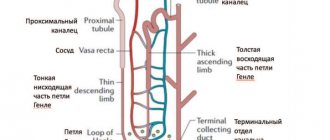
The formation of stones in the renal cavities (pelvis, calyces) is classified as an independent pathology, which is called nephrolithiasis. According to the structure and nature of the forming substance, kidney stones are of three types: phosphates, oxalates and urates. The last of them, urate kidney stones, are formed less frequently than oxalate stones, but more often than phosphate stones. The risk group for urate nephrolithiasis is men of childbearing age (20-55 years). Women are less susceptible to developing this pathology, but they are more likely to experience significant growths of urate stone (staghorn calculus), which can lead to kidney failure. How this form of urolithiasis is characterized, how it is treated and prevented, you will read in the article.
How are urate stones formed?
Potassium urate and sodium urate are acidic salts of uric acid that are formed as a result of metabolic processes, are part of urine and do not cause harm in small concentrations.
When the amount of urate increases, the filtering ability of the kidneys decreases, and uric acid salts crystallize and precipitate. The formation of stones begins - dense formations called uric acid or urate stones. If deposits are detected in the renal pelvis and calyces, the patient is diagnosed with kidney stones (nephrolithiasis). If the pathological process has affected the entire urinary system, a diagnosis of urolithiasis is made.
Even once having seen what urate kidney stones look like (pictured), it is unlikely that a person will want to carry this dangerous ballast in his body.
These are round deposits, smooth on top, ranging in size from 1 - 2 mm to several cm, usually yellowish-brown in color. The structure of uric acid stones is quite loose, thanks to which they can be dissolved and removed from the body without surgical intervention.
Symptoms
Urate stones dissolve even with ordinary water. Drinking plenty of fluids allows you to dissolve and remove all accumulated urate.
This is why adults almost never experience any symptoms. Urates are detected in adult patients only during laboratory or diagnostic testing.
Characteristic and quite noticeable signs are detected by the patient when, along with urates, an inflammatory process occurs in the kidneys.
The patient's blood pressure and temperature rise. The urine shows signs of hematuria. The process of urination is accompanied by frequent urges and severe pain.
Severe pain is localized in the abdomen or lower back. General weakness combined with nausea and vomiting further worsens a person’s condition.
A child whose kidneys have already formed urates often wakes up and is capricious. The baby becomes extremely active and develops, to some extent, faster than his peers.
If parents ignore changes in the child’s behavior and do not seek medical help, the child’s health condition will deteriorate significantly.
As a result, asthma attacks, vomiting, constipation occur in the morning, red spots appear on the skin, and uric acid crystals begin to accumulate under the skin and in the joints.
Description of the disease
Urolithiasis is a metabolic disease characterized by the formation of insoluble salts, which leads to the formation of stones in the kidneys, bladder, and ureters.
It can become chronic and recur. The number of stones and their location varies depending on the severity of the disease.
The development of urolithiasis most often results from poor diet, consumption of poor water, climate, taking medications, defects in the development of the urinary system, hyperparathyroidism, deficiency of vitamins A and D, the presence of inflammatory diseases such as pyelonephritis and cystitis, and heredity.
The main symptoms of urolithiasis include:
- Acute attacks of pain in the back or side under the ribs. The interval between attacks varies from 20 to 60 minutes. Over time, as the stone moves, the pain spreads to the abdomen, perineum and inner thigh.
- Frequent urge to urinate, presence of traces of blood in the urine.
- General weakness of the body. In the presence of pyelonephritis, nausea and vomiting are observed.
- Chills and high temperature, indicating the removal of the formation.
If you have the above symptoms, you should consult a urologist. He will order additional examinations and make a final diagnosis.
Symptoms of the disease
At the initial stage of the disease there are no symptoms. Urolithiasis, like other types of urolithiasis, produces symptoms only at an advanced stage or with renal colic. In the first case, a person may be bothered by nagging pain in the lower back, irritation and pain when urinating, and sometimes the appearance of blood in the urine (if the walls of the bladder are damaged by a calculus). Renal colic develops when the ureter is blocked by a stone on one side (extremely rarely - on both sides). Its symptoms are as follows:
- severe pain in the lower back;
- radiating pain to the pubic area;
- nausea, urge to vomit;
- increased gas formation;
- pain when urinating;
- turbidity, sediment, blood in the urine.
If colic is accompanied by an inflammatory process, body temperature rises. Pyelonephritis is a complication of urolithiasis, its treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor - otherwise the inflammation becomes chronic and leads to kidney failure.
Diagnostics
Increased acidity of urine can now be detected at home. Pharmacies sell special test strips that can be used to easily determine a urinary reaction. Laboratory tests can confirm the diagnosis - a general urine test (will show a shift in the reaction to the acidic side, the presence of uric acid salts), a general blood test (will reflect disturbances in protein and mineral metabolism).
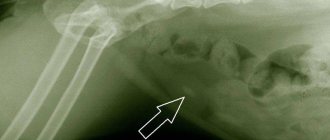
If urolithiasis occurs, it is necessary to conduct instrumental diagnostics. Due to their loose structure, urate stones are practically not detected by X-rays, but they are reliably detected by ultrasound, MRI, urography, and contrast-enhanced CT.
Possible complications
Nausea and vomiting are possible symptoms of urate stones in the body.
The main danger in the occurrence of stones is that symptoms do not appear for a long time. In the later stages, the main symptom of the presence of urate stones in the body is renal colic and its characteristic manifestations:
- sharp pain in the lumbar region;
- pain spreads throughout all organs of the genitourinary system (from the bladder to the adrenal gland);
- a painful attack cannot be stopped;
- presence of trembling in the body;
- nausea and vomiting;
- excessive gas formation;
- pain when urinating;
- gout;
- visual deviations from parameters in urine (turbidity, sandy sediment, blood inclusions).
An increase in body temperature is an alarming symptom that indicates an incipient inflammatory process in the kidney organs. The development of renal colic occurs when a stone interferes with the normal outflow of urine. At the first sensory or visual changes in the body, you should contact a specialist; timely identified pathology is corrected much faster than a neglected condition.
The main reason for the formation of urate stones in the kidneys is the acidic reaction of urine: if the pH {amp}lt; 5.5 there is a possibility of decreased urine output and salt deposits.
The main factors contributing to acidification of urine and provoking the development of kidney stones:
- living in regions with a dry, hot climate, where there is a high risk of frequent dehydration;
- the presence of high concentrations of hardness salts (Ca, Mg) in drinking water;
- lack of fluid intake;
- physical inactivity (sedentary or sedentary lifestyle);
- poor nutrition, such as excessive consumption of animal protein or debilitating fasting;
- disturbance of calcium metabolism.
The risk group includes people with a hereditary predisposition to the formation of urate kidney stones. They are recommended to periodically check the urine reaction using a special device - a pH meter or visual test strips “Uri-pH”. Normally there should be an alkaline reaction (6.0 - 7.0). If the indicator does not fall below 5.5 units for a long time, and the lifestyle remains the same, the person is actually protected from the formation of uric acid stones.
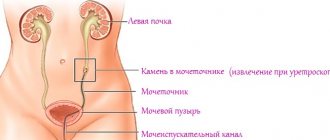
It is impossible not to feel obstruction, or, more simply, blockage of the urinary tract. Look at what large urate kidney stones look like in the photo, and imagine that one of them is blocking the left or right ureter.
Complete or partial obstruction increases urine pressure and stretching of the walls of the hollow tubular organ, and then the kidney.
A person experiences sudden unbearable pain in the lower back, usually on the right or left, in rare cases of a girdling nature. When trying to change the position of the body, stand up or lie down, no changes occur. Pain arises from the back and radiates to the lower abdomen and groin - these are characteristic signs of renal colic. At the same time, it is impossible to stop the pain; conventional analgesics do not help.
Increasing pain may be accompanied by other symptoms:
- bloating;
- intense gas formation;
- increased sweating;
- nausea, vomiting;
- chills and fever.
The last symptom may mean the development of inflammation in the kidney tissues, but in any case, the overall clinical picture is beyond doubt: the patient needs emergency medical care.
If the size of the stone allows it to pass through the ureter without damaging the walls, the attack goes away on its own. However, similar symptoms are observed with ectopic pregnancy, ovarian rupture or pancreatitis, so it is very important to promptly consult a specialist who can carry out a differential diagnosis.
Like any pathological process, the formation of urate stones progresses, and over time the calculus grows throughout the renal pelvis with processes in each calyx. A more severe disease develops - coral nephrolithiasis, when the gentle dissolution method no longer helps, and treatment of the pathology requires nephrolithotripsy, and in especially severe cases, removal of the affected kidney.
Uric acid deposits often provoke inflammation of the renal tubules (pyelonephritis), as well as the development of acute or chronic renal failure.
Against the background of a high concentration of uric acid, salts are deposited in the joints and a dangerous metabolic disease develops - gout.
There is no need to wait for the body to acquire a whole bunch of complications; modern diagnostic methods make it possible to detect uric acid deposits at the very beginning of their formation.
Symptoms most often develop unexpectedly. The main symptoms of pain are renal colic with its characteristic manifestations. Urate deposits in the kidneys usually cause unilateral intense pain in the lumbar region, but “girdling” pain is also possible. Urate and urate-oxalate kidney stones form in acidic urine.
Complications of kidney diseases appear in the human body as a result of untimely initiation of therapy for kidney diseases.
The most common complication of the disease may be the addition of an inflammatory process in the kidneys and urinary tract. Complications of urate nephrolithiasis include excessive growth of stones with the formation of coral stones, paralyzing renal activity and leading to uremia - intoxication of the body.
To prevent complications of the disease, it is worth consulting a specialist at the first symptoms, and, if necessary, undergo a diagnosis and begin treatment prescribed by a doctor.
In most cases, kidney stones form and grow without symptoms. Most patients become aware of their presence in the body after the onset of renal colic. Renal colic occurs when the urate stone reaches a fairly impressive size and interferes with the normal flow of urine.
The main symptoms manifest themselves in sudden acute pain in the lumbar region, which very quickly spreads to the abdomen and genitals. This pain is accompanied by a feeling of chills, nausea and vomiting. If renal colic is accompanied by elevated body temperature, this is a clear sign that an inflammatory process has begun in the kidneys against the background of urolithiasis. The causes of inflammation can be different, but the main one is stagnation of urine, which is an excellent environment for the development of bacteria.
Urates, even before the appearance of renal colic, may exhibit symptoms such as constant aching pain in the lower back, problems with urination (depending on the location of the stones).
Symptoms indicating the existence of kidney stones:
- unilateral sudden lumbar pain;
- pain radiating to the abdomen and bladder, as well as the genitals (the pain is practically uncontrollable, it is impossible to find a position to relieve the pain);
- nausea and vomiting;
- chills develop;
- flatulence develops;
- increased body temperature (rarely) is a very dangerous sign that indicates the onset of kidney inflammation;
- pain when urinating;
- cloudy urine (sometimes with grains of sand or stones).
Basically, the formation and growth of urates is asymptomatic. A person can become aware of their presence in the body when a phenomenon such as renal colic occurs, which occurs against the background of difficulty in the outflow of urine, which is hampered by the impressive size of urate stones.
Urate-type kidney stones cause the formation of symptoms such as sudden acute pain in the lumbar back, spreading to the abdomen and genital area. In addition, there is a feeling of chills and nausea, which often provokes the discharge of vomit.
In the case when renal colic occurs against a background of elevated temperature, one can judge the beginning of the development of an inflammatory process in the kidney area, which may be caused by stagnation of urine.
Depending on where the urates are localized, they can, before the onset of acute pain characteristic of renal colic, provoke the formation of symptoms such as impaired urination and aching pain in the lumbar region.
Additional symptoms indicating the presence of these stones are the following:
- development of flatulence;
- pain during urination;
- cloudy urine, which in some cases may contain grains of sand or small pebbles;
- development of gout in men.
It is very important that when the first deviations from the norm occur in the genitourinary system, as well as when pain occurs in the lumbar region, abdomen and genitals, urgently contact a qualified specialist to carry out the necessary diagnostics, identify the cause of the disorders and prescribe timely treatment.
Prevention of the formation of uric acid stones
By observing the drinking regime, you will avoid problems associated with urine acidification. For an adult, 1.5 liters of clean filtered water per day is enough; in hot weather, the norm increases to 2.5 liters. It is important to note that this applies to people who do not have serious cardiovascular disorders, a tendency to edema, or diagnosed renal failure.
As a preventive measure, periodically drink a course of herbal infusions that prevent stone formation, for example:
- juniper;
- lingonberry leaf;
- licorice and wheatgrass root;
- knotweed (knotweed);
- horsetail
Urate kidney stones are not a death sentence, so it is not necessary to adhere to a strict diet, but it is important not to abuse alcohol, salty and fatty foods.
Please note: all of the above recommendations relate to the prevention and treatment of kidney stones and are equally effective for urate stones in the bladder (urolithiasis). However, self-medication is unacceptable. Prescription of medications and herbal medicine should be carried out by a qualified specialist - a nephrologist.
Source
Based on the sources of formation and chemical composition, stones are divided into several types:
- Urate. Dense and smooth to the touch. They have a yellow-orange color. Localized in all organs of the genitourinary system. Their presence can only be diagnosed using ultrasound. The main causes of formation include: gout, deficiency of B vitamins, large amounts of uric acid, gastrointestinal diseases, excess purines in the diet. They are treated using conservative methods. It is recommended to drink alkaline water and follow a diet.
- Oxalate. They have a dense structure with sharp edges and spikes, black or dark brown in color. Their presence is diagnosed based on the results of a urine test and an image of the kidneys. They are formed due to a lack of magnesium and B vitamins, diabetes mellitus, metabolic failure, and pyelonephritis. This type of formation does not dissolve. They are removed through surgery.
- Struvite. Formed under the influence of infection and bacteria. These are soft gray formations with a smooth surface. They pose a threat to health, as they are characterized by accelerated growth. They can transform into a coral-like subspecies with the presence of spines. The main causes of occurrence: alkaline reaction of urine, infections, bacteria. Removed surgically.
- Phosphate. Color varies from white to light brown. They feel soft, smooth or rough to the touch. They are prone to rapid growth and, over time, can fill the entire cavity of the shelf. Their presence is diagnosed using x-rays. Sources of formation: gastrointestinal infections, excessive consumption of dairy products, metabolic failure. Dissolved with the help of medications, diet and mineral water.
In each clinical case, the treatment regimen is determined individually. The therapeutic complex depends on the test results and the severity of the disease. When the first warning signs appear, go to the doctor.
Prevention
After removing urate stones from the body, it is necessary to take all preventive measures against recurrence of formations.
For these purposes, a drinking regime must be provided. The amount of liquid consumed should vary between 1.5-2 liters. It is better to use purified still water as a liquid.
Additionally, they monitor their diet. It is better to give preference to plant-based and fermented milk foods.
Consumption of animal protein is also important for the body. In this case, it is necessary to control the dosage of meat eaten.
Additionally, meat dishes or legumes are best consumed together with herbs or fresh vegetables.
You need to closely monitor your health. At the first unpleasant sensations or characteristic symptoms, seek help from a specialist.
Timely diagnosis and subsequent therapy will help avoid the formation of large stones. In this case, it will be possible to avoid surgical intervention and possible complications.
Video on the topic
Urate kidney stones appear mainly in people in the age group from 22 to 50 years.
Situations often occur when the development of this pathology provokes the occurrence of various complications.
The composition of the urate type of stones in the genitourinary system of organs contains almost exclusively salts that are formed by uric acid. These substances can accumulate both in the kidneys, ureters, and in the bladder cavity. And if the diet continues to include the consumption of fast carbohydrates and fast foods, then the increased concentration of uric acid salts will begin to transform into urate-type stones.
The size of urates can vary within varying limits depending on the degree of development of the pathology. They have a fairly smooth surface with a yellow-brown tint, as well as a heterogeneous, loose texture, thanks to which these stones can be gotten rid of with the help of a special diet in combination with special medications.
According to most experts, the formation of urate in the kidneys is preceded by the following number of factors:
- hereditary predisposition, laid down at the genetic level, which can pass from generation to generation;
- high level of uric acid concentration in urine, which occurs against the background of metabolic disorders in the body;
- unfavorable working conditions with low physical activity or increased physical activity;
- improper monotonous diet, as well as frequent fasting;
- geographical factor of residence with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- drinking water with a certain chemical composition;
- lack of B vitamins in the body;
- regular use of analgesic drugs;
- low rate of kidney production of urine.
The formation of urate stones can be facilitated by the formation of an acidic urine reaction, which can be independently determined using a special rapid test, the normal values of which are results from 6.0 to 7.0.
Reasons for education
Urate stones in human kidneys can form due to high levels of uric acid salts, insufficient urine formation and increased acidity.
Uric acid salts
They are the result of metabolic processes in which proteins are involved. It is impossible to get rid of this final product; salts will always be present in the body in high or low concentrations. But by eating fermented milk products, you can change the urine environment, making it more alkaline and thereby preventing the formation of urate stones.
Insufficient urine production
If the formation of urine is not fast enough in a person, the concentration of uric acid salts increases and they begin to form a sediment, forming into dense formations.
High acidification of urine with insufficient rate of its formation can be changed with the help of ordinary water - it should be consumed in increased quantities, at least 2 liters per day.
High acidity of urine
You can determine this indicator at home - purchase special test strips and carry out the procedure according to the instructions. If the acidity of urine is increased, this means a high risk of formation of urate tissues - such a concentration of acid will necessarily provoke a decrease in the rate of urine formation - the main cause of the formation of urate stones. In medicine, a number of factors predisposing to the formation of urate stones have been identified:
- physical inactivity - a sedentary lifestyle;
- incorrectly composed diet - predominance of fatty/spicy foods in the menu, insufficient fluid intake;
- insufficient amount of vitamin B supplied to the body.
Traditional Treatments
Taking medications is indicated in the presence of small stones that do not cause disruption in the functioning of the organ. Therapy is carried out using tablet and liquid forms of drugs. Most often used:
- Phytolysin. Produced in paste form based on onion peels and parsley. Before use, the drug is dissolved in 100 ml of warm boiled water with added sugar (honey). Take 1 tsp. pasta three times a day. Phytolysin softens and dissolves stones of various types.
- Urolesan. Available in the form of drops with the addition of mint and fir oils. Has an antibacterial effect. Directions for use: children aged 7-14 years - 5-6 drops, adults - 8-10 drops three times a day. Drops are placed on sugar (if you have diabetes, on bread). Urolesan dissolves the phosphate type of stones.
- Canephron N. The drug is produced in the form of drops with the addition of extracts from centaury and rosemary. It has an anti-inflammatory, diuretic, analgesic effect. The drug is suitable for children aged 12 years and older. Recommended dose: 50 drops three times a day. Used to prevent the formation of new stones.
- Phytolith. Produced in capsule form. The composition contains: bird knotweed, St. John's wort, horsetail, avisan. Relieves spasms and inflammation, has a diuretic effect. Can be taken from 12 years of age. Directions for use: 1 capsule three times a day before meals. Phytolith dissolves all types of stones.
- Cyston. Dosage form: tablets. Formula based on Didymocarpus stem and Saxifraga reed. Has an antiseptic, diuretic, anti-inflammatory effect. Directions for use and dosage: children aged 2-6 years - 0.5 tablets, children aged 6-14 years - 1 tablet, adults and children over 14 years old - 2 tablets three times a day after meals. Cyston dissolves oxalate and phosphate types of stones.
- Spilled Available in capsule form. The formula contains silkworm, cubeba pepper, phyllanthus, kidney tea and papaya. Improves the metabolic process, relieves inflammation. Adults are recommended to take 5 capsules three times daily with meals. Softens oxalates.
- Xydiphone. A solution that regulates the process of calcium metabolism. The composition of the drug contains etidronic acid. Directions for use and dosage: children aged 3-10 years - 1 tsp. twice a day, adults and children over 10 years old - 1 tbsp. l. three times a day. The solution is diluted in a ratio of 1:9 with distilled water (for example, 450 ml of water is needed for 50 ml of the drug). Store in the refrigerator. Take 30 minutes before meals. Xidifon prevents the formation of phosphate and oxalate stones.
The most effective way to dissolve urates and phosphates is by taking medications. The remaining varieties are resistant to traditional treatment methods. But medications can help the broken pieces come out quickly and prevent subsequent relapses.
Options for the development of kidney stones
The danger of the disease lies in its asymptomatic course. In the best case, pathology is detected, for example, during a medical examination; this, as a rule, occurs at the initial stage of stone formation. If there are urate stones in the kidneys, their dissolution and diet completely eliminate the progression of the disease and possible serious consequences.
Another case: minor deposits can form, collapse and wash out on their own if the acidity of the urine is compensated by drinking plenty of water (at least 1.5 liters per day) and a healthy diet.
When the processes of stone formation in the kidneys disrupt the production of urine, and large deposits impede its outflow, the symptoms of the pathology appear suddenly and in the most severe way.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of urate kidney stones is standard for urolithiasis:
- laboratory tests of urine and blood;
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder;
- CT scan.
As part of the diagnosis of urolithiasis, as a rule, an x-ray with the use of a contrast agent is also performed, but specifically for the detection of urate stones, this type of examination is not important - the type of stones in question is simply not visible on the x-ray. An ultrasound examination will be more informative - the doctor will be able not only to confirm the presence of urate stones in the kidneys, but also to determine their size and shape.
In the video about urate kidney stones:
ethnoscience
Since ancient times, decoctions of medicinal plants have been used to treat urate stone formations in the kidneys; today, their use also provokes faster dissolution of urate stones. To prevent the appearance of formations of this type, it is recommended to drink decoctions of rose hips, berries and leaves of strawberries, leaves and buds of birch.
When urate stones form, in addition to the main method of therapy, it is strongly recommended to follow a special dietary regimen. The diet for urate in the kidneys and bladder is quite varied, so the patient will be able to fully enjoy food if he correctly compiles a menu of permitted foods.
- Many doctors exclude meat from the diet of a patient with urates, because it contains purines - the causes of the formation of stones of this type. Meat can only be consumed boiled, and only low-fat varieties (veal, poultry).
- There are no restrictions on fresh vegetables. Of course, you should give preference to light salads made from cucumbers, which have a diuretic effect, as well as pumpkin and cabbage. You can eat boiled or baked potatoes.
- As for berries and fruits, it is worth paying attention to watermelon, which promotes general cleansing of the kidneys. You can make compote from the berries and prepare fruit drinks.
- In the case of urates, dairy and fermented milk products can be consumed in any quantity. They can be eaten either fresh (milk, sour cream) or after heat treatment. You can cook porridge with milk.
- Buckwheat, millet, oatmeal and other natural grains will only bring benefits. They can be cooked in either water or milk, depending on individual preferences.
- Bakery products and flour products. Bread made from wholemeal flour is recommended. You can diversify the menu with pasta.
There is also a fairly impressive list of foods that you should definitely completely exclude from your diet. These are meat broths, pickles and pickled products, sausages, mushrooms, chocolate, cocoa, fish and fish broths, alcoholic drinks, tea, coffee.
The use of herbs helps to remove sand and small stones, prevent the formation of new stones, and normalize the metabolic process. The most effective traditional methods of treatment are:
- Infusion of rose hips. To prepare 1 tbsp. l. crushed dry berries are poured with 1 cup of boiling water. Leave for 6 hours. Then the infusion is filtered and drunk 1 tbsp. three times a day. Rosehip helps soften phosphate stones.
- Porridge made from oat grains. Unrefined grains are washed and poured with boiled water in a ratio of 1:2. After 12 hours, the pulp is ground in a blender. Eat instead of breakfast. You can add honey or sugar. Porridge helps soften urates.
- A decoction of grape leaves. During cooking, 1 tsp. dried leaves pour 200 ml of water. Cook for 2-3 minutes. Take 50 ml 3-4 times a day. The decoction helps dissolve oxalates.
- Solution for softening mixed stones. Mix St. John's wort, rose hips, knotweed, oregano, sage, lemon balm (30 g of each type of herb) and pour in 450 ml of boiled water. Leave for 30 minutes and then filter. Divide into three parts and drink half an hour before meals. Treatment period: 7 days.
But the use of such methods of therapy is effective only at the stage of remission of the disease. Before you start taking herbal solutions, you need to find out the size of the stones (they should not be more than 5 mm in diameter). Carefully follow the regimen for preparing infusions and decoctions to prevent possible complications.
Diet principles for dissolving urate kidney stones
- Monitor your calorie intake. The daily norm increases to 2800 kilocalories.
- You are allowed to consume the most carbohydrates - four hundred grams. Proteins can be consumed in the amount of 70-80 grams, fats - no more than 90 grams.
- You need to adhere to the following diet: 5 meals a day, excluding too cold foods from the diet.
- It is useful to arrange fasting days - fruit, dairy, vegetable.
Allowed foods during the diet against urate stones
- sweet fruits and berries
- milk products
- vegetables: eggplants, potatoes, bell peppers, pumpkin, cucumbers, cauliflower, zucchini
- watermelons
- pasta
- rye bread, white wheat bread
- buckwheat, wheat porridge
- citrus
- eggs from which the yolks have been removed (no more than 1 yolk per day is allowed)
- jam, jelly and compotes
- honey, marshmallow, marmalade
- Tea with lemon
I recommend eating more apples, pears, and grapes from fruits, and watermelons from berries. It is these products that contribute to the alkalinization of urine.
During this regimen, you need to drink about 2-3 liters of fluid daily.
Citrus fruits can be eaten if oxalates are not observed in the urine. If oxalates are present in the urine test, then limited consumption of oranges is allowed. You should also limit your potato consumption.
Prohibited foods during the diet against urate stones
- meat by-products and meat of young animals
- fish
- broths of all types: from meat, mushrooms and fish
- smoked meats and pickles
- vegetables: lettuce, parsley, green onion, sorrel
- from fruits: Antonov apples, currants, cranberries, lingonberries and other fruits with high acidity
- legumes
- flour
- alcohol
- cocoa, chocolate, coffee, sweets
- It is necessary to limit salt consumption and maintain its daily intake.
Thus, in case of urolithiasis, accompanied by the formation of stones from uric acid salts (urates), we can recommend diet No. 6, i.e. the same as for gout.
Features of cooking during a diet against urate stones
Despite the diet, absolutely everyone always wants to pamper themselves with a piece of freshly prepared delicious meat. In this case, you can afford it. I want to tell you about the products, features and principles of cooking meat that should be followed when dieting against urate in the kidneys.
As I already wrote above, urate stones are formed from uric acid salts, the formation of which is promoted by special substances - purines. The largest amount of purines is found in meat, fish, mushrooms, offal: liver, kidneys, lungs. When these products are cooked, most of these substances are boiled down and remain in the broth. Therefore, any meat broths are strictly contraindicated. Meat is only allowed boiled or steamed.
- Before cooking, soak the meat in a saline solution for about three hours.
- Prepare the first courses using vegetable broth; the meat can be cooked separately and placed on a plate when serving.
- Place the meat immediately into boiling water.
Dissolution with mineral water
Due to their porous structure, urate stones are easily dissolved. However, the process of removing stones from the body is not always painless, and during the examination, concomitant urinary tract infections may be detected in the patient.
Therefore, in most cases, the doctor prescribes complex therapy using several drugs:
- stone dissolution: “Blemaren”, “Urolesan”, “Solimok”, “Canephron”;
- expansion of the urinary tract: “Spazmalgon”, “No-shpa”, “Papaverine”;
- elimination of infectious and inflammatory processes: “Amoxiclav”, “Nitroxoline”, “Klaforan”;
- pain relief: “Revalgin”, “Ketorol”, “Baralgin”.
To prevent the formation of new deposits, it is important to convert the urine reaction from acidic to alkaline. To do this, the patient is recommended to drink more fluids, including alkaline mineral waters, for example, Borjomi or Kislovodsk Narzan. And of course, a diet for urate kidney stones is an important condition for complete recovery and prevention of the deposition of uric acid salts.
Mineral waters remove excess salt, restore the imbalanced balance, and flush the kidneys. Auxiliary components that are part of the water (iron, copper, magnesium, tungsten) dissolve stones.
Drinking mineral water is recommended in case of small stones (up to 8 mm), after removal of large formations for prophylactic purposes, in the presence of high levels of salt in the urine. Dissolves urates, oxalates and phosphates.
Dosage regimen: 200 ml 5 times a day for 30 days. You need to drink mineral water half an hour before meals and 2 hours after it. Recommended brands of mineral waters: in the presence of oxalates and urates - Borjomi, Essentuki 17, Naftusya, Truskavetskaya; phosphates - Mirgorodskaya, Smirnovskaya.
Treatment
Urate stones are the only ones that can be dissolved, so doctors must take this point into account when prescribing treatment and carry out conservative therapy, prescribing tablets and drops that dissolve stones.
There is also surgical treatment for urolithiasis with the formation of urate stones, but this is an exception and is carried out only if the stones have acquired the coral type.
ethnoscience
Before starting treatment, you should definitely visit a doctor, clarify the diagnosis and make sure that it is urate stones that have formed in the kidneys and that they can be treated with folk remedies.
Dissolving and removing urate stones from the kidneys is possible thanks to the following recipes:
- Take oats in grains and, without peeling them, pour them into a thermos and pour boiling water over them. The oat grains should fill the thermos halfway, but boiling water will need to be added to the top. The product is infused for 10-12 hours, then the resulting mass is wiped and the resulting “porridge-jelly” is consumed for breakfast without adding spices and seasonings.
- Combine strawberry leaves with black currant leaves in equal quantities, add half of the resulting volume of knotweed herb. Take 1 tablespoon of the resulting herbal mixture. pour 200 liters of boiling water and leave for 30-40 minutes, strain. Take the infusion prepared according to this recipe, 2 tablespoons before each meal.
To achieve the release of urate stones, you can use the following recipe:
Take and mix burdock roots, horsetail, woodruff and elderberry (black) flowers in equal quantities. Take 2 teaspoons of the mixture, pour 200 ml of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. Take the prepared infusion 1/3 cup before meals, at least three times a day.
To remove urate stones, you can also drink “independent” decoctions of carrot seeds, walnut leaves, fennel, and celandine. Decoctions are prepared according to the classical scheme - 1 tablespoon of plant material per glass of boiling water. Cardamom will also help remove urate stones: pour 1 teaspoon of ground cardamom into 150-200 ml of boiling water and leave for 10-15 minutes, drink 1/3 cup three times a day before meals.
Medications
Acute symptoms can be treated with medications - patients are prescribed drugs with antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory effects. Antispasmodics actively relax smooth muscles and, as a result of this action, the narrowing of the duct disappears and urate stones or sand can freely exit along with the urine.
If during examinations a patient is diagnosed with a disorder of purine metabolism, then he will be prescribed medications from the category of uricostatics (for example, Allopurinol). Drug therapy necessarily includes the prescription of magnesium oxide, and if the doctor detects an increased level of calcium salts, Hypothiazide tablets. Any medications for urate kidney stones are prescribed in standard dosages.
Surgical intervention
This type of treatment is performed extremely rarely, in only 3-5% of all cases. The main indicator for surgical treatment is the degeneration of urate stones into coral-shaped stones - they acquire a more dense structure, their edges become “prickly, sharp”, they occupy 90% of the renal pelvis and cannot pass out naturally.
Doctors use minimally invasive methods for surgical treatment, most often shock wave lithotripsy, which allows you to get rid of 90% of all stones in the urinary system. Shock waves, passing through soft tissues (without damaging them), reach the urate stone and begin to crush it. As a result, only fine sand remains in the kidney, which does not need to be removed with medications, since it is released naturally over time (with urine).
Diet
Patients need to pay special attention to nutrition. The following should be excluded from the menu:
- animal products and meat (liver, heart, pork and beef);
- meat and fish broths;
- red wine and beer;
- any canned food.
Limit the consumption of fish and seafood, legumes, chocolate and coffee, strong tea and cocoa, baked goods (including wheat bread). But the menu for people who have been diagnosed with urate stones must include any fruits, all fermented milk products, buckwheat, eggs, lemon, wheat groats and rose hips.
Food should be consumed in small portions and often - at least 5 times a day.
Since urate stones are quite easy to dissolve, patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids. Preference should be given to alkaline mineral waters - for example, Borjomi, Essentuki mineral water.
Dietary requirements
Therapeutic methods for treating urate kidney stones must be combined with a special diet. Dietary food for urates should be as varied as possible, so during treatment you can get maximum pleasure from the food you eat, if it is advisable to create a menu from the list of allowed foods.
Meals should be divided, 5-6 meals a day. The following types of products must be present in the diet:
- chicken eggs;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- cottage cheese and hard cheese;
- fresh fruit and vegetable crops;
- buckwheat and wheat groats;
- nuts and seeds.
Exceptions should be:
- fatty varieties of meat and fish;
- alcohol and tobacco products;
- sorrel and onion;
- bakery products;
- chocolate;
- salt;
- spices;
- legumes and seafood.
An equally important place in treatment is given to maintaining water balance and drinking the maximum level of fluid. Contraindications to which may include the development of renal failure, a predisposition to the appearance of edema and disorders in the cardiovascular system. To get rid of urates, alkaline drinking in the form of mineral water is also recommended, but carbonated drinks that contain phosphoric acid should be completely excluded from the diet.
In order to speed up the process of dissolving kidney stones, you need to adhere to a diet. Each type of formation implies its own dietary characteristics:
- Oxalates. Limit the amount of foods with high levels of oxalic acid: lettuce, sorrel, spinach, citrus fruits, dairy products, potatoes. Magnesium carbonate (2 g per day) is used as an auxiliary component.
- Urats. Limit foods that contribute to the production of uric acid: kidneys, liver, brains, meat-based broths. Reduce the amount of vegetable fats consumed. Use citrate solutions (uralit, magurlit) and fresh lemon juice.
- Phosphates. Exclude dairy products. Reduce the amount of vegetables and fruits consumed. Increase the amount of consumption of meat, fish, baked goods, and vegetable oils. Reduce the amount of liquid.
In all cases (except for cases of the presence of phosphates), you should drink up to 3 liters of liquid per day. This helps the small pebbles come out. The entire amount of drink is distributed evenly throughout the day. Drink the first glass of water immediately after waking up, the last one an hour before bedtime.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent the development of a disease such as urolithiasis, you should follow some rules of prevention. First of all, lead an active lifestyle. Take about 10,000 steps a day. This will benefit not only the kidneys, but the entire body.
Another important factor: a rational and balanced diet. Limit foods that contain oxalic acid. Add protein foods, vegetables, fruits. Don't forget about your drinking regime: drink about 2.5 liters of water per day.
The process of dissolving kidney stones is quite long and requires patience. Don't self-medicate! If you have any suspicious signs, contact your doctor immediately. The choice of treatment methods is based on the type of stones and their size.
The doctor must conduct all the necessary tests and then prescribe a treatment regimen on an individual basis. Do not abuse traditional methods of therapy! Some components may cause an allergic reaction in the patient, which will lead to a deterioration in the general condition of the body and aggravate the course of the disease.
Therapeutic nutrition for kidney stones
A proper diet will not only cleanse the kidneys of pathological deposits, but will also prevent their reappearance. The basis of nutrition should be the following products:
- vegetables, preferably cucumbers, tomatoes, pumpkin, carrots, beets;
- fruits with a diuretic effect - apples, mangoes, dried apricots (dried apricots);
- berries – watermelon, cranberries, lingonberries;
- cereals – millet, buckwheat, oatmeal;
- nuts and seeds;
- milk, fermented milk products and drinks;
- pasta and baked goods made from wholemeal flour.
It is better to exclude fish, fatty meat and any meat broths during treatment. Of course, you should refrain from smoked meats, pickles and alcohol, and reduce the consumption of tea, coffee and chocolate.
If you have urate stones in the kidneys, dissolving them with the help of medications and diet gives excellent results, however, by adhering to the basic rules of prevention, you can avoid relapse.