The carotid arteries are extremely important vessels in the human body, which are located on both sides of the neck, on the sides. They are responsible for the body’s “supply” of blood to the face and higher to the brain. Naturally, any disturbance or difficulty in the functioning of the carotid arteries is extremely dangerous to health and life.
Disruption of the carotid arteries is dangerous to health
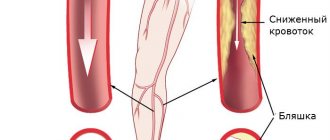
Carotid artery stenosis is a disease at the intersection of cardiology and neurology. Its origin lies in cardiac and vascular pathologies that caused brain damage. During the development of such a disease, a process of narrowing the distance between the vessels occurs from small to complete. This process is called "occlusion".
The development of carotid artery stenosis is fraught with a decrease in the intensity of blood exchange between the brain and the rest of the body. In turn, this leads to metabolic disorders in brain tissue and the development of ischemia. Without timely diagnosis and timely treatment, such problems cause a stroke.
Factors and reasons for the development of the disease
Carotid artery stenosis often develops against the background of vascular atherosclerosis (up to 90% of all cases of the disease). Atherosclerosis is a degenerative disease in the body that develops during age-related changes. Often the causes of its appearance are a sedentary and unhealthy lifestyle, abuse of fatty foods, and lipid metabolism disorders. Also, specific plaques characteristic of this disease appear as a reaction to injury to the vessel wall.
Therefore, you can get atherosclerosis and its complications during a fight, traumatic blows or, for example, playing sports. Substances that accumulate in a damaged vessel can cause blockage, even complete obstruction.
There are other diseases that can cause carotid artery stenosis:
- syphilis;
- tuberculosis;
- collagenosis;
- nonspecific aortoarteritis;
- endarteritis;
- fibromuscular dysplasia;
- thromboembolism and thrombosis.
There are also certain phenomena that narrow the lumen of the artery:
- heart and vascular defects;
- aneurysmal dilatation of the aortic arch;
- malignant and benign tumors that are located along the vessels.
As you can see, all these diseases are classified as quite serious and complex. It should be noted that stenoses and the factors that provoke them affect the male part of the population much more often than women. This may be due to the more widespread addiction to alcohol and smoking.
Here are the predisposing factors for the development of stenosis, characteristic of most cases:
- alcohol addiction;
- smoking;
- being overweight and having an unhealthy diet;
- hypertension;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- abnormalities in the location of organs in the body;
- increased blood clotting;
- spasm of the vascular bed as a cause of stressful conditions;
- genetic predisposition;
- heart failure;
- pathological changes in the shape and location of the artery;
- old age.
Elderly people are susceptible to carotid artery stenosis
Causes
Factors of stenosis of neck vessels are mainly metabolic in nature, less often cardiac, endocrine in origin.
Possible points include:
- Arterial hypertension. Stable increase in tonometer readings.
- Hormonal diseases. Lack or excess of substances of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, hypopituitarism (dysfunction of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland).
- Atherosclerosis. It has already been said about it. More often, stenosis of neck vessels is blocked by cholesterol plaques. Develops as a result of a metabolic disorder.
It may be a consequence of negative heredity, a genetic factor, or a third-party diagnosis. Including diabetes and many others.
Identification is necessary as part of the development of effective treatment tactics.
- Congenital and acquired vascular defects. Including aneurysms (sac-like protrusions or diffuse, fusiform nature), malformations (abnormal areas of connection of vessels of different types).
- Vasculitis. Inflammation of the internal lining of the blood supply structure. Has an infectious or autoimmune origin.
In the vast majority of cases, the culprit is atherosclerosis (more than 92% of recorded situations).
Can we
How is the disease characterized?
According to the list of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), carotid artery stenosis has code 165.2. The disease itself is classified according to three main characteristics:
- type of development;
- features that are caused by atherosclerotic plaques;
- degree of narrowing.
The disease is divided according to the degree of narrowing as follows:
- Small - from 0 to 29 percent.
- Moderate - from 30 to 50 percent.
- Subcritical - from 51 to 69 percent.
- Critical - from 70 to 99 percent (critical stenosis). Often accompanied by mental disorders.
- Absolute occlusion - 100 percent.
Measurements of the degree of narrowing are carried out using specialized studies called hagiographic.
Research into atherosclerotic plaques, one of the causes of the disease, helps specialists obtain additional data about the disease and better treat stenosis. They are characterized by the following characteristics:
- Location and view. There are plaques of segmental, semi-concentric and concentric types, as well as with smooth and uneven surfaces.
- Presence of complications. Plaques are divided into:
- without complications,
- with and without hemorrhages,
- as well as those that form a blood clot.
- Prevalence. Plaques are characterized depending on their size - elongated and local type.
- Structure. Plaques are divided into homo- and heterogeneous.
- Form. Thrombotic, hemodynamic and microembolic.
General cerebral symptoms
The clinic depends on the specific stage of the process, its form, and the root cause of the deviation from the norm.
General cerebral neurological manifestations are represented by a group of disorders:
- Decreased speed of intellectual activity. Lethargy. Formally, the productivity of mnestic and cognitive activity remains at a normal level, but the intensity decreases, which manifests itself in the inability to quickly answer a question. Solve the given problem (simple logical statements and arithmetic examples are used).
- Insomnia. Accompanies the patient from the very beginning, progressing gradually but steadily.
It is represented by the inability to fall into an unconscious state or frequent awakenings (in most cases).
It is extremely painful for patients. It can only be treated with sleeping pills and not always and not for a long time.
- Headache. Medium intensity. Paroxysmal, lasting from several tens of minutes to a couple of hours.
They are localized in the occipital region, temples, and can cover the entire skull, spreading diffusely, including to the eyes, neck, and facial area.
The reflected nature of the discomfort blurs the clinic and does not allow the patient to adequately assess his well-being.
- Instability of the emotional background. Lability. At one moment a person is euphoric, at another he becomes irritable and explodes over a minor reason. And in the third - deeply depressed, whiny, in apathy, does not want to do anything, and does not make contact well. And so on in a circle in different variations.
- Dizziness. Inability to stand on your feet or navigate in space due to significant discomfort. Also called vertigo.
It occurs in attacks and does not last long, no more than a couple of hours. Ends with complete regression of the state. A regular option is possible. Or even a constant flow to a small extent.
The patient attributes the discomfort to the weather and the “garbage” diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia, which does not exist in nature.
- Inability to adequately perceive, remember information, and then reproduce it. Which is again classified as a mnestic disorder.
General cerebral symptoms may be accompanied by objective changes. These are easily fixed by instrumental methods.
For example, blood pressure often drops. 20-30 mmHg less than the normal working norm for a particular patient. Or even lower, depending on the type of pathological process and its stage.
Symptoms of carotid artery stenosis
Minor manifestations of the disease usually do not cause any unusual sensations in the patient’s body. If you suspect you have carotid artery stenosis, knowing the symptoms is essential. Cholesterol accumulates in the body for quite a long time (years), and therefore it is very difficult to immediately find out about the development of the disease. Sometimes the onset of a “manifested” condition is indicated only by a stroke or ischemic attack.
More precisely, stenosis of the common carotid artery can be indicated by a short-term (up to 1 hour) disturbance of cerebral circulation, which results in a stroke. Self-healing of brain functions after such a disorder occurs on its own, but sometimes motor functions, speech, gait and sensory functions have to be restored over a fairly long period of time.
Important ! Any stroke is too alarming a sign that requires immediate medical attention!
As a rule, the most frightening symptoms of stenosis (stenosis may not be the only cause) disappear within 20 minutes to an hour. Here is a partial list of them:
- dizziness and fainting;
- difficulties with swallowing and chewing food;
- serious difficulties with coordination, loss of balance;
- complete blindness of one eye or a veil before the eyes;
- temporary loss of speech and memory;
- nausea and/or vomiting.
- decreased or temporary loss of vision on one side.
Decreased or loss of vision occurs with carotid artery stenosis
Possible complications and prognosis
The prognosis for life with a disease such as carotid artery stenosis, the successful treatment of which largely depends on the prompt response of the patient himself, his relatives and specialists to the alarming symptoms that arise, can be quite disastrous.
Unfortunately, the human brain is not able to accumulate oxygen reserves, and therefore requires a constant “supply” of it, which the body provides through arterial blood. An acute lack of oxygen in the brain leads to irreparable damage to nerve cells. They begin to die after 3–5 minutes in the absence of a fresh portion of oxygen. The condition when the body experiences such a shortage is called a transient attack. Multiple transient attacks in many cases have a fatal outcome for the patient, since they develop a massive stroke. This is accompanied by the death of vital brain tissue, which, alas, is incompatible with life.
Carotid artery stenosis and its complications can lead to:
- paralysis and paresis;
- various visual impairments, including blindness;
- failure of vital organs;
- speech problems;
- fatal outcome.
However, with timely intervention (surgical if necessary), the most negative consequences of the disease are completely preventable.
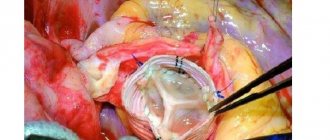
Surgical method for treating carotid artery stenosis
Diagnostics
Timely diagnosis of stenosis in the presence of certain symptoms is the only factor that helps prevent severe consequences. To clarify the diagnosis, the patient must undergo a series of medical tests. The main method is cerebral angiography.
An auxiliary diagnostic method used for clarification is magnetic resonance therapy and ultrasound examination of the carotid artery.
Ultrasound examination of the carotid arteries
Treatment of narrowing of the carotid arteries
It should be noted right away that treatment with various drugs that does not require surgical intervention is possible for stenosis with a septal lumen of up to 50 percent. Even if acute symptoms of the disease have not yet appeared, surgical intervention must be performed before the onset of short-term ischemic attacks.
Therapy has the most beneficial effect if the patient has non-stenotic changes in the walls of the carotid arteries. The course of therapy in this case is carried out with the help of medications.
If doctors are dealing with stenosis, it is not possible to manage only with medications in all cases. Only 20 to 40 percent of patients are successfully treated without surgery.
When determining the path of treatment - surgical or medicinal - the person's medical history, classification of stenotic changes and the general clinical picture are taken into account. In old age (after 70 years), only drug therapy is used - the patient’s heart may not withstand the overload during surgery.
If we touch on such an issue as the cost of surgery for carotid artery stenosis, you can find that it amounts to 250–300 thousand rubles (carotid artery stenting). Carotid endarterectomy is also possible. This is an operation to remove the inner lining of the artery along with atherosclerotic plaques. It is effective and applicable for subcritical narrowing of the artery (60 - 70%). The cost is noticeably lower - from 40 thousand rubles.
The diet for post-carotid artery stenosis is a diet that is usually taken for atherosclerosis. In the practice of inpatient treatment, it is called “Diet No. 10”. The diet of a patient with stenosis should contain 10 - 15% of calories from the normal number for a person of the same age and physique. The diet includes a restriction in fluid intake; you should drink no more than 1.5 liters per day, including coffee and tea.
Typical example of menu no. 10:
- breakfast: curd pudding or semolina porridge, tea;
- lunch: 100 g apples;
- lunch: barley with vegetables in water, baked meat, compote;
- dinner: mashed potatoes with fish (boiled), fruit pilaf, tea with milk;
Separately, it is worth highlighting folk remedies for treating, in particular, the internal carotid artery. Attempts to cure this disease with folk remedies are perceived by doctors as very controversial, but in any case, before using them, you need to consult a specialist.
Anatomical location and topography
The place where the carotid artery is located in the neck is the anterolateral surface of the neck, directly under or around the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It is noteworthy that the left common carotid (carotid) artery branches immediately from the aortic arch, while the right one comes from another large vessel - the brachiocephalic trunk, emerging from the aorta.
Location of the common carotid artery
The area of the carotid arteries is one of the main reflexogenic zones. At the site of bifurcation there is the carotid sinus, a tangle of nerve fibers with a large number of receptors. When pressure is applied to it, the heart rate slows down, and with a sharp blow, cardiac arrest may occur.
Note. Sometimes, to stop tachyarrhythmias, cardiologists apply pressure to the approximate location of the carotid sinus. This makes the rhythm become less frequent.
Carotid sinus and topography of nerves relative to the carotid arteries
Bifurcation of the carotid artery, i.e. its anatomical division into external and internal can be topographically located:
- at the level of the upper edge of the laryngeal thyroid cartilage (“classic” version);
- at the level of the upper edge of the hyoid bone, just below and in front of the angle of the lower jaw;
- at the level of the rounded corner of the lower jaw.
We previously wrote about blockage of the coronary artery and recommended bookmarking this article.
Important. This is not a complete list of possible places for bifurcation of a. carotis communis. The location of the bifurcation can be very unusual - for example, under the mandibular bone. Or there may be no bifurcation at all, when the internal and external carotid arteries immediately depart from the aorta.
Diagram of the carotid artery. “Classical” version of bifurcation
The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, the external carotid artery supplies the remaining structures of the head and anterior surface of the neck (periorbital region, masticatory muscles, pharynx, temporal region).
Options for the branches of the arteries supplying the organs of the neck from the external carotid artery
The branches of the external carotid artery are represented by:
- the maxillary artery (from 9 to 16 arteries depart from it, including the palatine descending, infraorbital, alveolar arteries, middle meningeal, etc.);
- superficial temporal artery (supplies blood to the skin and muscles of the temporal region);
- pharyngeal ascending artery (from the name it is clear which organ it supplies with blood).
Also explore the topic of vertebral artery syndrome in addition to the current article.
External carotid artery - diagram
We also recommend studying this topic:
The structure of the right and left subclavian arteries
Trifurcation of the left internal carotid artery is a normal variation that can occur in two types: anterior and posterior. In the anterior type, the internal carotid artery gives rise to the anterior and posterior cerebral arteries, as well as the basilar artery. In the posterior type, the anterior, middle and posterior cerebral arteries emerge from the internal carotid artery.
Important. People with this type of vascular development have a high risk of developing an aneurysm, because blood flow is unevenly distributed throughout the arteries. It is known for sure that about 50% of the blood is “poured” into the anterior cerebral artery from the internal carotid.
Branching of the internal carotid artery - anterior and lateral
Folk remedies
Unfortunately, there are no herbs or plants that can eliminate blood clots or normalize the curvature of the arteries. The means of therapy used by people are mainly aimed at strengthening the walls of blood vessels with the help of substances beneficial to the body, losing weight, as well as eliminating the causes of the disease and normalizing metabolism.
Hawthorn jam will reduce stress on the heart
Classic folk remedies for the treatment of stenosis:
- Decoction of plantain and golden mustache.
- Hawthorn berry jam. Its use can significantly reduce the load on the heart of a sick person. To prepare, pour boiling water over the hawthorn berries and leave the mixture overnight. In the morning they need to be taken out of the water and ground in a bowl. After this, sprinkle the berries generously with sugar and make the jam using the traditional approach. You should take this jam once a day for a week, on an empty stomach, by dissolving a tablespoon of jam in a glass of water.
- Garlic tincture with honey and lemon.
- A mixture of honey and onion juice.
Before using these remedies, you need to make sure that the patient is not allergic to herbs. The cost of using such methods is noticeably lower than professional treatment, but you need to remember how to treat the disease without risk: only in combination with professional medicine methods and only with the permission of a doctor!
Also in treatment and prevention, household treatment methods are used, which serve to generally strengthen the body, for example, contrast shower . Used to quickly relieve vascular spasms. Every morning and evening you should pour your head first with hot and then with cold water. Such a shower can be taken for the whole body - this is a generally accepted method of hardening.
Carotid artery stenosis is a dangerous consequence of atherosclerosis and a number of other diseases, which, in turn, has quite frightening symptoms and development prognosis. Fortunately, modern medicine makes it possible to treat it, and a timely response to the disease will allow the patient to save his life and get rid of most of the serious consequences.