preventive chemotherapy or radiotherapy is carried out (it all depends on the type of tumor) to prevent relapse.
Breast cancer: metastases
Most forms of breast cancer have the ability to metastasize. The main routes of metastasis are the lymphatic route and the path of blood vessels. Tumor cells, entering regional lymph nodes, provoke degeneration and malignancy of the cells of the lymph nodes themselves.
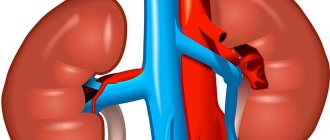
Once in the bloodstream, the first barrier organs (liver, lungs, spleen, kidneys) begin to suffer first.
The presence of metastases indicates the extent and prevalence of the disease. And if a localized tumor can be excised and adequate therapy can be carried out, the presence of metastases significantly aggravates the situation and therapy for the disease is transferred to the category of palliative.
This treatment is aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition and improving general condition. There is no talk of a complete cure in this case.
Surgery for breast cancer
The extent of the operation always depends on the stage of the disease. It is generally accepted that with the help of surgical intervention, the greatest effect can be achieved in stages 1 and 2 of the disease. At these stages, it is possible to preserve the mammary gland as an organ. After excision of the tumor, therapy is prescribed based on histological examination of the cells of the excised tumor.
When cancer is determined to be stage 3, radical removal of the gland is performed with excision of regional lymph nodes. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of techniques is also prescribed. After radical surgery, the woman becomes disabled.
Stage 4 may be contraindicated for surgery, it all depends on the general condition of the patient and the extent of metastases in the body.
Life after breast cancer surgery
If the patient is operated on in the first stages of the disease with preservation of organs, then it is possible to return to a normal lifestyle within six months, after undergoing preventive therapy.
But after radical removal of the organ and lymph nodes, women acquire disability from group 3 to group 1, depending on the limitations in self-care activities. In these cases, the operation is followed not only by treatment, but also by a fairly long path of rehabilitation.
Some restrictions should be remembered after oncology therapy: • Do not be exposed to sunlight for a long time • Do not stand for a long time near heating surfaces • Do not walk in the hot weather.
• Eliminate bad habits
There are many such recommendations, we have listed only a small part of them. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
Breast cancer prevention
• Balance your sex life
We wish you physical and psychological health. Be attentive to yourself.
Elena the contemplator
formulazdorovya.com
• Mastopathy is characterized by the presence of many nodular seals in the tissue
• Mastitis is an inflammatory disease of glandular tissue and gland ducts (purulent, serous)
• Fibroadenoma is a benign formation in the breast tissue, usually consisting of fibrous connective tissue
• Upon self-examination, you may find a lump in the gland tissue; it can be of different sizes and not single • Painful sensations may be present
• Upon visual inspection, you can notice obvious asymmetry and changes in shape
• Ulceration, peeling, or crusting may be present in the areola area.
• Feeling of pain in the axillary area (regional lymph nodes)
• Discharge from the nipple (provided you are not a nursing mother) of various types, especially bloody
• Skin hyperemia and swelling
All these symptoms indicate the terrible disease CANCER. If you detect at least one of the listed symptoms during a self-examination, do not delay visiting a doctor.
• A mammogram is an X-ray examination of the breast in 2 projections.)
• Surgery to remove tumor formation from tissues. • Hormone therapy is carried out if it is confirmed that the tumor is hormonally active and can adequately respond to treatment • Radiation therapy is carried out to slow down the growth of the tumor and transfer it to a state in which surgery is possible
• Targeted (sighted) radiotherapy, in this case only damaged tissue areas are irradiated and there is practically no overall effect on the body
• Therapy with anti-cancer drugs or chemotherapy is prescribed to patients on an individual basis and with individual selection of drugs
• The tumor size exceeded 2 cm in diameter • The tumor is not hormonally active • The patient is of childbearing age
• Upon histological analysis, the tumor cells were poorly differentiated
• The skin becomes pale, itching or redness may occur, symptoms of an allergic reaction
With timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment, the prognosis for full recovery is very high. At the same time, surgical intervention will not be so radical. In the most positive cases, everything can be done even without surgery and non-invasive treatment (radiotherapy, chemotherapy)
Most forms of breast cancer have the ability to metastasize. The main routes of metastasis are the lymphatic route and the blood vessel route. Tumor cells, entering regional lymph nodes, provoke degeneration and malignancy of the cells of the lymph nodes themselves. Once in the bloodstream, the first barrier organs (liver, lungs, spleen, kidneys) begin to suffer first.
You should remember some restrictions after oncology therapy: • Do not be exposed to sunlight for a long time • Do not stand for a long time near heating surfaces • Do not walk in the hottest part of the day
• Eliminate bad habits
• Get rid of bad habits
• Balance your sex life
Breast cancer causes a large percentage of deaths among women. The main reason for such statistics is late access to specialists for research and treatment.
Manifestation of breast cancer
In order for the treatment of pathology to give an effective result, you should be more attentive to your body, notice the slightest changes that will help to promptly recognize the disease in the early stages.
The first signs of breast cancer are difficult to determine, which is why this disease is dangerous, as it destroys a woman’s body with virtually no symptoms. Therefore, it is very important to notice the disease in time. The pathology manifests itself as a small neoplasm—it is this that is a sign of breast cancer.
But if you know what the signs of breast cancer are at an early stage, you can avoid the serious consequences associated with this disease.
How to recognize the disease
Girls and especially women during menopause should make it a rule to check the condition of the mammary gland and lymph nodes in the armpit once a month.
Any detected changes should not cause fear, but they should not be left to chance. You need to contact a specialist.
What should you look out for during self-diagnosis?
- Any compaction of the mammary glands - nodules, peas, tumors. They can be identified even with the naked eye. When palpated, such a compaction resembles cartilage or a soft ball that does not have clear boundaries.
It is this initial sign that leads eighty percent of women to a mammologist.
- Any discharge from the nipple outside of pregnancy and lactation should be cause for concern. This anomaly does not depend on the menstrual cycle. The amount of fluid released increases. The discharge can be different - with ichor or pus, transparent or cloudy yellowish, and others. It is precisely this manifestation of pathology that should concern a woman and refer her for consultation.
- Cancer can manifest itself in the form of wounds or abrasions that are non-healing and develop into ulcers. They can be single in their initial manifestation, and then spread and merge with each other.
- A change in breast shape and general appearance is also a signal to contact a mammologist. With neoplasms, the skin texture changes. “Lemon peel” appears, the dermis becomes wrinkled in the affected areas, and the skin color changes from pinkish to purple. Swelling of the gland may occur.
All of these changes should be warning signs.
- Symptoms of breast cancer manifest themselves in the form of nipple deformation and changes in the areola. The nipple may be pulled inward or flattened, peeling and irritation of the areola may appear.
- The first symptoms may be hidden in the armpit in the form of swelling in this area or enlarged lymph node.
Important! Mammography is required for women over forty years of age. Those who have had cancer in their family should be tested from the age of 35.
Women have secondary signs of breast cancer that should be alarming.
This is a multifactorial disease. Its development is associated with changes in the genetic material of breast cells under the influence of certain external influences.
Cancer can develop in connection with previous pathological processes in breast tissue - repeated dishormonal hyperplasias, in which foci of fibrocystic mastopathy (fibroadenomatosis) are formed.
The first signs of breast cancer are the appearance of lumps. This is how a node, cyst, or tumor can manifest itself. It is this symptom that most often forces a woman to consult a mammologist. In more than half of the cases, the neoplasm turns out to be benign.
Lumps in the chest can be detected by palpation during self-examination. The large size of the glands poses some difficulties, since in this case the woman may not notice the appearance of a neoplasm. Sometimes the tumor can be seen during external examination. These can be formations with a clear or fuzzy contour, round or elongated.
If a woman is not expecting a baby or is not breastfeeding, ductal discharge can also be a sign of breast cancer. Such discharge does not depend on the phase of menstruation.
With the further development of the oncological process, the discharge often becomes stronger. They can be different: colorless, bloody, purulent.
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason for examination by a mammologist.
Thrush, localized in the mouth, is contagious and is transmitted from person to person - through kissing, sharing utensils, through contaminated food, etc. Even if the carrier of a fungal infection does not observe the manifestation of symptoms of the disease, he can infect another - the one who who has weaker immunity?
Acute infectious diarrhea is watery, loose stools more than three times a day or watery, loose, bloody stools more than once a day.
One of the main causes of bacterial tonsillitis is close contact with a sick person, from whom bacteria can be transmitted in several ways:
- through shared bedding;
- during kisses;
- when using shared utensils.
Bacterial tonsillitis in a child can be caused by non-compliance with personal hygiene rules in kindergarten or school. Germs can be transmitted through shared office items and through active communication.
Young children are particularly susceptible to the disease and therefore it is very important to detect it in time and begin treatment immediately. The disease can be recognized in a young child by the following signs:
- increased moodiness for no reason;
- periodic crying;
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- refusal to eat.
You may also experience increased salivation, swollen lymph nodes, and redness of the throat.
The causes of brucellosis are undoubtedly microbiological in nature.
The causative agent of brucellosis was first discovered in 1886 by D. Bruce, who named the bacterium he discovered Micrococcus melitensis. Subsequently, Bang and Striebold obtained similar microorganisms during infectious abortions in cows, and J. Traum obtained similar microorganisms from pigs.
In 1920, all these microorganisms were grouped into one genus, named Brucella (in honor of the discoverer).
The beginning of serological studies of material for brucellosis disease was laid by A. Wright and D. Semple in 1897. Subsequently, the Wright agglutination reaction acquired one of the leading roles for the diagnosis of this infection.
Brucella are small ovoid gram-negative bacteria that do not have spores or flagella. A distinctive feature is slow growth.
Among the pathogenicity factors of Brucella, endotoxin and hyaluronidase should be noted.
Brucella quickly dies when boiled and exposed to disinfectants, but they are highly resistant to low temperatures: for example, in meat, even if frozen, they remain for up to 5 months, and in milk for up to 1.5.
People from young to old suffer from purulent meningitis: in our practice, the youngest patient was not even a month old, and the oldest was over 80 years old.
Statistics say that most often patients catch meningitis in the spring.
Why is it at this time that the immune system cannot resist a dangerous infection? The fact is that it is during this period that the causes of meningitis become more pronounced.
Previously, we quite often recorded cases of mass disease. Now that mandatory vaccination is carried out against this infection, people are getting sick less often. The causes of diphtheria are infection. There are no other causes of diphtheria.
Anyone who has not yet been vaccinated against diphtheria is at risk. Immunocompromised patients may also get sick, even if they received the vaccine on time. You need to improve your literacy level. What is diphtheria: symptoms, causes and treatment of the disease in children and adults. Everyone, without exception, should know about this.
These patients will experience the disease in a mild form: with slight malaise, sore throat and runny nose. True, this condition can last more than a month. In addition, during this period, patients become infectious.
Diagnostics
If lumps are detected in the breast, a woman should undergo examination by a mammologist. First of all, the specialist pays attention to external signs: changes in the shape of the breasts, nipples, the appearance of asymmetry, and discharge. Mammography is required, which is performed using X-ray equipment. Ultrasound is often prescribed as an additional method. These methods allow you to visualize formations in the mammary glands, their location, shape, contours, and sizes.
To determine the nature of the tumor, a biopsy is required. Using this technique, under ultrasound control, a needle is inserted into the tumor, which removes a small fragment of altered tissue. Next, they are sent for histology - the study of tissues and cells under a microscope. To identify atypical cells, immunohistochemistry is sometimes required, in which a histology specialist applies a special chemical composition to the tissue to help identify pathological cells.
In some cases, for example, if the cancer is ductal, ductography is indicated, in which a contrast agent is injected into the ducts of the gland, and then an x-ray is taken.
When a malignant tumor is detected, an ultrasound is prescribed to identify the metastatic process, including in the lymph nodes. Since metastases can appear not only in the lymph nodes, but also in other organs, an ultrasound of the peritoneum and a chest x-ray are prescribed.
If the first signs of breast cancer are detected, the patient undergoes a blood test for tumor markers. A cancer patient has specific proteins in their blood that are not found in a healthy body.
Why is it dangerous?
Breast cancer is a dangerous and rapidly progressing disease. Often this pathology leads to complete removal of the breast, and at the last stage - death.
The pathological process is dangerous because it spreads into the chest. Metastases can spread to the adjacent breast. Sores that appear due to long healing are often the cause of infection. If left untreated, metastasis spreads to all organs. Possible postoperative complications that can be corrected with medication:
- swelling of soft tissues;
- curvature of the spine as a result of changes in load due to breast removal on one side;
— motor dysfunction of the shoulder joint;
- disruption of the immune system due to the removal of part of the lymph nodes.
Symptoms of breast cancer in men
Breast cancer is much less common in men than in women, and it most often affects men over 60 years of age. The causes of breast cancer are hereditary factors, as well as poor ecology. There is a high risk of illness among workers associated with atomic radiation. When undergoing radiation therapy necessary to treat diseases of the chest, the risk of developing cancer also increases significantly.
What are the symptoms of breast cancer in men? Typically, signs of cancer manifest themselves in different ways. Most often, lumps are found in the breast tissue. They are easier to find because men have small breasts. The neoplasm becomes noticeable at later stages. Enlarged mammary glands in men may not always be a sign of cancer. Also, in some cases, changes appear in the nipple, its retraction, and the appearance of discharge (transparent or bloody). An inflammatory process in the nipples in the form of wounds and ulcers is possible.
Like women, men show changes in the lymph nodes. Typically, the increase occurs in the axillary area that is closer to the affected mammary gland.
Do breasts hurt with cancer? Pain in the breasts and nipples can occur when pressed or touched. Usually pain appears in the area where the tumor is located.
First signs
It is very difficult to recognize cancer in the early stages. Symptoms of breast cancer are also characteristic of other breast diseases. Therefore, many girls and women, discovering the first signs (lumps, discharge from the nipples, redness of the skin), delay going to the doctor. Meanwhile, the tumor progresses.
The following symptoms are identified:
- The presence of compactions in the area of the mammary glands, on the surface or deep in the tissue.
- Changing the shape of the breast.
- Indentations that are especially visible if you raise your hands.
- Discharge from the nipples (typical of later stages).
- Skin redness, peeling.
- Pain on palpation (typical of later stages of the disease).
The difficulty is that these same symptoms are also characteristic of benign tumors. Therefore, it is very important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
Serious symptoms include the following:
- brown or yellow nipple discharge, blood
- painful lump, especially irregularly shaped
- enlarged lymph nodes on the side of one breast
- chest pain before menstruation (unless caused by other diseases)
- severe pain in the chest
These signs also do not necessarily indicate cancer, but indicate a serious illness that requires immediate treatment.
First signs of breast cancer
As mentioned above, every woman should know what the first symptoms of developing breast cancer are. Of course, knowledge does not always bring positive results. Very often, a woman is afraid of what is happening to her body, closes herself off from others and completely immerses herself in her problem, or, on the contrary, mistakenly ignores it.
In any case, those who are familiar with the main signs of cancer are more prepared for it and are safer.
So, the main signs of breast cancer include:
- A formation in the mammary gland that is easily palpable, especially when lying down. Very often, a woman herself notices a new lump that has appeared at the moment when she bathes in the shower. Sometimes its size can be so tiny and small that she will not even think that it is the initial stage of cancer
- Painlessness of the resulting formation. Rarely does a neoplasm cause discomfort to a woman, which is why it is so difficult to recognize
- Changing the shape of the breast. This occurs if the formation increases and is located relatively shallow. In this case, the breast may change shape, become asymmetrical, and a certain ball will be visible
- The skin on the chest may retract, which directly indicates the onset of the disease.
- Nipple retraction
Unpleasant sensations in the breast, namely in the part where there are cancer cells. Typically, cancer is found in only one of the two mammary glands, which is why discomfort is felt directly in the one where the tumor appeared - Nipple changes. Very often it begins to swell and becomes denser. And often it is drawn into the chest itself. This usually happens when the tumor is located close to the nipple
- Nipple discharge. One of the obvious symptoms that almost every woman notices is a kind of discharge from the nipples. And if normally there is little such discharge, then if a woman has cancer, it will be intense, and sometimes mixed with blood.
- The lymph nodes in the axillary area enlarge, and all the nodes in this group enlarge; they become similar to the touch to a bunch of grapes
If the tumor is large, there will be the following signs:
- Easy palpation of the tumor, especially if you press the chest to the chest
- If you pull back the nipple, the resulting tumor will change its place
- The skin around the nipple thickens
Despite the fact that the first signs of the development of breast cancer are quite bright and understandable, only a small number of representatives of the fair half of humanity attach importance to them.
Almost all malignant tumors in the early stages of development are very difficult to detect, and breast cancer is no exception. Symptoms of the onset of the disease can only be detected during a random examination.
A woman who feels pain in the mammary gland and discomfort for a long time for no apparent reason should immediately be examined by her doctor. The first symptoms of breast cancer are expressed by compaction, changes in the size and shape of the mammary gland, its swelling, and deformation.
As the tumor develops, the nipple becomes deformed and bloody or yellowish discharge may flow from it. The skin at the site of the lesion changes somewhat, it becomes wrinkled, retracted, dry, and changes its color.
The lymph nodes in the armpit become enlarged; in some cases, they are noticeably enlarged above or below the collarbone. A slight swelling appears in the shoulder and breast area.
When you raise your arm from the side where the tumor is developing, a depression or dimple appears on the chest.
How to recognize breast cancer in women? The first signs are difficult to detect at an early stage. When palpated, a small, hard tumor is felt. Lymph nodes in the armpits become enlarged. Chest pain appears. The woman feels general weakness.
There are many risk factors for the development of this life-threatening cancer. Among them, we can separately note the early onset of menstruation (before 12 years), hereditary predisposition, radiation exposure, obesity, long-term smoking, the onset of menopause after 55 years, etc.
For early diagnosis, methods such as:
- independent feeling of the breast;
- inspection;
- examination;
- Ultrasound of glands;
- fluoroscopy of the glands (mammography);
- biopsy (microscopic examination of cells obtained from a neoplasm).
Signs of breast cancer in women and its treatment are directly dependent on the form of cancer, the stage of the disease and the degree of spread of metastases.
Treatment
Treatment for breast cancer begins after diagnosis. The main methods are surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Surgical treatment is aimed at removing the tumor and the mammary gland in whole or in part. To prevent the metastatic process and the development of a new formation, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are performed. During a mastectomy, surgery is also performed on the lymph nodes, since metastases most often affect them too.
Using the radiation method, treatment is carried out at the site of the tumor, as well as on the lymph nodes. Often, after such therapy, side effects such as skin hyperemia, rash, breast engorgement, and general weakness develop.
Combined with surgery, chemotherapy gives encouraging results. Treatment is carried out using drugs that are prescribed strictly individually. Side effects include symptoms such as deterioration in health, vomiting, and hair loss. After the course, these symptoms usually disappear. Hormonal treatment may also be prescribed.
Surgical interventions
Before treating the tumor with organ-conserving surgery, neoadjuvant chemotherapy is performed. Its goal is to destroy micrometastases and improve operating conditions. This increases the patient's chance of survival after systemic treatment before surgery.
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy treatment for breast cancer allows the doctor to recognize whether the therapy has been prescribed correctly. If the patient has a non-palpable tumor, before such treatment a mark is placed on the problem area, with the help of which the damaged areas are accurately removed during the operation.
To determine the extent of damage to the axillary lymph nodes, a biopsy is prescribed. With this manipulation, not all lymph nodes are removed, but only the single sentinel one is removed. If there are no cancer cells in it, then excision of other nodes is not necessary. Using this method, organ-preserving treatment is carried out, leaving nodes that are not affected by metastases. The operation prevents complications such as lymphedema. This has a positive effect on the patient’s subsequent rehabilitation.
Complications
With breast cancer, an inflammatory process of tissues located close to the formation may develop. Also, sometimes bleeding and liver failure are possible from large tumors, which is associated with the presence of a metastatic process. Bone fractures and the development of pleurisy are common. After surgery, an inflammatory process in the operated area and lymph stagnation are possible.
The prognosis for women is good in the early stages of breast cancer. The prognosis is much worse in advanced forms of cancer, in the presence of metastasis.
Stages of breast cancer in women
It was already mentioned above that the sooner the disease is identified, the higher the chances of proper treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to consider what stages of breast cancer exist.
- Zero. This is a non-invasive stage of cancer. A malignant neoplasm is localized only in the mammary gland and does not spread beyond it. The disease, which is diagnosed at this stage, can be successfully treated in all cases. But alas, due to neglect of her health at this stage of the pathology, a woman very rarely consults a doctor. Although signs of breast cancer can be detected already at this stage.
- First. At this stage, cancer cells gradually invade adjacent breast tissue. The size of the malignant neoplasm at this stage is approximately 2 cm. The lymph nodes are not yet affected. The bulk of all cases of the disease are determined at this stage. The treatment also shows quite effective results.
- Second. In addition to nearby tissues and the mammary gland, cancer cells affect those lymph nodes that are located on the same side . The size of the neoplasm is 2-5 cm.
- Third. At this stage of cancer, nearby tissues become infected, the mammary gland itself, and the lymph nodes are fused to each other. The size of the neoplasm is more than 5 cm.
- Fourth. This stage of the disease is the most difficult. The neoplasm begins to move far beyond the boundaries of the chest - the internal thoracic lymph nodes, supraclavicular lymph nodes, into the lungs, axillary part, bone tissue, brain, liver. Unfortunately, treatment at this stage is almost ineffective. Naturally, treatment can somewhat prolong the patient’s life, however, it is absolutely impossible .