What's happened
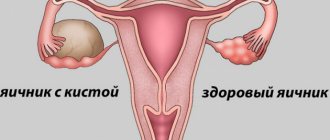
An endometriotic cyst on the ovary differs from other types in its development mechanism, which in most cases is manifested by damage to both the left and right ovary. The disease is common and occurs as a consequence of the development of genital endometriosis, in which mucous cells located on the inner surface of the uterine body penetrate the vagina, uterine tubes, ovaries and peritoneal cavity.
Formed lesions are hormonally dependent, and therefore may be subject to a menstrual-like reaction. With the constant growth of the endometrioid layer, a cystic formation begins to form.
The pathological process is more common in the female half of the population of reproductive age (from 30 to 50 years). In most cases, it is combined with endometrial hyperplasia and uterine fibroids.
Sometimes it reaches up to 12 centimeters in size. In addition, if there are no glands in the cystic walls, then we can talk about the appearance of an endometriotic type cyst.
Diagnosis of pathology
The insidiousness of the disease lies in the peculiarities of its course. An endometrioid cyst can be sluggish with hidden symptoms or manifest as severe discomfort in the uterus and ovaries, intensifying during menstruation.
If in a woman's body cells identical to the endometrium are located outside the uterus, they are classified as endometriosis. It is with the appearance of small endometrial nodes on the surface of the ovary that the disease begins. Endometriotic nodes increase in size with each menstrual cycle, similar to the endometrium in the uterine cavity. The accumulated menstrual fluid forms a thick mass in the resulting cavity.
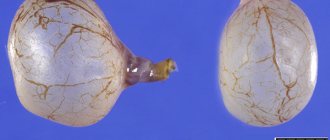
What a “chocolate” cyst looks like is shown in the photo below.
You can suspect the presence of an endometrioid cyst if you have symptoms such as:
- nagging pain in the ovarian and lumbar region, intensifying with the onset of menstruation;
- the appearance of brown spotting before and after menstruation;
- deterioration of general condition caused by symptoms of intoxication;
- increase in abdominal size;
- heavy periods;
- shortening of the menstrual cycle caused by prolonged menstruation;
- the appearance of pain during sexual intercourse;
- inability to become pregnant for a long time against the background of regular sexual activity without the use of contraception;
- disturbance of defecation (frequent constipation) and urination.
There are 4 stages of development of endometrioid ovarian cysts:
| Stage | Characteristic |
| Stage I | Small punctate lesions on one or both ovaries |
| Stage II | Cyst of one of the ovaries measuring up to 6 cm |
| Stage III | Cysts of both ovaries up to 6 cm in size with possible transition to the serous integument of the uterus and appendages, the walls of the pelvis |
| IV stage | Bilateral ovarian cysts measuring more than 6 cm with the process spreading to neighboring organs and the appearance of adhesions |
The choice of treatment method and further management tactics will depend on the stage of the process.
The presence of an endometrioid cyst on the ovary can be confirmed using instrumental and laboratory research methods:
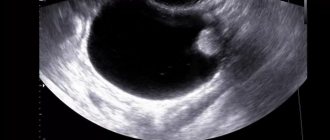
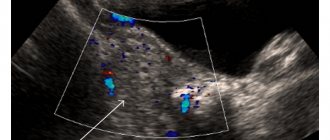
- Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to determine the presence of pathological cavities, their size and location. On the monitor screen, the contents of the cyst are displayed in white. To obtain more extensive information (absence of hemorrhage in the walls of the cyst), ultrasound is combined with Doppler ultrasound to study the speed of blood flow in the vessels.
- Laparoscopy remains the most informative method for diagnosing neoplasms inside the ovaries, which makes it possible to determine the type of pathology, the nature of the exudate contained, and the presence of adhesions.
- A biopsy followed by histological examination is used as an additional diagnostic method if the oncogenic nature of the disease is suspected.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is used when a dermoid cyst is suspected to exclude the presence of fatty deposits inside the cavity.
Special research methods are carried out to refute other diseases that have similar symptoms:
- uterine fibroids;
- rectovaginal endometriosis;
- fallopian tube endometriosis;
- uterine sarcoma;
- corpus luteum cyst;
- follicular cyst;
- dermoid cyst;
- ovarian tumor.
In most cases, endometrioid cysts are diagnosed in women of reproductive age under 40 who cannot fulfill the dream of motherhood. Reproductive dysfunction occurs due to abnormal growth of the endometrium behind the uterine cavity, which prevents the advancement of the egg in the desired direction.
Causes
Despite the fact that there are many theories regarding the development of endometriosis, it has not yet been possible to establish the exact predisposing factors. If we consider the implantation hypothesis, then an endometriotic cyst can form against the background of retrograde menstruation. This is a condition in which tissue cells, along with blood discharge, penetrate the ovaries, abdominal cavity and uterine tubes.
The introduction of endometriotic fragments can also occur during surgery when the mucous membrane of the uterine body is injured.
There is an assumption that lesions may arise as a consequence of metaplasia of residual elements of embryonic tissue, a decrease in immune defense, or due to gene abnormalities, when endometriosis is a family disease.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Differences between cytology and colposcopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
The reasons for the development of endometrioid ovarian cysts also include:
- frequent stressful situations;
- pathologies ;
- excess weight ;
- unfavorable environmental factors;
- endometritis.
In addition, the dependence of the cyst on endocrine system disorders was established, which are accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of progesterone against the background of an increase in estrogen, a malfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
In what cases can a cyst rupture?
If the tumor has reached a fairly large size, then at a certain moment it may rupture and fluid may spill into the abdominal cavity. This can happen for various reasons. For example, a rupture can be the result of a severe bruise, active sexual intercourse, or excessive physical activity.
Rupture of an endometrioid ovarian cyst is accompanied by acute pain in the pelvic area, elevated temperature, unusual discharge, decreased blood pressure, and stool disturbances. If such symptoms are detected, the woman needs immediate medical attention.
Symptoms
The manifestation of the clinical picture will largely depend on the stage and spread of the disease. As a rule, the initial stages of the formation of a cystic formation can be asymptomatic, so a woman may not be aware of the presence of pathological disorders in the body for a long time.
As the disease progresses, the following symptoms begin to appear:
- pain in the lower abdomen, the intensity of which may increase with the onset of menstruation;
- uncharacteristic menstrual discharge;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- disturbance of the urinary process.
As the tumor gradually increases, compression of the ovarian tissue occurs. With this condition, infertility and hormonal imbalance occur. The pathology is also accompanied by changes in the menstrual cycle, deterioration in the appearance of the skin, and increased hair growth in those areas of the body where women should not have hair.
An endometrioid cyst can be dangerous because when it ruptures, the contents penetrate into the cavity of the peritoneal space, causing peritonitis. This process causes severe pain, which intensifies during sex or after excessive physical activity.
Initially, the left or right side hurts, after which the syndrome spreads throughout the entire abdominal area. Over time, body temperature rises, nausea, vomiting, and stool disturbances appear. This condition requires emergency surgery to prevent death.
Symptoms of endometrioid ovarian cyst
Small endometrioid cysts do not appear for a long time. But as soon as the cyst increases in diameter, various clinical signs appear.
First of all, patients are concerned about pain in the lower abdomen and/or lumbar region. The pain can be aching or pulling, and it intensifies during menstruation. An increase in the intensity of pain during menstruation is associated with stretching of the cyst capsule as a result of its filling with blood. Due to this indirect fact (an increase in the size of the formation after menstruation), one can judge the presence of an endometrioid cyst.
Some cysts grow very quickly, which is dangerous if they rupture, while others, on the contrary, do not increase in size and freeze for years.
In addition, the woman notes menstrual irregularities. Menstruation becomes heavy, prolonged and painful. Bloody discharge appears before and after menstruation. Intermenstrual bleeding in the middle of the cycle is possible.
Patients also complain of discomfort and unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse.
Since adhesions form in the abdominal cavity, the following occurs:
- problems with bowel movements (constipation);
- flatulence;
- urinary disorders.
The woman’s neuropsychic state also suffers, and her reproductive function is disrupted.
However, very often, apart from the inability to get pregnant, nothing worries a woman.
Diagnostics
To identify an endometriosis formation on the ovary, you need to visit a gynecologist. The doctor first interviews the patient and collects all the necessary information regarding her life history and complaints.
After this, a gynecological examination is performed, during which it is possible to determine whether the right or left ovary is enlarged. However, with small cysts, there may be no change in the appendages.
To make an accurate diagnosis, an additional diagnostic examination is prescribed.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound can detect even the smallest tumors, the size of which varies within one centimeter.
Laparoscopic method
Laparoscopy can be performed as a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure. With its help, the structure of the genital organs and the extent of the pathological process are assessed.
Blood test for tumor markers
With the development of endometriosis, these indicators usually exceed the norm. In this case, the tumor marker CA-125 must be taken into account. Deviations of the ROMA and REA indices beyond normal values may not be observed.
Culdocentesis
This method is a puncture of the peritoneal cavity, which is carried out through the posterior vaginal fornix. Cell structures that were obtained in aspirate or washout are examined.
Assessment of the condition of the stomach and intestines
As the pathology progresses and degenerates into a cancerous tumor, metastatic tumors are detected in these organs. The procedure is carried out with the aim of eliminating the oncological process in them. X-rays of the lungs are also performed.
Diagnosis of the disease
Only a gynecologist can make a correct diagnosis. The inflammatory process in the reproductive system is manifested by pain, enlarged appendages, compaction and adhesions in the pelvis. All these phenomena can be detected during examination on the chair.
To more accurately diagnose the problem, additional procedures will be required:
- Analysis for determination of the tumor marker CA-125 in the blood. Increased levels will indicate that a tumor has formed in the body, which releases a special antigen.
- Ultrasound allows you to reliably examine all pelvic organs. Today, this method is the safest and most effective, as it allows you to observe the dynamics of cyst development.
- Using MRI, information can be obtained about the size, content and location of the pathological neoplasm. This diagnostic method allows you to more accurately determine the extent of the disease.
- Laparoscopy makes it possible to visually assess the tumor as well as its contents. This diagnosis is carried out through a puncture in the abdominal cavity into which a video sensor is inserted. Often this study ends with endoscopic surgery, which allows you to completely remove the cyst.
A timely detected endometrioid ovarian cyst will cause less damage to a woman’s reproductive system, and in combination with an effective course of treatment, the problem will be completely eliminated.
Treatment
Experts recommend removing the cyst laparoscopically. This operation is considered the most effective and safe. Surgery is performed under general anesthesia.
To access the tumor, 3 incisions are made in the peritoneum. Through them, a small laser is inserted into the cavity. It is with the help of such a device that the endometriotic tumor on the ovary is removed.
The main advantage of this method is that after it there are practically no traces of the operation left, and the recovery period after the operation does not take much time. After just 14 days, the patient can return to her normal life.
About the disease
Endometrioid ovarian cyst, according to the ICD-10 code, refers to “non-inflammatory lesions of the ovary, fallopian tube and broad ligament of the uterus (N83).”
An endometriotic cyst is often mistakenly called endometriotic or endometrial.
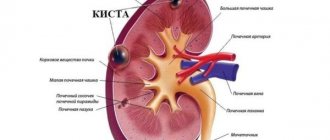
On ultrasound it appears as a tumor or capsule consisting of endometrial cells of the tissue lining the inside of the uterus. In the center of the sac is condensed bright brown menstrual blood. Because of the color of the contents, the endometrioid cyst is also called “chocolate”.
It occurs due to pathological growth of the endometrium of the uterus, in which the cells of the inner layer begin to grow outside its boundaries, attaching to the loose tissue of the ovary.
Important! An endometrioid cyst is considered one of the most dangerous, as it has a tendency to grow rapidly, and when it ruptures and releases its contents, it causes acute peritonitis. If the walls of a large cyst (more than 10 cm) are damaged, then the abundant release of menstrual blood clots accumulated in the cavity can be life-threatening for the patient and requires urgent surgical intervention.
Also, this type of cyst is prone to inflammation and the appearance of purulent foci, which then spread to the ovary itself, tubes and uterus.
Difference from other cystic formations
Endometrioid cyst is hormone dependent.
At a certain period of the menstrual cycle, its tissue begins to bleed, just like the cells of the endometrium itself in the uterus.
Almost every month the tumor increases slightly in size.
If a hormonal imbalance occurs (a sharp jump in estrogen production), then growth can be very rapid.
A distinctive feature of a chocolate cyst is that there are no glands in its walls.
Education almost always occurs against the background of internal endometriosis. The size of the tumor is usually small, ranging from 3-5 centimeters, and rarely exceeds 20 cm in diameter.
Patient age
Mostly, the neoplasm appears in women aged 28 to 50 years. Among women who postpone the birth of their first baby until later, the tumor is much more common than among those who gave birth before the age of 30.
After the onset of menopause, an endometrioid cyst is almost never detected initially. It is not diagnosed in girls during puberty.
Is the formation on the right and left appendage different in any way?
Most often, endometrioid cysts occur on both ovaries.
Since the blood supply to the right gland is more intense than to the left, the tumor on the right will always grow faster than the left. Also, with unilateral development of the cyst, it is diagnosed more often on the right ovary.
Symptoms and treatment for both cysts of the right and left ovaries are the same.
Can it resolve on its own?
The tumor cannot completely disappear without surgery. Hormonal therapy, folk remedies and dietary changes can only slow down its growth and, in some cases, reduce its size by a couple of centimeters.
Important! Since a neoplasm is extremely dangerous and can cause complications when a cyst is detected, you must carefully follow your doctor’s recommendations and do an ultrasound every 6 months to monitor tumor growth. If the size increases significantly, laparoscopy will be required.
Is treatment possible without surgery?
It is sometimes possible to treat small cystic tumors with conservative therapy. Since endometriosis is accompanied by hormonal imbalance, the tactics of therapeutic measures, first of all, are to restore it.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Echosigns of adenomyosis
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
For hormonal therapy, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- antiestrogens – Tamoxifen;
- androgens – Testenate, Sustanon-250;
- anabolic steroids – Retabolil, Methylandrostenediol;
- progestogens - Duphaston, Gestrinone and others.
The treatment regimen and dosage are selected only by a specialist in each case individually.
In addition to drug therapy, vitamins, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs and immunomodulators are prescribed.
Sometimes it is enough to only treat with drugs without surgery. However, then the risk of relapse increases several times.
Treatment methods
Conservative therapy helps slow tumor growth and reduce the severity of unpleasant symptoms. This treatment is permissible only for small formations on the left and right ovaries that are not prone to growth and rupture.
If there are risks of complications, those wishing to have children in the future are offered surgical removal of endometrioid lesions while preserving the ovary itself.
Depending on the size of the cyst, laparoscopy or laparotomy is performed.
Reference. In severe cases, if it is impossible to preserve the ovaries, the glands themselves are removed along with the cyst, sometimes along with the uterus. This operation is rarely performed on women under 50 years of age.
Treatment without surgery
First of all, the gynecologist will prescribe hormonal therapy, anti-inflammatory and painkillers, as well as vitamin therapy and herbal teas to maintain immunity.
If the size of the cyst is small, the doctor will select contraceptives for the patient to stabilize hormonal levels, and will also prescribe painkillers and antispasmodics to relieve pain and discomfort as the tumor grows.
Laparoscopy and laparotomy
In most cases, the doctor chooses laparoscopy to remove a small chocolate cyst.
Removal surgery is performed through small punctures in the abdominal cavity and allows the affected tissue to be removed without affecting the ovary itself.
During surgery, the cyst tissue is “husked” and removed.
Laparoscopy is performed only on young women who want to have children in the future. In many other cases, laparotomy is performed with removal of the ovary, since subsequently the incompletely removed cyst tissue can degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
Only the attending physician, who knows the whole picture of the disease, can decide whether to remove the cyst or not.
Further treatment after removal using laparoscopy is aimed at restoring the body.
Folk remedies
To treat small cysts and slow down their growth, herbal medicine using herbs containing phytohormones can be prescribed.
These are red brush and hogweed; they contain natural analogues of the female hormone progesterone. For treatment, a packet of a mixture of herbs is brewed with a glass of boiling water, infused for 10 minutes, then squeezed. The resulting infusion must be drunk in three doses. The course is 30 days, then you need to take a break of two weeks and repeat the treatment.
Since the endometrioid cyst is hormone-dependent, increasing the production of progesterone can slow down its growth and relieve pain.
Important! For any type of cyst, the use of sage is strictly prohibited, as it contains a natural analogue of estrogen and can cause a sharp growth of the tumor.
Is it necessary to delete
The question of removing a cystic formation depends on a number of factors. First of all, it is necessary to take into account the presence of clinical manifestations and the woman’s plans for her pregnancy in the future.
If the cyst does not cause concern, in this case you can only get by with drug treatment. However, when the tumor grows and is accompanied by a large number of unpleasant symptoms, doctors recommend removing it. In addition, in the absence of therapy in such situations, various kinds of consequences can occur.
Treatment of endometrioid ovarian cyst
Treatment of endometrioid ovarian cysts is carried out by a gynecologist or gynecologist-endocrinologist.
Treatment can be either conservative or surgical. The method of therapy is selected individually in each specific case and depends on:
- woman's age;
- size of formations;
- her mood for pregnancy;
- clinical manifestations.
Small cysts are subject to conservative therapy. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin, ibuprofen) are prescribed as symptomatic treatment to relieve pain during menstruation. Taking vitamins and sedatives is indicated.
To stop the growth of the cyst, hormone therapy is prescribed. These can be combined oral contraceptives; the duration of their use depends on the effectiveness of treatment and the extent of the process. It is possible to prescribe gestagens (premalut, norkolut).
In order to create artificial menopause and reduce the size of cysts, Zoladex, Danazol, Buserilin and other antiestrogens are prescribed. It should be noted that hormonal therapy is not always effective, and some endometrioid cysts remain “insensitive” to hormones.
When deciding on surgery, hormone therapy is prescribed as a preoperative preparation to slow down the growth of cysts or reduce their size. If possible, the operation is performed laparoscopically, preserving part of the ovary. The cyst is desquamated and the ovaries are sutured. If the cysts are too large, the ovaries are removed completely (oophorectomy). During surgery, endometrioid heterotopias on the peritoneum are excised and adhesions are dissected.
Hormone therapy continues in the postoperative period.
The optimal option for rehabilitation after an endometriotic cyst is pregnancy, which can be planned after six months when large cysts are removed or immediately if the cysts were small.
Complications
If the cyst is small in size and does not affect female reproductive function in any way, then it can be present in the body for several years and will not make itself felt in any way.
If the pathological process progresses, then the appearance of various kinds of complications cannot be ruled out. Severe disease, as a rule, leads to infertility and the formation of adhesions in the pelvic organs.
When contents penetrate the peritoneum, peritonitis may begin to develop, which in the absence of emergency medical intervention often ends in death.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of an endometrioid cyst, experts recommend adhering to certain rules:
- treat diseases affecting the organs of the female reproductive system in a timely manner
- a balanced diet;
- vitamin complexes regularly
- monitor hormonal levels;
- gynecological at least twice a year for preventive purposes.
Drug treatment
Drug (conservative) treatment is prescribed to patients whose cyst size does not exceed 5 centimeters. The basis of the course is hormonal drugs in combination with the following substances:
- preoral contraceptives with the same dose of hormones (that is, monophasic: rigevidon, regulon, novinet, femoden, diane-35, logest, silest);
- testosterone derivatives - norsteroids (norethisterone, norethinodrel, ethynodiol diacetate, linestrenol, norgestrel, levonorgestrel, norgestimate, gestodene, desogestrel, dienogest);
- long-term injections and implants (progesterone derivatives: Depo-Provera, Megestron);
- injections that block the pituitary gland (gonadotropin-releasing hormones: orgalutran, cetrotide);
- derived androgenic substances (methyltestosterone, testosterone propionate);
- drugs that suppress the process of pus reproduction (aspirin, lysine monoacetylsalicylate, diflunisal, phenylbutazone, clofezon, indomethacin, sulindac, diclofenac, piroxicam, ibuprofen);
- sedatives without a hypnotic effect (altalex, bellaspon, bromcamphor, tincture of valerian, validol, glycine, dormiplant, persen, sympatil, sanason);
- antidepressants;
- drugs that reduce the tone of the muscles of internal organs and have an analgesic effect (andipal, aminophylline, bralangin, valemidin, gedelix, drotaverine, influbene, spasmalgon, pentalgin, papazole, no-shpa);
- anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics;
- vitamin complexes (with a high content of ascorbic, folic acids, and vitamin E).