Which drug should be used to treat liver diseases: “Gepabene” or “Essentiale”? In any case, the choice of medication should remain with the attending physician, who, after studying the results of the diagnostic examination, determines the advisability of using a particular medication. "Gepabene" is a combined herbal remedy, the action of which is aimed at normalizing the functioning of the liver in various ailments. You should take the medication after reading its instructions.
Release form and composition
Gepabene is produced in hard, gelatinous, light brown capsules. The contents of the capsules are powder, the color of which varies from orange-brown to light brown, with light inclusions.
The active ingredients of the drug are the following herbal components:
- Dry extract of the herb fumaria officinalis 275.1 mg (including protopin 4.13 mg);
- Dry extract of milk thistle fruits 83.1 mg (including silymarin 50 mg, silibinin 22 mg).
The auxiliary components of the drug are: corn starch, microcrystalline cellulose, silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, talc, macrogol 6000, copolyvidone, titanium dioxide, purified water, gelatin, black iron oxide, red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide.
There are 10 capsules in blisters, 3 blisters in cardboard packages.
Composition and effect on the body
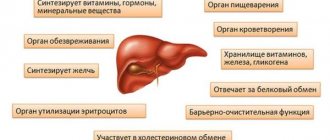
Gepabene is a complex hepatoprotector with a choleretic, hepatoprotective, and antispasmodic effect. It improves appetite, has a positive effect on digestive processes, and keeps the body in good shape. The medicine is available in gelatin capsules with powder inside. The active ingredients of the drug are:
- fumaria officinalis extract. It is often used for hepatitis and biliary dyskinesia, due to the fumarin alkaloid contained in the herb;
- extract of ripe milk thistle fruits, which contains flavonoids: silibinin, silicristin, silydianin. These substances are known for their healing properties and are good for poisoning.
Composition and use of Gepabene
Gepabene's auxiliary ingredients include:
- microcrystalline cellulose, which cleanses the intestines;
- corn starch;
- talc;
- povidone;
- magnesium stearate;
- silica.
The capsule shell consists of:
- yellow and black iron oxide;
- gelatin;
- titanium dioxide;
- water.
Fumarin stabilizes the production of bile and promotes its rapid entry into the intestines, relieves spasms, and has a general strengthening effect on the entire body, including the immune and nervous systems. Flavonoids accelerate the regeneration of hepatocytes, stimulate the synthesis of functional proteins, prevent fat oxidation and prevent further destruction of liver cells in the case of chronic pathologies.
Flavonoids are practically insoluble in water. When they react with alkalis, they form salts due to their natural acidic properties. Once in the intestines, they are absorbed in a split state, providing the effect of the medicine. Two hours after administration, the maximum concentration of active ingredients is reached in the blood. The half-life of metabolites is about six hours.
Gepabene is a long-acting herbal medicine. To achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, you need to drink it for at least 3 months.
Thanks to such a powerful composition and action, Gepabene is prescribed for complex therapy of the liver and bile ducts for:
- hepatitis of various origins;
- postcholecystectomy syndrome;
- complex treatment of ADHD;
- cirrhosis and fatty liver.
Indications for use
According to the instructions, Gepabene is indicated for use as part of the complex treatment of the following diseases:
- Chronic hepatitis (including chronic persistent, subacute and chronic active forms);
- Biliary dyskinesia, including after cholecystectomy (surgical intervention to remove the gallbladder);
- Liver cirrhosis;
- Fatty liver degeneration;
- Toxic-metabolic liver damage, including xenobiotics;
- Chronic toxic liver damage.
Gepabene or hepatrin which is better reviews
We live in a difficult world and often, due to work or the call of our hearts, we abuse alcohol. In addition, according to statistics, approximately 20% of the population has various liver diseases that can result in cirrhosis.
Only in the countries of the former USSR are various hepatoprotectors actively used by both doctors and fellow citizens in the hope of healing the liver with one magic pill. Unfortunately, simple ways don't work.
I will try to answer some common questions, based on the facts of evidence-based medicine, but doing it in simple non-scientific language: - is there a safe dose of alcohol - when are hepatoprotectors needed at all - various miracle drugs that “help the liver” - to drink or not to drink: - Essential phospholipids - milk thistle preparations (silymarin) - ademetionine - ursodeoxycholic acid - metadoxyl - ornithine aspartate (Hepa-Merz)
In Russia, the bulk of liver damage occurs due to alcohol. How do you know if your liver is suffering from alcohol? It’s very simple, there are WHO recommendations on this matter. For men, the SAFE dose of pure 100% ethyl alcohol per DAY is 40 g. For women, it is half as much as 20 g. What is the composition for men: - vodka, cognac, rum, etc. 40% - 100 ml - dry wine 10% - 400 ml - beer 5% - 1 liter
If you drink as much or less per DAY, then nothing threatens your liver (unless, of course, there is concomitant viral hepatitis, for example - then even these doses are toxic). In addition, this dose may be redistributed unevenly throughout the week. For the liver, it doesn’t matter whether you drink 0.7 tequila once a week on Saturday or drink a couple of glasses at night. Those. You can consume no more than 280 g of alcohol per week WITHOUT ANY RISKS
If you consume more, then most likely your liver is suffering. However, the liver recovers very quickly - it has fantastic regeneration. Remember the myth about Prometheus - the eagle pecked his liver every day, and by morning it grew back.
Therefore, the first signs of liver damage will appear no earlier than after 5 years. Further progress up to cirrhosis occurs depending on the volume of consumption. By drinking 60 g of alcohol a day, you may not live to see cirrhosis (they just don’t live that long), but by consuming, for example, 200 ml, cirrhosis may develop within 10–15 years.
Keep in mind that the liver never hurts - well, there are no pain receptors there, so signs of the disease usually appear only at the stage of advanced cirrhosis, when it is too late to drink Borjomi.
Another important consequence: if you worked hard all week at work, and on Friday you relaxed with friends and, with a friendly conversation, persuaded a liter of Scottish whiskey - YOU DO NOT NEED TO TAKE ANY LIVER PILLS - everything will be fine with her. Take better care of taking headache pills and drinking plenty of fluids.
- the liver capsule can hurt - this is the outer shell of connective tissue. When there is a blow to the liver, the latter often ruptures and a hematoma (internal bleeding) occurs, which compresses the surrounding tissues and nerves - hence the pain. When hepatitis occurs, the liver almost never hurts. Only if it increases greatly, then this very capsule stretches and pain occurs.
When are hepatoprotectors needed?
In general, the class of drugs known as hepatoprotectors exists only in the former USSR. Most drugs are not even registered in Europe and the USA. Some are used for narrow indications.
Most often in the world, all these essentials and heptrals are registered as dietary supplements. Those. Drink it if you want, or don’t drink it, there will be no harm, but no benefit either.
So, briefly, when a doctor can prescribe a drug: - alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis - hepatoprotectors are in addition to the main treatment - YOU MUST STOP DRINKING. Otherwise, take pills or don’t eat, neither will help. - non-alcoholic fatty liver disease - in fat people and people with type 2 diabetes, fat is deposited in the liver. In a simplified form, the fat in the liver cells begins to oxidize and destroy them. The main approach to treatment: weight loss, physical activity, cholesterol reduction, antidiabetic drugs (Siofor, etc.) Hepatoprotectors are prescribed to achieve an effect more quickly. - chronic viral hepatitis - hepatoprotectors are prescribed for the prevention of cirrhosis ONLY IF antiviral therapy FAILS or IS NOT POSSIBLE.
There are also a number of serious diseases (primary biliary cirrhosis, drug-induced hepatitis, etc.) when individual hepatoprotectors can be prescribed, but you, my dear readers, are better off not even knowing about these diseases.
The main conclusion: hepatoprotectors are prescribed as an adjuvant. Moreover, the doctor must choose it. After watching enough commercials about the adventures of a liver on legs, you don’t need to run to the pharmacy and buy all sorts of crap there...
Now about the drugs.
Essential phospholipids (essentiale, essentiale, resodlut, phosphogliv)
.
The idea was fantastic - knowing that cell membranes are destroyed in the liver, adjust these same phospholipids so that they fit into the gaps in the cell wall.
Something like this: a cannon is firing at a brick wall, and instead of foraying behind enemy lines, you bring up a string of trucks loaded with bricks. But the funny thing is that when you take the Essentiale tablet, all these “bricks” do not enter the liver, but are distributed throughout the body, where they are successfully metabolized. These are the pies with kittens!
Pure bullshit - all studies have proven that they never help anyone. The last study that finally buried Essentiale and Co. was conducted in the USA on heavily drunk veterans of the Vietnam War - the result was logical: what you drink Essentiale, what you don’t drink - it makes no difference, the main thing is to drink slightly less.
Sofosbuvir daclatasvir cure hepatitis C
By the way, the French from Sanofi, the manufacturer of Essentiale, are not closing their plant only because 99% of these wheels are sold to Russia, Ukraine and other countries of the former USSR. NO ONE ELSE IN THE WORLD (even in the Republic of Chad) needs this shit.
Conclusion - do not transfer money! Our doctors (especially therapists who have seen enough advertising for zombies) often like to prescribe this crap. My advice as a gastroenterologist is that at least you can save money on this component of treatment.
Milk thistle preparation silymarin (Karsil, Legalon, Silimar, Silibor, Hepa-Bene, etc.)
This drug really works. By the way, silymarin is the only antidote (antidote) for the alkaloid of the toadstool. It’s really advisable to take it before you consume this toadstool.
This is a powerful antioxidant. If necessary, it is prescribed for long-term use for at least 3 months, especially for toxic hepatitis. Slows down the progression of liver cirrhosis, which has been proven. BUT THERE IS NO POINT TO TAKE A COUPLE OF TABLETS AFTER BOOKING!
Again, it is better not to save money, but to spend money on German Legalon, which contains the purest chemical substance, and not on cheap Karsil, which contains much less silymarin.
Ademethionine (Heptral, Heptor).
In the world it is registered as a MEDICINE only in Russia, Italy and Germany (well, also in Australia as a veterinary drug). In other countries it is a dietary supplement, because all the research failed miserably.
It costs a little more than a damn. The effect is doubtful. Competent doctors know that Heptral is very effective if you drip it into a vein. But the tablets don’t do a damn thing - this is because when taken orally, only 5% of the drug is absorbed in the intestine. So, most of what you paid a lot of money for will end up in the toilet.
In Russia they really like to prescribe these pills to rich alcoholics, and they really like to drink them after another binge. And the tests really are getting better. This is explained by the fact that in case of alcoholic liver disease, if you stop drinking, the tests themselves will begin to improve quite quickly - remember Prometheus. Conclusion: if, if necessary, the doctor prescribed you to “drip” Heptral, this is good, and then taking the pills is a pure transfer of money.
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA, Ursofalk, Urdoxa, Ursosan).
A very effective drug, especially for severe liver damage. Unlike Essentiale and Heptral, it really works, which has been proven. However, I do not advise you to take it without a doctor’s recommendation. Not everyone needs it and not always.
Metadoxyl.
Actually it is not a hepatoprotector, but is used to relieve withdrawal symptoms in alcoholics. I am writing about it because it has a pleasant property - it enhances the metabolism of alcohol in the body. If you need to drink a lot, but don't want to get drunk, take 2-3 capsules immediately before drinking. Metadoxil will also be very useful in the morning, when you need to quickly get out of a hangover and sober up faster. But it does not protect the liver.
Ornithine aspartate (Hepa-Merz)
.
At one time he was given a lot of publicity on the radio, incl. the late Trachtenberg. HAS NO EFFECT ON THE LIVER AT ALL! THIS IS A PURE RUN FROM THE MARKETING DEPARTMENT. This drug is very effective for short-term recovery from hepatic coma, because... it binds components in the blood that are toxic to the brain. DRINKING IT TO PROTECT THE LIVER IS POINTLESS.
Summary:
- Essentiale, Heptral tablets, Hepa-Merz - we drink it if we want to throw away our money. In other cases - FUCK YOU! — silymarin (Legalon) — we drink as prescribed by the doctor. We also eat 2 tablets of 140 mg each before eating questionable mushrooms (but it’s better to throw away the mushrooms) - UDCA (Ursofalk) - we drink only as prescribed by a doctor - Metaboxil - we drink if we need to get drunk slowly and dry out faster.
(c) Goblin_Kooka
Source: ibigdan.livejournal.com
Vbythfkmyfzdjlfhgbvbrhjkbnf[dgjxrf[
Directions for use and dosage
The herbal medicine Gepabene is intended for internal use. Capsules are taken after meals and washed down with half a glass of water. The standard dosage of the drug is 1 capsule three times a day.
If the patient experiences pain at night, additional use of Gepabene before bed in the amount of 1 capsule is recommended.
The daily dose of the drug, at the discretion of the attending physician, can be increased to 6 capsules, divided into several doses. The duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician individually, and depends on the type of disease, the severity of its course and the effectiveness of therapy.
Elderly patients do not require dose adjustment.
Side effects
The use of Gepabene is generally well tolerated by patients. If the recommended dosage is followed, the herbal medicine does not cause side effects. In rare cases, the following negative reactions from various vital systems of the body cannot be excluded:
- Digestive system: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, heartburn;
- Urinary system: increased diuresis;
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue: alopecia (baldness);
- Cardiovascular system: sudden feeling of heat in the face and upper part of the body;
- Vestibular system: dizziness, sweating, changes in blood pressure, loss of balance, loss of coordination of movement.
In addition to the above side effects, Gepabene can cause the development of allergic reactions in the form of urticaria, rashes, itching on the skin due to hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
special instructions
Gepabene is not recommended for use in children and adolescents under 18 years of age, since there is no clinical experience with the use of this phytotherapeutic drug in pediatrics.
It is also not recommended to use Gepabene during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The exception is strict indications when the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risks to the fetus/child.
Gepabene capsules contain silymarin, which can have an estrogen-like effect, so the phytotherapeutic drug is recommended to be used with caution in patients with hormonal imbalances and diseases such as carcinoma of the prostate, ovaries, uterus, breast, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, etc.
If Gepabene is used in excessive dosages, it is theoretically possible to develop abdominal pain and diarrhea. In this case, the patient should stop taking the drug and consult a doctor.
Due to inhibition of the cytochrome P450 system, Gepabene is able to enhance the effect of drugs containing vinblastine, diazepam, lovastatin, clopidogrel, warfarin, ketoconazole, alprazolam, fexofenadine.
Women taking estrogen replacement therapy or oral contraceptives should be aware that silymarin, which is part of Gepabene, may reduce the effectiveness of these drugs.
Description and instructions for the drug Gepabene
Gepabene is a combination drug that contains substances of plant origin.
Gepabene has the following properties: normalization of the amount of bile secreted, relief of spasm of the bile ducts and bladder, which facilitates the entry of bile into the intestines, antioxidant and membrane-stabilizing activity, stimulation of protein synthesis, regeneration of liver cells. Gepabene should be taken during or after meals with plenty of water. Its maximum concentration in the body occurs 2 hours after ingestion. The half-life of Gepabene from the body is about 5-6 hours. About 80% of the drug is excreted in the bile. If it enters the intestine, re-absorption may occur due to the breakdown of its components by local microflora. The course of treatment is determined individually for each patient, taking into account the severity and nature of the disease.
While using Gepabene, you must follow the diet, regimen, and other medications prescribed by your doctor, and in no case should you consume ethanol.
There is no data on the effect of Gepabene on driving.
The drug is available with a doctor's prescription.
Release form: capsules in packs of 30 or 100 pieces.
Analogs of the drug - Simepar, Uniliv, Levasil.
Gepabene is used for:
- chronic hepatitis;
- chronic liver damage (toxic);
- liver cirrhosis;
- fatty liver;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- postcholecystectomy syndrome (after removal of the gallbladder).
Gepabene is contraindicated for:
- acute phase of inflammatory diseases of the liver or biliary tract;
- hypersensitivity to one of the components of the drug;
- children's age (up to six years).
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the drug can be used, but only strictly as prescribed by a doctor, if it has been determined that the expected effect exceeds the risk to the fetus or child.
Side effects and overdose of Gepabene
- allergic reactions;
- on the part of the cardiovascular system, a feeling of “hot flashes” is possible;
- increased urinary excretion;
- nausea;
- bowel dysfunction;
- general weakness.
In case of overdose, bowel dysfunction and abdominal pain may occur. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately stop taking the drug. Treatment is symptomatic.
Analogs
Based on the similarity of the mechanisms of action and belonging to the same pharmacological group, the following drugs can be classified as analogues of Gepabene: Arnica tincture, Allohol, Artichol, Artichoke extract, Artibel, Berberine, Artichoke Sandoz, Barberry leaves tincture, Immortelle sandy flowers, Tanacehol, Tansy flowers, Salvat, Gepatsinar, Corn columns with stigmas, Konvaflavin, Holos, Holosas, Liobil, Rosehip low-vitamin fruits, Holagol, Olimethin, Odeston, Choleretic collection No. 2, Gepatsinar, Bonjigar, Hofitol, Cynarix, Rafacholin C, Holemaks, Flamin, Tsikvalon.