Description
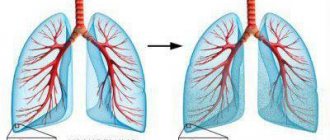
Pneumosclerosis is a pathological process characterized by the replacement of pulmonary connective tissue, which is accompanied by impaired elasticity and gas exchange in the affected areas.
The process is irreversible; the condition gradually worsens due to the proliferation of connective tissue, which is unable to perform the functions assigned to the lung tissue. Such a progressive process requires medical attention, because without treatment there is a threat of disability and even death from complications. Pneumosclerosis develops as an outcome of inflammatory or dystrophic lung diseases, and is more common in men aged 50 years and above.
There are limited and diffuse pneumosclerosis, which differ in the prevalence of the pathological process in the lungs. Diffuse pneumosclerosis is much more severe due to the large volume of damage to the lung tissue.
Based on the severity of replacement of pulmonary connective tissue, the following are distinguished:
- pneumofibrosis – precedes pneumosclerosis, characterized by alternation of airy lung tissue and altered areas;
- pneumosclerosis - compaction and replacement of the lung parenchyma with connective tissue;
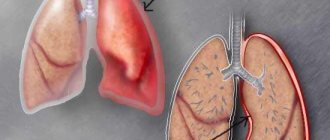
- pneumocirrhosis – develops as an outcome of pneumosclerosis, characterized by complete replacement of the lung tissue, vessels, bronchi with connective tissue, compaction of the pleura, as a result of which the lungs decrease in size, which leads to a displacement of the mediastinal organs towards the lesion.
Pneumosclerosis can be the outcome of the following diseases:
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), chronic bronchitis;
- past infectious lung diseases;
- injuries and wounds of the chest, including the lungs;
- pulmonary sarcoidosis;
- prolonged course of pleurisy;
- foreign bodies in the bronchi;
- hereditary lung diseases.
Despite the various causes of pneumosclerosis, the mechanism of the disease remains the same for everyone. It consists of a violation of the ventilation function of the lungs and the drainage function of the bronchi, and is also accompanied by impaired lymph and blood circulation. Such changes can lead to the development of chronic respiratory failure, so it is important not to ignore the symptoms of respiratory diseases, but to immediately seek help from a doctor.
Description of the disease and its types
What is pulmonary pneumosclerosis? This is a rather dangerous disease, the development of which is accompanied by the replacement of lung tissue with connective tissue. Its occurrence is caused by inflammatory changes directly in the respiratory system. Simultaneously with these processes, gas exchange is disrupted and tissue elasticity is noticeably reduced. As a result, the connecting elements grow, the bronchi become deformed and decrease in volume.
Pneumosclerosis of the lungs
The term “pneumosclerosis” was first coined by R. Laennec back in 1819. Then the scientist used it to refer to pneumonia in the chronic stage, developing as a result of bronchiectasis. This disease can strike a person at absolutely any age. Pneumosclerosis is diagnosed several times more often in representatives of the stronger sex.
There are several classifications of the disease in question.
Depending on the spread of the disease in the respiratory system, diffuse and focal pneumosclerosis are distinguished.
In the first case, the pathological process spreads to 1 or 2 lobes of the lung, causing disruption of the tissue structure in this area. Against the background of such changes, the volume of the organ decreases sharply, and gas exchange ceases to function.
Focal or limited pneumosclerosis is accompanied by tissue compaction. With this form of the disease, the number of affected areas is much smaller. A detailed study reveals the presence of sclerotic zones with purulent exudate.
According to the degree of intensity of development of the pathological process, it is customary to distinguish the following types of pneumosclerosis:
Pneumofibrosis. Fibrous tissue grows in the lung tissue.- Sclerosis. The pulmonary elements are completely replaced by connective tissue, which severely deforms the bronchi.
- Cirrhosis. Collagen replaces the pleura, and lung performance decreases.
Determining the type of disease allows you to prescribe the most effective therapy.
In addition to those listed above, there are other forms of the disease. They are usually classified according to the location of the lesion:
- Peribronchial pneumosclerosis. With this pathology, the connective parenchyma grows around the bronchi.
- Interstitial. The source of the disease is usually pneumonia of the same name. Its main target is the area near the vessels and bronchi.
- Perivascular. The pathological process affects the areas surrounding the blood vessels. Also included in this category are perilobular and alveolar forms of the disease.
Pneumosclerosis - diagnosis
The results of diagnostic data will depend on the extent of lung damage. When listening over the area of localization of pneumosclerosis, weakened breathing and wheezing are detected. Externally, a receding chest may be detected. The following methods are used to diagnose pneumosclerosis:
- Radiography. Pneumosclerosis is detected on x-ray even at the asymptomatic stage. Using the image, you can determine the extent of the lesion and the nature of the disease.
- Bronchoscopy. In this type of diagnosis, pneumosclerosis is defined as chronic bronchitis. Helps to identify the strength of pathological processes.
- Peak flowmetry, spirometry. In the presence of pneumosclerosis, this type of examination will indicate a decrease in the vital capacity of the lungs and a decrease in bronchial patency.
- MRI and CT scan of the lungs. These types of diagnostics help to obtain detailed information about the pathology of the respiratory system and identify difficult-to-detect hilar pneumosclerosis.
Diagnostic methods
What is pneumosclerosis and what are its signs is clearly shown by radiography. In the pictures you can see the slightest changes occurring in the lung tissue, the degree of their severity and distribution. The method helps to establish a diagnosis when there are no pronounced symptoms of pneumosclerosis. On an x-ray taken in frontal and lateral projections, you can see the tumor in the lung.
The size of the affected area is determined by the pulmonary pattern and branching of the bronchi. Signs of pneumosclerosis identified using radiography can reflect symptoms of concomitant diseases. Normally, connective tissue should not be visible in the image. When it is enlarged, one of the following types of cellularity can be detected over the pulmonary pattern - fine, medium or coarse. A similar pattern means the presence of inflammation of the alveoli.
When there is a need to study intralobular connective tissue to determine the extent of its damage, a tomographic study is performed along with radiography.
Methods for detecting the disease are not limited to hardware methods. A respiratory function test helps establish a diagnosis. It helps identify deterioration of pulmonary diffusion and ventilation impairment. For this purpose, spirography is used. The method is one of the most convenient. For diagnosis, it is not necessary to insert various instruments into the respiratory tract.
Pneumosclerosis - causes
Considering pulmonary pneumosclerosis, what it is, and how to treat it, doctors are trying to find out the reasons leading to this condition. Among the main causes of the disease are:
- pulmonary pathologies (pulmonary thrombosis, mycosis, pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, pleurisy);
- heart and vascular diseases;
- alcoholism;
- active and passive smoking;
- ionizing radiation;
- work involving inhalation of gases and dust;
- side effects of certain medications;
- chest injuries.
Pneumosclerosis develops more often in older people and people of pre-retirement age than in people under 50 years of age. This is due to a decrease in the immune function of the body, slagging of organs, and deterioration of metabolic processes. Pneumosclerosis, which develops at this age, can immediately cover a large area and lead to a sharp deterioration in health. For this reason, it is important to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of this disease for diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of the disease
For the development of any disease, a push is needed, this also applies to a disease such as diffuse pulmonary pneumosclerosis. The reasons for its manifestation are the following:
- Lung diseases.
- Inflammation.
- Chronic bronchitis.
- Flu.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Heart failure.
- Pneumoconiosis.
- Collagen diseases.
- Various childhood infections.
- Traumatic injuries.
- Radiation influence.
- Foreign bodies that are hidden in the bronchial tree.
Ventilation of the lungs is impaired, which has a negative effect on the blood circulation and lymphatic system. All this, combined, promotes the growth of connective tissue.
The causes of the disease may also include:
- Ineffective treatment of pathologies that occur in the respiratory system.
- Chest and lung injury.
- Connective tissue disease.
- Poisonous substances.
- Lung diseases that are inherited.
- Some medications.
Causes of the disease.
The mechanism of development of pneumosclerosis is usually associated with other diseases that have not been treated. For example:
- pneumonia,
- peribronchitis,
- Chronical bronchitis,
- tuberculosis,
- pulmonary sarcoidosis,
- mycosis,
- alveolitis,
- hereditary diseases.
In particular, injuries and wounds to the chest can lead to pneumosclerosis.
One of the reasons for the appearance of pathology may be a hemodynamic disorder in the pulmonary circulation.
Not the least role in the development of the disease is played by the radiation received and the intake of toxic medications.
Often pneumosclerosis appears after suffering from staphylococcal pneumonia with an abscess.
Symptoms
Photo: ceemax.in
The severity of the symptoms of the disease depends on the severity of the process, which, in turn, depends on the volume of affected lung tissue. Focal (local) pneumosclerosis usually does not manifest itself in any way, and for quite a long time a person does not suspect its presence. Sometimes patients with focal pneumosclerosis complain of a slight cough with scanty sputum. Diffuse pneumosclerosis is more severe, since the pathological process covers a large volume of lung tissue. The first symptom that a person notices is shortness of breath. Initially, it appears only after intense physical exertion. In this case, a person does not immediately suspect the possibility of illness and does not consult a doctor, since even healthy people may experience shortness of breath after prolonged exercise. However, the condition gradually worsens, shortness of breath begins to bother you when lightly running, walking, and even at rest. In addition, people with diffuse pneumosclerosis are bothered by a cough. At first it is rare, then it becomes intrusive with the release of mucous or mucopurulent sputum.
Against the background of these specific symptoms, general symptoms are observed in the form of weakness and increased fatigue, leading to decreased ability to work, and the disease is often accompanied by a decrease in body weight.
Due to a decrease in the volume of functioning lung tissue, chronic respiratory failure gradually occurs. Externally, this condition manifests itself as cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin). Depending on the stage of chronic respiratory failure, the localization of cyanosis varies. For example, at the subcompensated stage, blueness of the lips and fingers and toes is observed. During the decompensation stage, cyanosis spreads to large areas of the body.
Symptoms of the disease.
The peculiarity of the limited form of pathology is that it does not manifest itself in any way, except that a person may occasionally be bothered by a cough.
Diffuse pneumosclerosis always manifests itself as shortness of breath, and if it first occurs after an increase in physical activity, then after that it occurs at rest. The skin tone becomes bluish. Another sign of a problem may be the so-called. “Hippocrates fingers” - the upper phalanges expand. Fingers become like frogs.
Cirrhosis of the lung makes itself felt by gross deformation of the chest and atrophy of the intercostal muscles. Internal organs may become dislodged.
Symptoms of pneumosclerosis
Symptoms of pneumosclerosis largely depend on the location of the pathology, as well as on the type of disease. With diffuse pulmonary pneumosclerosis, shortness of breath and cyanosis are usually observed.
Shortness of breath initially appears only with significant physical exertion. The fact is that even when part of the alveoli is damaged, reserve alveoli, of which there are quite a lot in the lungs, are included in the ventilation process. Therefore, the appearance of shortness of breath may be a sign that the damage has gone so far that even numerous reserve alveoli cannot cope with ventilation of the lungs.
In this case, the respiratory rate may not change; difficulty and prolongation of exhalation are more often observed.
Cyanosis, that is, a bluish coloration of the skin and mucous membranes, caused by a high content of reduced hemoglobin in the blood, is a consequence of hypoventilation of the alveoli, impaired diffusion of oxygen in them and changes in hemodynamics.
Also, with diffuse pneumosclerosis, patients often complain of cough. At first it appears only occasionally, then intensifies, accompanied by the separation of purulent sputum.
With limited pneumosclerosis, there may be no shortness of breath and cyanosis, but when listening, you can notice moist rales in the same place - usually in the lower parts.
X-rays help identify pneumosclerosis. The research usually gives a very clear picture:
- the pulmonary pattern is deformed due to excessive growth of lung tissue around the bronchi and in the interstitium;
- Rough, heavy shadows emanate from the root, gradually disappearing towards the periphery.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Treatment with folk remedies
If the disease is detected, diffuse pneumosclerosis of the lungs, treatment with folk remedies also gives positive results.
A few recipes to help you.
- Creeping thyme, common thyme, blue eucalyptus, common oats. One of these herbs is taken in the amount of one tablespoon. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave in a thermos overnight. Starting in the morning and throughout the day, the decoction is taken hot. Once a month the type of grass changes.
- The onion is being cooked. Grind with sugar. Every two hours, take one tablespoon. The onion can also be boiled in milk. It will be more efficient.
- For seven days, place two aloe leaves on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator. After this, grind the leaf. Mix it with honey - two tablespoons - and two glasses of young red wine. Leave for fourteen days in a cool, dark place. Take the product in this way, one tablespoon before each meal, but no more than four times.
For a disease such as diffuse pulmonary pneumosclerosis, treatment with folk remedies is used quite often. Just remember that you should not resort to such salvation from the disease without consulting a doctor.
Treatment of pulmonary pneumosclerosis
In most cases, pneumosclerosis is curable, but much depends on the progression of changes in the lungs and the speed with which respiratory and heart failure develop, as well as on the specific type of disease.
The most severe situation occurs when a “honeycomb lung” forms, as well as when a secondary infection develops, complicating the disease. The formation of a “honeycomb lung” leads to a sharp exacerbation of respiratory failure, increased pressure in the pulmonary artery and the development of cor pulmonale, a cardiac pathology in which the ability to work, quality and life expectancy are significantly affected. The development of secondary infection, tuberculous or mycotic processes can lead to death.
Pneumosclerosis is treated by pulmonologists or therapists. The patient may be admitted to the pulmonology department if there is an acute inflammatory process in the lungs or if complications develop.
As for therapy, it is based on eliminating the factors that led to the occurrence of pathology. Limited pneumosclerosis, which does not manifest itself clinically, does not require active therapy. If, with pneumosclerosis, the inflammatory process worsens, the doctor may prescribe antimicrobial, expectorant, mucolytic, and bronchodilator drugs. Bronchoscopy also helps, allowing for improved drainage of the bronchial tree.
For heart failure, cardiac glycosides and potassium supplements are recommended.
Diffuse pneumosclerosis, as well as a disease in which an allergic element is observed, is treated with glucocorticoids.
Surgical treatment (resection of the affected part of the lung) is necessary for fibrosis and cirrhosis, destruction and suppuration of lung tissue.
Today, specialists often use stem cells to restore the normal structure of the lungs and their gas exchange function.
Do not forget about physical therapy, massage, oxygen therapy and physiotherapy, simple breathing exercises to improve the function of external respiration.
Diffuse pneumosclerosis
Diffuse pneumosclerosis is the outcome of various pathological processes, as a result of which connective tissue elements grow in the lungs, displacing normal functioning lung tissue, and gas exchange is disrupted. In the structure of pneumosclerosis, diffuse and focal forms occur in approximately equal proportions. At the same time, if focal pneumosclerosis does not cause a clinically significant impairment of pulmonary function, then diffuse one can lead to the development of arterial hypoxemia, chronic respiratory failure, pulmonary heart disease and other disabling complications. The most important task of pulmonology is to restrain the progression of pathological processes in the lungs, prevent disability and significantly improve the quality of life of patients with diffuse pneumosclerosis.
Prevention of pneumosclerosis
You can take measures that will significantly reduce the likelihood of the disease occurring. Necessary:
- prevent respiratory diseases;
- promptly treat colds, infections, bronchitis, tuberculosis, lung diseases;
- Take precautions when interacting with pneumotoxic substances and carefully take pneumotoxic drugs prescribed by your doctor.
If there is a risk of inhaling dust or gas at work, respirators must be used. At the workplaces of grinders, glass cutters, etc. it is necessary to install exhaust ventilation, and exhaust ventilation must be installed in mines.
Quitting smoking, hardening, light physical exercise, and physical therapy also help prevent pneumosclerosis.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Pneumosclerosis of the lungs: life expectancy.
Only a doctor can give specific numbers, and even then not always. A lot depends on the stage of pneumosclerosis, as well as on timely treatment. If you immediately noticed signs of pneumosclerosis and treated it instead of the disease that caused it, then everything can be done without serious consequences. And if it comes to a lung transplant, then everything is not so rosy...
- With limited pneumosclerosis, there are usually no external symptoms; sometimes a cough with a small amount of sputum appears. When examined by a pulmonologist, chest cavity may be detected on the affected side.
- With diffuse pneumosclerosis, the patient is bothered by shortness of breath, which at the beginning of the disease appears only during physical exertion, but as the process progresses, it appears at rest. On examination: the patient's skin is pale and cyanotic. A characteristic symptom is Hippocratic fingers, which are thickenings and modifications of the fingers that become similar to drumsticks. Basically, diffuse pneumosclerosis has the clinical picture of chronic bronchitis. Patients complain of coughing, sometimes with purulent sputum. Aching chest pain, weight loss, malaise and increased fatigue may appear. Hypertension also develops in the pulmonary circulation.
- With cirrhosis of the lung, the following symptoms develop - gross disturbances in the structure of the chest, the intercostal muscles atrophy, the mediastinal organs and trachea are displaced to the affected side.
Complications of pneumosclerosis
- Severe ventilation disturbances
- Cardiovascular failure
- Respiratory failure
- Emphysema
Forms of the disease
Pneumosclerosis is classified depending on the degree of lung damage. There are focal and diffuse forms of pathology.
In focal or local forms of pneumosclerosis, disturbances in the elasticity and gas exchange of the pulmonary parenchyma are not observed. There is compaction and the formation of purulent foci on the lung tissues, varying in size. Depending on the size of the affected areas, focal pneumosclerosis is divided into small focal and large focal. In this form, the disease can proceed unnoticed by the patient himself, and manifest itself only in minor signs that are characteristic of any other diseases of the respiratory system, for example, a frequent cough accompanied by the release of a small amount of sputum. Pathology is diagnosed only when the patient is examined using an X-ray machine.
Diffuse or widespread form of pneumosclerosis is characterized by damage to the entire lung tissue. In this case, there is a violation of the structure of the lungs, their compaction and reduction in volume, and a decrease in ventilation functions.
Diffuse moderate pneumosclerosis is not as severe as compared to the main form of the disease, and also poses less danger to the body. But, based on the fact that the disease progresses rapidly, it is very important to identify and eliminate signs of even moderate pneumosclerosis at the very early stages of its development. In this way, it is possible to avoid many unwanted health consequences.
According to the degree of damage, pulmonary pneumosclerosis is divided into fibrous, ordinary sclerosis and cirrhosis.
In the fibrotic stage, the lesions are limited and alternate with healthy areas.
With sclerosis, the respiratory organs lose their original airiness, become denser and smaller.
The cirrhosis degree, as the most severe, is characterized by a complete replacement of the lung parenchyma with connective tissue.
It is worth mentioning separately pneumosclerosis of the basal segments, which develops in the lower parts of the main respiratory organs. The cause of its occurrence in most cases is inflammation of the lower lobes of the lungs.
Treatment
The main thing in the treatment of pneumosclerosis is to eliminate the causes that led to the development of pneumosclerosis. During the inflammatory period, patients are indicated for hospitalization. Limited pneumosclerosis, as a rule, does not require active medical interventions. If it is aggravated by inflammatory processes, adequate antibacterial therapy is prescribed, expectorants, mucolytics and antitussives are prescribed. Sometimes bronchoalveolar lavage is performed (improving bronchial drainage). With the development of cardiovascular failure, cardiac glycosides and potassium preparations (Panangin) are prescribed.
In addition to drug therapy, physical therapy has a good effect. Prescribe chest massage, physical therapy, and oxygen therapy courses.
In some cases, pneumoxlerosis requires surgical intervention. For focal pneumosclerosis, resection of the affected area of the lung is performed.
Photo: likar.info
At each appointment, the doctor performs a general examination of the patient, with the help of which the person’s condition is preliminarily assessed. With pneumocirrhosis, you can detect a deformation of the chest, which will be noticed not only by the doctor, but also by the patient himself. By auscultating the lungs, the doctor listens for weakened breathing, wet and dry rales. It should be noted that such an auscultation picture is characteristic of diffuse pneumosclerosis; with focal pneumosclerosis, the results of auscultation of the lungs differ little from the norm. Next, the doctor writes out a referral for an X-ray examination of the lungs. With the help of this study, it is possible to detect changes in the lung tissue, assess their prevalence and severity. An x-ray reveals an increase in the pulmonary pattern; with cirrhosis, a decrease in the size of the affected part or the whole lung is determined, due to which the mediastinal organs shift to the affected side. The lower parts of the lungs can take on the appearance of a porous sponge, in which case the lung is called “honeycomb”. A more detailed assessment of the structure of the lung tissue is provided by CT and MRI.
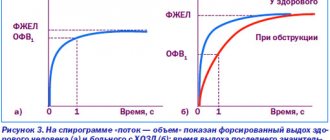
With pneumosclerosis, the volume of normally functioning lung tissue decreases, as a result of which the lungs do not cope 100% with their immediate functions. To establish this, an assessment of external respiratory function is prescribed. This research method helps to assess the ventilation function of the lungs using graphical recording and subsequent processing of the obtained data on a computer. Using a test with bronchodilators (dilators that dilate the lumen of the bronchi), it is possible to identify reversible or irreversible bronchial obstruction. Bronchoscopy can also detect this phenomenon. This endoscopic technique aims to visualize the tracheobronchial tree.
Photo: sanatoriy-kirova.ru
To prevent the development of pneumosclerosis, you should promptly treat respiratory diseases, take precautions when interacting with pneumotoxic substances, and do not delay going to the doctor if characteristic symptoms occur. When working in hazardous industries, it is important to use respirators that prevent dust and chemicals from entering the respiratory tract. In addition, the immediate production management must take care of the proper operation of exhaust ventilation.
When diagnosing pneumosclerosis, treatment begins with lifestyle changes. First of all, it is recommended to stop smoking, as cigarettes can aggravate bronchial obstruction. All family members must understand that there is a concept of passive smoking, so it is important not only for the patient himself to forget about cigarettes, but also for the people living in the same living area. Meals should be fractional, complete, sufficiently filled with vitamins and microelements. Despite the fact that pneumosclerosis is accompanied by shortness of breath, especially when playing sports, you should not completely give up physical exercise. It is necessary to arrange long distance walks and perform therapeutic exercises.
Considering that with pneumosclerosis, the lungs cannot fully provide the body with the necessary amount of oxygen, oxygen therapy is used. This treatment helps saturate the blood plasma with oxygen, which leads to a decrease in the severity of shortness of breath. However, safety rules should be observed, since frequent or excessive use of pure oxygen or inhalation mixtures with high oxygen concentrations can lead to oxygen intoxication.
For the symptomatic treatment of cough, expectorants are used to promote the separation of sputum. For the same purpose, mucolytic agents are prescribed, which dilute sputum, thereby facilitating its removal.
Diagnostics
With such symptoms, you should contact a pulmonologist, who will be able to identify shortness of breath, deformation of the fingers and cyanosis typical of the disease. During examination, the doctor records weakened breathing, wet and dry rales.
To confirm diffuse pulmonary pneumosclerosis, radiography or computed tomography is performed, with which you can see emphysema, a decrease in the volume and pattern of the organ.
In order to more accurately examine changes in the bronchi and blood vessels, specialists can use bronchography or angiopulmonography. Spirometry or plethysmography allows you to check the functions of external respiration. In rare cases, a transbronchial lung biopsy is required. A morphological study is also carried out. It is necessary to differentiate this pathology from bronchial asthma, bronchitis, vasculitis or heart failure.
Nutrition for pneumosclerosis
If a person is diagnosed with pneumosclerosis, he should reconsider his lifestyle and diet. Although an unhealthy and unbalanced diet is not the direct cause of pneumosclerosis, it does affect the general state of health. The task of nutrition for pneumosclerosis is to maintain strong immunity and general tone of the body.
The following well-known principles should be observed:
- The diet must be balanced so that the body receives all the necessary substances, proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the correct ratio.
- The menu should include a large number of foods with vitamins, vegetables and fruits.
- You should take care of the variety of products on the menu so that all the necessary microelements are supplied with food.
- To increase the body's defenses, it is recommended to consume honey, lemons, kiwi, bell pepper, ginger, sauerkraut, garlic, radish, rose hips, and various berries.
Pneumosclerosis of the lungs - life expectancy
Basal pneumosclerosis refers to diseases that lead to irreversible consequences. Lung tissue changes its structure to a more dense one, after which it cannot be returned to its original state. If the disease is focal in nature and is not complicated by pulmonary emphysema, then the prognosis for pneumosclerosis can be favorable. With proper treatment and constant prevention of complications, the patient can continue his normal life.
Weak immunity, bad habits, extensive lesions or diffuse lesions, concomitant diseases, and improper treatment can cause the patient’s condition to worsen and shorten life to several years. How long a patient with pneumosclerosis can live will depend on the severity of the disease, its rate of progression and general health.
Medicines
Photo: proizjogu.ru
Medicines are not able to relieve the patient of pneumosclerosis; they only alleviate the symptoms of the disease. Cough with pneumosclerosis is unproductive; to correct this, expectorants and mucolytics are prescribed. Ambroxol is the most common drug due to its low cost and sufficient effectiveness. The drug achieves its effect by stimulating the glands of the bronchial mucosa. This increases the content of the mucous component of sputum, which facilitates its release. The drug is well tolerated, side effects are extremely rare. For example, in case of individual intolerance to the components of the drug, an allergic reaction develops, which can manifest itself as urticaria or angioedema. Other side effects observed less frequently are: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headaches, general weakness.
Bromhexine is another drug that is used to thin phlegm. Not for use in children under 3 years of age and pregnant women (1st trimester). In all other cases, there are no strict contraindications to the use of the drug. People who have an allergic reaction to the active substance, bromhexine hydrochloride, should be treated with caution. Such people should notify their doctor in advance about the presence of an allergy to a previous drug intake, so that the doctor can select another drug with the desired effect.