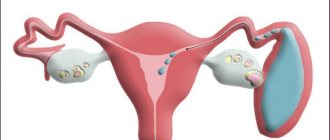
Uterine fibroids are benign accumulations of connective tissue (tumor). Fibroids can be diagnosed during a gynecological examination and confirmed through ultrasound (US), computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Fibroids can also form in other organs, but most often such tumors are found in the ovaries, uterus, mammary glands and skin. Fibroma occurs either as a single node or in clusters. The fibrous joint in the uterus can reach several centimeters.
By nature, fibromas are benign; they extremely rarely develop into dangerous malignant forms. Fibroids are characterized by the absence of pronounced symptoms. Signs appear gradually and with increasing intensity. Most often, the tumor is found between the ages of 30 and 35 years.
Classification of fibroids
Fibroids are divided according to location:
- submucosal (ripe under the mucous membrane of the uterus, causing pain, spasms and bleeding);
- subserous (grow on the outside of the uterus above the mucous membrane, mature without symptoms, and upon reaching a large size interfere with the functioning of neighboring organs);
- interstitial (occurs in the wall of the uterus, increasing its size, are the most common);
- interligamentous (formed between the supporting uterine ligaments, removal is associated with a high risk of vascular damage);
- stalked (fibromas with a stalk, bending of the stalk provokes severe pain);
- parasitic (tumors attach to other organs).
Symptoms of the disease
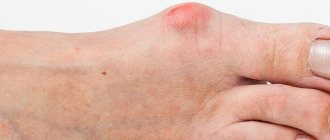
soft fibroma - initial stage
In the initial stage, fibroma looks like a small bump on the skin in the form of a pink hemisphere. The stalk may be thinner than the edges of the dome, and the fibroma in this case looks like a mushroom. But at the first stage, as a rule, there is no leg. If you press on it with a hard object, a clear dent will form.
Soft fibroids are usually small in size, since they consist mainly of plastic tissue. They reach sizes up to 3 cm in diameter and, when pressed, easily move to the side.
Due to its delicate structure, the formation has a wrinkled surface. It often happens that the tumor is painful when pressed. This is due to its location on the body. In addition, it is easy to injure, especially if it is located in places where it often comes into contact with clothing or is under hair and a person touches it, for example, with a comb.
Hard fibroids are more likely to form on hard and smooth skin surfaces, such as the back and legs. They reach several centimeters in diameter, are located deep in the skin and feel quite hard to the touch. Small growths on long stalks most often form in groups of several pieces.
Causes
The exact causes of fibrous tumors are not clear. This may be due to increased sensitivity to estrogen or a hereditary predisposition, although these factors do not guarantee the development of fibroids.
Women at risk:
- with late menarche (first menstrual discharge);
- terminated pregnancy;
- those who have not given birth before the age of 30;
- with diabetes mellitus;
- experienced childbirth with complications;
- resorting to curettage (one or more times);
- with arterial hypertension;
- using contraceptives with estrogen (also when treating menopause with these drugs);
- with chronic diseases of the genital organs;
- without regular sexual contact (preferably with one partner);
- overweight and obese;
- with thyroid diseases;
- unable to adequately cope with stress;
- with physical inactivity.
It has been proven that representatives of the Negroid race are more often diagnosed with fibrous tumors. The European race is less susceptible to fibroids. Also, the risk of fibroids depends on the woman’s age. In young girls under twenty years of age, benign tumors occur only in 20% of cases. The chances increase to 30% at age thirty and 40% at age forty.
Little girls before menarche and women during menopause are protected from fibroids. This is justified by the fact that uterine fibroids occur only under a certain hormonal state. This is why fibroids often increase during pregnancy, when the influence of estrogen increases. It is noteworthy that after childbirth and normalization of hormonal levels, the fibrous tumor decreases to its previous size.
During menopause, when the concentration of hormones (especially estrogen) decreases, fibroids often decrease in size and disappear altogether. During this period, even old fibroids no longer grow.
Fibroma: types, symptoms, treatment, why it is dangerous
Fibroma is a benign formation that does not pose a threat to human life and consists of hard collagen and elastic fibers.
The neoplasm has various habitats: scalp, face and body, internal organs, bones, nails.
The ICD-10 code (D21) classifies this disease as a benign tumor, which can sometimes develop into cancer. 60% of women suffer from this disease.
Types of fibroids
The following common types of fibroids have been found:
- Non-ossifying fibroma is a large formation on the bone surface, consisting of fleshy yellow or brown fibers mixed with blood. Teenagers and children are at risk of developing this type of fibroid. Practically does not occur in people over 30 years of age. Bone islands do not require surgical intervention, dissolving on their own, and are diagnosed only with the help of X-rays, scintigraphy and computed tomography. There are no external signs of fibroma. The growth does not cause pain or discomfort, presenting difficulties for detection and diagnosis. Does not require treatment or biopsy.
- Desmoid fibroma is a dense skin growth with a bumpy surface that lives on the skin of the back, abdominal area, limbs and chest. The diameter of the tubercle ranges from 1 mm to several centimeters. In 5% of cases it turns into cancer. To make a diagnosis, the oncologist analyzes the biopsy. The tumor is removed only if it is benign. After surgery, relapse is possible. Desmoid predominantly occurs in women. The causes of the appearance of a skin bump are unknown, but it is believed to occur as a result of trauma and skin damage.
- Odontogenic fibroma is a hard fibrous tissue that has clear boundaries and occurs in the oral cavity. It develops slowly, without causing discomfort or pain to a person. Reaching a decent size, it causes jaw deformation, pain and bloating in the oral area. The only way to get rid of the disease is surgery. The diagnostic method is x-ray.
- Chondromyxoid fibroma is a rare tumor consisting of cartilaginous tissue and multinucleated cells, and is a yellow intraosseous formation. As the disease develops, it gradually moves to the joints and spreads to the muscle tissue area. The disease is accompanied by progressive pain, swelling and hampers movement of the limbs. It can be removed by curettage, but in 25% of cases it reoccurs. Localization of formation: ribs, skull, spine, humerus and pelvic bones. Most often occurs on the tibia. Diagnosed by x-ray.
- Ameloblastic fibroma is a rare formation consisting of soft, epithelial tissue in the form of a miniature capsule and rarely develops into a cancerous tumor. The risk group includes men over 21 years of age. The tumor is localized in the oral cavity and provokes tooth loss in the area where it lives. The cyst is detected by x-ray. To avoid relapse, it is removed surgically.
- Non-osteogenic fibroma is a pathological defect that causes changes in the femur and provokes resorption of tubular bones. The presence of a bone tumor does not cause concern, but without timely treatment, a pathological bone fracture occurs. Over time, fibroids can resolve on their own.
Internal organs
This location makes it difficult to detect the tumor.
- Uterine fibrosis involves the formation of connective tissue in the muscles of the reproductive organ. A uterine tumor-like lesion does not cause cancer and is accompanied by pain and bleeding if it increases in size.
- A breast tumor is a small ball that is detected on palpation and is accompanied by noticeable progressive pain. The end result of the development of education is oncology.
Removed breast fibroadenoma
- Ovarian damage does not appear at the initial stage. Reaching a substantial size, the formation brings anxiety in the form of pain in the lower abdomen, depletion of vitality, difficulty breathing, bloating and constipation.
- Pulmonary fibrosis is dangerous, affecting both respiratory organs. Accompanied by pressure on internal organs and a feeling of heaviness. A bronchial tumor is determined by the following signs: difficulty breathing, wheezing cough, hemoptysis. Precedes bronchitis, pneumonia and tuberculosis.
- Bone damage is characterized by unexpected and, at first glance, causeless fractures. The initial stage passes without symptoms. Most often occurs in children and adolescents. Does not require long-term treatment or surgery. Bone fibrosis resolves without outside medical help.
Oral lesions
- The appearance of a growth on the tongue does not pose a danger to human health and can only cause discomfort. If you try to remove the growth or cause damage, the tumor may develop into a malignant one.
- A tumor of the ligament and larynx affects the muscle folds of the internal oral cavity and ligaments. Recognized as the most common type of fibrosis. Occurs in people who actively use their voice in their profession: speakers, teachers, artists, professors. The presence of a tumor negatively affects voice quality. Frequent coughing, hoarseness and difficulty breathing appear. It is detected by external examination: soft pink growths in the tonsil area are visible in the throat. Removing a tumor in the pharynx has a huge advantage: relapse after surgery is impossible.
- Maxillofacial fibroma is a single cystic formation that has a round shape and a mucous surface and is located in the jaw and oral cavity. Palpation does not bring any unpleasant sensations. It is advisable to remove the pathology to avoid transformation into a malignant tumor.
Skin damage
Soft tissue fibromatosis occurs on the skin surface and in the oral cavity. This phenomenon occurs at any age and is not determined by gender. Damage to the skin covers different areas.
Fibrosis on the face manifests itself in the form of soft or hard growths of various sizes and shapes that do not cause pain upon palpation. Facial pathology is not life-threatening and can only bring aesthetic displeasure.
Skin fibrosis affects a variety of parts of the body. The pathological phenomenon occurs in the area behind the ear of the left or right ear, on the back, on the surface of the thigh, on the chest and limbs. This includes swelling on the lip and nail. Damage to the foot and hand was repeatedly noted. Skin pathologies are characterized by having a round shape with clear boundaries and a brown or pink color.
People who have reached 40-45 years of age are at risk. The occurrence of pathology is associated with aging of the skin, heredity and the presence of diabetes mellitus. Skin fibrosis does not cause cancer, but doctors strongly do not recommend removing growths, as this leads to the reappearance of fibromatosis, which is already malignant.
Atheromas belong to skin cysts. This pathology is characterized by blockage of the sebaceous glands, causing the appearance of a residual cyst that looks like a boil or an inflamed pimple. The presence of a tumor is detected in the subcutaneous adipose tissue.
The inside of the atheroma is filled with a white cheesy liquid, which is a product of the activity of the sebaceous glands and has an unpleasant odor. Both single and multiple occurrences on the skin were observed. Localization: skin of the face, head, back, genitals.
Brings pain, swelling and redness during periods of inflammation. The tumor is localized in the parietal region and in the hairline area.
Intradermal pathology of the finger does not cause pain at an early stage of development and appears as a small node on the finger or hand. An aesthetic defect occurs as a result of insufficient intake of vitamins, poor nutrition, dry skin and metabolic disorders. The formation of pathology is detected under the skin, despite the bulge.
Periungual or subungual pathology occurs near or under the nail plate and shows a purple, dirty yellow or blue color. Brings discomfort and aching pain when reaching a respectable size.
Most often it forms on the toes, causing discomfort to the patient. Pathologies arising in the nail area are not difficult to diagnose.
If pathology occurs, the patient must undergo examination for the occurrence of the disease.
Fibrosis of the leg is a hard, single tumor that has a dense consistency and is accompanied by painful sensations. Negatively affects blood circulation in the leg area.
Treatment is carried out with drug therapy or surgery.
Doctors strongly do not recommend ignoring this disease, as there is a possibility of blood poisoning and, as a result, death is expected.
Symptoms of the disease
Characteristic symptoms of a tumor are aching pain and bloating. Most often, the disease is asymptomatic, it depends on the type and location of the formation.
These include desmoid, non-osteogenic, ameloblastic, non-ossifying and odontogenic types of formation. The chondromyxoid form is accompanied by progressive pain.
Symptoms of fibroids are determined by the stage of development of the disease and appear in the vast majority of cases, reaching large sizes.
Causes
The causes of its occurrence have not yet been fully elucidated, but the occurrence of this disease is influenced by the following factors:
- The presence of bad habits, especially alcohol and tobacco addiction.
- Skin damage and trauma.
- Polluted urban habitat.
- Poor nutrition, especially excessive consumption of sweet, fatty, starchy and spicy foods.
- Viruses.
- Weak immunity.
- Radiation.
- Dishormonal balance.
- Excessive UV exposure.
Diagnosis
The process of detecting formation also depends on the type and location of occurrence.
Benign tumors of internal organs can be detected using X-rays, computed tomography, scintigraphy, biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging and by external examination in the case of superficial skin formations.
Determining the many types of fibroids is difficult due to their asymptomatic nature and slow development. A tumor of the female reproductive system is detected by ultrasound.
During diagnosis, there is a risk of confusing a fibroma with a lipoma. How does the pathology described in the article differ from lipoma? Fibroma can consist of both soft and hard tissues. Lipoma consists of soft fibers. Lipoma does not carry the risk of cancer, while fibroma in some cases can be malignant.
Treatment and removal of the tumor
Surgery, oncology and dermatology are areas of medicine that contribute to the timely diagnosis, treatment and removal of fibroids. There are many professional clinics specializing in these issues.
Removing fibroids is fraught with negative and dangerous consequences, requiring prior consultation with a professional doctor. Treatment of pathology depends on the type, origin and degree of complexity.
Fibroma must be removed if it is malignant. Methods of treatment and tumor removal:
- Laser removal is a quick and effective way to get rid of skin defects. Removal requires a single procedure, and the recovery period lasts a maximum of 14 days. Removing a tumor with a laser is one of the safest ways to get rid of the disease. The procedure does not cause pain and does not leave scars.
- Removal of fibrosis with an electric knife is reproduced using electric current and is carried out both with and without the use of an anesthetic.
- The method of removal with an electrocoagulator is applicable to pathologies formed on the surface of the skin. The procedure involves the use of electric current to cause necrosis of fibrous tissue, resulting in the death of the skin defect. Cauterization leaves thermal burns. Coagulation is prohibited when removing malignant tumors, in the presence of herpes and somatic diseases. The wounds remaining after the procedure heal quickly without leaving marks. A light spot remains at the site where a large wart or papilloma was removed.
- Bloodless removal of fibroids by radio wave occurs using a radio knife and does not leave injuries or burns. Recommended for people with sensitive skin. Removal takes a maximum of five minutes. Recovery of the operated skin area lasts seven days.
- Laser vaporization treatment is used for diseases of the cervix and the occurrence of skin pathologies. During the procedure, the doctor adjusts the depth of the laser beam and controls its movement. This method is used in cosmetology and surgery. Laser technology does not leave spots, scars or scars after removal, unlike surgery, which leaves stitches behind. After the operation there are no complications or difficult rehabilitation period.
To prevent a new one from growing after fibroma removal, correct diagnosis and quality treatment are necessary.
How dangerous is fibroma, and why can’t this disease be ignored?
The consequences of ignoring pathology are dire if the disease becomes malignant. This is the main danger of the disease.
To avoid negative consequences, it is recommended to consult a doctor at the first signs of pathology.
It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate or remove tissue fibrosis on your own without undergoing the appropriate studies and passing the necessary tests!
Select the city, desired date, click the “find” button and make an appointment without waiting in line:
Source: //onko.guru/dobro/fibroma.html
Symptoms and signs
Often, uterine fibroids do not manifest themselves in any way, but statistics indicate pronounced symptoms in every fourth fibroid carrier of childbearing age. If there are no symptoms, treatment may not be necessary. The intensity and nature of the symptoms are determined by the type of fibroma and its size.
The most common manifestations of fibrous tumors in the uterus:
- heavy bleeding;
- discharge with blood clots;
- pain in the lower abdomen or lower back;
- anemia, developing against the background of prolonged blood loss, accompanied by dizziness, weakness, fatigue, low blood pressure, pallor, uncontrollable trembling of the limbs;
- pressure in the pelvis, in the bladder area, accompanied by frequent urge to urinate, incontinence, or, conversely, urinary retention;
- pressure in the intestines may be accompanied by constipation or bloating with pain;
- pain in the legs (mainly in the back);
- noticeable enlargement of the abdomen, which is often attributed to pregnancy or weight gain;
- pain during sex.
Symptoms can appear with varying intensity depending on the location of maturation and the size of the fibroid, which puts pressure on the pelvic area and neighboring organs. Sometimes fibrous formation can cause the impossibility of conception or provoke premature birth.
Types of soft fibromas
Fibroma of the soft tissues of the head is a fairly common localization, especially in the area of natural folds of the skin. In oncological practice, it is customary to distinguish the following types of acrochordons:
- Small form. Primary elements are represented by multiple papular rashes in the head and neck area. The neoplasms are soft and painless. The color of pathological lesions is light brown.
- A thread-like growth that can reach 2 mm in length and 5 mm in width.
- Large view.
Diagnostics
Often, fibrous formation is diagnosed during a routine examination by a gynecologist. To determine the size of fibroids, they resort to two-handed vaginal examination. The doctor assesses the fibroma as a dense, lumpy formation by touch.
For a more detailed study of fibroids, transvaginal ultrasound of the pelvis is used (the sensor is inserted directly into the vagina). The doctor can clarify the type and size of the node, determine the density and risk to neighboring organs. Ultrasound helps distinguish fibroma from ovarian cystoma.
It is worth remembering that transvaginal examination is performed with an empty bladder. Before the procedure, you need to abstain from food that contributes to excessive gas formation. The procedure requires a towel, napkins and a condom (special for ultrasound or regular with a smooth surface).
Another method for diagnosing fibroids is x-ray or ultrasound hysterosalpingography. The study is used to determine the presence of a submucosal tumor in the endometrial cavity.
If bleeding occurs between menstruation, doctors recommend diagnostic curettage. They also resort to endometrial biopsy followed by histological analysis of the extracted tissue. Studying the sample will help create a plan for further treatment.
In extreme cases, fibroids are diagnosed using CT and MRI. The methods help to discard suspicions of uterine sarcoma and ovarian cyst.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is needed to accurately diagnose fibroids when an ovarian tumor is suspected. Laparoscopy will become the best diagnostic method if non-invasive methods are ineffective.
Basic diagnostic methods
In terms of early diagnosis, this disease does not pose any particular difficulties. The diagnosis is determined based on visual examination of the affected area of the epidermis. For example, soft tissue fibroma of the thigh is identified by the specific shape and location of the tumor. In doubtful situations, the oncologist may resort to a biopsy, which consists of a histological and cytological examination of a small area of atypical tissue.
On topic: Fibroma: photo and description. What do fibroids look like?
Uterine fibroids and pregnancy
Small fibroid tumors that do not cause symptoms do not affect conception. The exception is fibroids in the fallopian tubes, which prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
However, despite the fact that fibroids do not reduce the chances of pregnancy, they affect its course. Large tumors can lead to incomplete development of the fetus, since they occupy some part of the uterus that the child needs. Lack of space can cause miscarriage and premature birth.
Also, large fibroids change the position of the child, which significantly complicates childbirth. For patients with such fibroid nodes, cesarean section is recommended.
The most dangerous phenomenon for childbirth is cervical fibroid of the uterus. The knot prevents the baby's head from coming out and can also cause sudden and heavy bleeding. Pregnant women with fibroids are managed with great care.
Modern treatment
Specific therapy is required for tumors that are located in an area of permanent injury or that cause aesthetic discomfort to the patient.
Conservative method
Small pathological lesions can be treated with injections of the drug "Diprospan". The product is injected through a thin needle into the center of the formation in an amount of 0.2 ml. The effect of the drug is aimed at stimulating the involution of atypical cells, which can ultimately lead to the disappearance of fibroids.
Soft fibroma - removal
Surgical removal of the affected area is carried out when the process has spread extensively, involving the deep layers of the dermis in the mutation. Radical intervention includes local anesthesia, excision of fibroids and cosmetic suturing of the wound surface.
Surgical excision is carried out in the following ways:
- Cryodestruction:
The technique involves applying liquid nitrogen to the tumor site, which provokes a local decrease in temperature. As a result, pathological cells are destroyed and rejected. A significant disadvantage of cryodestruction is the formation of a scar or scar.
- Electrocoagulation:
Exposure to high frequency current is accompanied by the death of the formation. This method of treatment is indicated for pathology sizes up to 1-2 cm.
- Laser therapy:
This manipulation consists of layer-by-layer evaporation of the atypical epidermis under the influence of laser radiation. Ultimately, the operated area heals by primary tension of the skin, which leads to the most favorable treatment outcome. Today, laser therapy is the most popular method for removing soft fibroids.
- Radio wave coagulation:
Cyber-knife technology excises tumor-affected tissue absolutely painlessly and bloodlessly. This makes the method highly effective. The only drawback is the high cost of the procedure.
Treatment of uterine fibroids
Diagnosis and treatment of fibroids is carried out by a gynecologist or gynecologist-endocrinologist. All patients with fibroids are registered with a doctor. Asymptomatic small fibromas must be studied over time (several ultrasound sessions or other studies at different intervals). Observation is indicated for women before menopause, because fibroids often disappear on their own during the postmenopausal period.
Treatment with medications
Conservative treatment is effective for fibroids in pregnant women up to 12 weeks. The regimen is also recommended in the absence of bleeding and pain. Conservative methods are the only method for treating fibroids in patients with contraindications to surgery.
In the treatment of fibroids, the following drugs are used: iron-containing, vitamins, hormonal, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Treatment with medications should be based on hormones:
- to reduce steroids produced by the ovaries, androgen derivatives are prescribed for 8 months without interruption;
- to normalize the growth of the endometrium during cell proliferation, gestagens are used for 8 months, but such drugs have little effect on fibroids (only for small nodes against the background of hyperplasia);
- to slow down the growth of fibroids and prevent pregnancy, they use the Minera hormonal system, which is placed in the uterus to regularly release the progestin hormone levonorgestrel into the cavity;
- to slow down the growth of small nodes, use combined oral contraceptives (COCs) for at least 3 months in a row;
- To reduce the level of estrogen, gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is used (it interferes with the blood supply to the uterus and, accordingly, fibroids, but the effect remains only while taking GnRH, so it is used mainly before operations).
Antigonadotropins
Antigonadotropins bring more results. This applies to both conservative treatment and preparation for surgical intervention. Antigonadotropins can shrink fibroids, perform an endoscopic procedure, and save organs.
Three treatment regimens with antigonadotropins are used:
- combination with estradiol;
- several courses with breaks;
- high doses for several weeks, followed by reduction.
The effect can be assessed only a month after the first administration of the drugs. Antigonadotropins have the advantages: no effect on the blood, do not become hostile to the body, and do not accumulate. However, side effects are possible (headaches, sweating, depression, memory loss, weakening of bones, swelling, seborrhea). Also, hormonal therapy leads to hot flashes, mood swings, and vaginal dryness. Sometimes taking hormones causes pseudomenopause and osteoporosis.
After conservative treatment of fibroids, the menstrual cycle is restored, but estrogen levels are also restored, which leads to the fibroids returning to their original size. This happens over 3-4 cycles. Symptoms may recur, but the second time they are not as pronounced.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is necessary in case of pronounced symptoms and growth of fibroids under the mucosa.
Indications for surgery:
- sudden and heavy bleeding;
- severe pain;
- compression of organs;
- large size of the fibrous node;
- uterine fibroids against the background of endometriosis (growth of the endometrium of the uterus beyond its boundaries);
- fibroma and ovarian tumor;
- fibroma necrosis.
Treatment options:
- Uterus removal.
- Minimally invasive treatment.
- Organ-preserving operations.
- Conservative laparoscopy.
- Conservative myomectomy.
- Hysteroresectoscopy.
- Supravaginal amputation of the uterus.
To preserve the genital organs in women of childbearing age, the following procedures are used:
- Conservative vaginal myomectomy.
- Laparoscopy.
The doctor’s task is to remove the fibroid using enucleation and preserve the uterus. If the tumor develops under the mucosa, a hysteroscopic myomectomy is performed. It allows you to avoid incisions and remove the fibroma through a hysteroscope.
Sometimes fibroids are treated with ultrasound ablation. The method involves treating fibroids with high-frequency ultrasound. If you preserve the uterus, there is no guarantee that fibroids will not appear again.
Radical measures include hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) through the vagina, with open access or laparoscopically.
The most effective treatment for fibroids today is uterine artery embolization. In the process, all the vessels that feed the tumor are blocked. And without blood and hormones, fibroids cannot function. The method is the most gentle.
Reasons for appearance
Today, doctors do not know exactly the reasons for the appearance of fibroids on the skin and internal organs. Experts identify several factors that can lead to the formation of tumors. These include:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Mechanical and thermal injuries, chemical exposure.
- Violation of metabolic processes.
- Problems with hormonal balance.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine glands.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
It is necessary to avoid frequent mechanical injuries to the feet, so it is imperative to choose shoes that do not rub or pinch.
It has been established that certain pathologies, including diabetes and acromegaly, contribute to metabolic disorders in the body, which leads to the appearance of fibroids on the legs and arms.
Complications after fibroma
Uterine fibroids very rarely turn into a malignant tumor. Only in 1% of cases the node underwent dangerous changes.
The most dangerous complications of fibroids:
- twisting of the leg of the knot causes acute pain in the abdomen;
- tumor necrosis is accompanied by fever, pain, and softening of the node;
- Bleeding from fibroids can be sudden and severe, leading to anemia.
Complications after surgery are possible. As after any operation, there remains a risk of developing infection, bleeding, adhesions in the pelvis and uterus, which can cause infertility. The prognosis for pregnancy after surgery is 40-60%.
Symptoms of skin fibroids
A benign connective tissue tumor is classified according to a number of characteristics. This takes into account the type, location, localization, speed of development, etc.
In the legs, tumors can affect various tissues. On this basis, fibroma is divided into:
- Skin. It can be hard and soft. The hard one is represented by a compaction or growth with a wide base. The color is practically no different from the surrounding skin or has a pinkish tint. Most often observed on the surface of the foot, lower leg, and toe. A soft fibroma is similar to a wrinkled sac, connected to the skin by a thin stalk. The formation often results from scarring of the skin after surgery;
- Chondromyxoid. Formed by cartilage tissue. It is observed quite rarely. It is localized in the joints of the legs and signals itself with pain during movements and loads. It is characterized by relapses and is dangerous due to the risk of taking on a malignant form. This type of fibroma is most common in the knee joints;
- Non-ossifying. It is located on the bones, and more often affects damaged areas, resulting in fractures and cracks. More common in children and adolescents. Often causes thinning of the bone and leads to its weakening.
Prevention
By studying the factors that provoke tumors, specific conclusions can be drawn. To avoid suffering from fibroids, you should be careful about your health. In particular, prevent unwanted pregnancies, not have abortions, use contraceptives correctly, correct hormonal levels, consult a gynecologist for any symptoms and treat inflammation.
To avoid any problems with the reproductive system, you should lead a healthy lifestyle and carefully choose your sexual partners. A woman needs to eat right and take extra vitamins. It is necessary to keep your weight under control. In order to promptly diagnose and treat fibroids, you need to regularly visit a gynecologist and perform an ultrasound.
Some doctors recommend special prevention of fibroids - to realize reproductive function. Saving your first pregnancy will help avoid fibrotic formations. So the first pregnancy should take place at the age of 22, the second closer to the age of 25, the third is desirable before the age of 35. It is also recommended to breastfeed your baby for at least 4 months. This will help normalize prolactin levels and stop the growth of fibroids.
Late pregnancy with the first child leads to the fact that all the characteristics of the uterus suffer. Abortions and chronic inflammation also damage the muscular layer of the uterus.
A woman should avoid excessive ultraviolet radiation and high temperatures. Uterine fibroids are usually diagnosed at 30-35 years of age, but if there are hereditary risk factors, the tumor can develop at 20.
Fibroma in children - photo, removal and consequences
Benign formations that do not tend to spread from their primary location are called fibromas. They develop from fibrous or connective tissue in any organ of the body. They have a wide base or are located on a stalk.
Fibroma in children develops in 40% of cases. Basically, they appear after two years and are asymptomatic for a long time. In 7–8% of patients, a fibromatous condition is present. This means that not one tumor appears, but several at once.
Classification by place of education includes two main types:
- Tumors that form in the skeletal and cartilaginous structure (bones of the arms, legs, ribs).
- Tumors of soft tissues: muscles (fibroids), fat cells, blood vessels (angiofibromas), skin, glands (fibroadenomas).
As the child grows, benign growths can also cause harm by pinching blood vessels or nerve endings. These conditions cause pain, and weakened bones predispose to pathological fractures.
Bone fibroma in children
The most common types are:
Non-ossifying:
They consist of fibrous tissue and are attached directly to the bone. Typically found in actively growing sections of long bones, such as the flared end of the lower femur and the tibia.
Sometimes the humerus is affected. More common in males. No surgical intervention is required.
Such a fibroma on a child’s leg may disappear without any treatment when the baby gets stronger.
Symptoms:
Some children feel swollen and tender to the touch. 2% of young patients complain of constant dull pain not associated with physical activity. Sometimes the reason lies in a microcrack or minor fracture.
Heteroplastic osteoma:
Exophytic mass consisting of connective tissue of the bones of the skull and paranasal sinuses. Sometimes classified as a developmental anomaly.
Symptoms:
The tumor is hard, round, and painless to the touch. Reaching large sizes, a fibroma on a child’s head can put pressure on the skull, deforming it and causing pain, swelling, and problems with brain activity.
Osteoid osteoma:
A small lump that grows in a person's long lower limbs or spine. In children, it is stimulated by rapid development and can cause deformation of bone structures.
Osteochondroma (exostosis):
Osteochondroma arises from the cortex of the long bone adjacent to the plate. Fibroids of the knee joint in children usually contain bone and cartilaginous elements, so they predominantly develop in the lower end of the femur or tibia (tibia), as well as in the forearm.
Simple cysts:
Fluid-filled formations whose surface consists of fibrous compounds. Typically occur in the upper extremities and shoulder girdle. This type of fibroma primarily affects children between 5 and 15 years of age, but can also occur at older ages.
Asymptomatic, but manifest as pathological fractures even after minor injuries.
Treatment differs from that of other fibroids and includes injections of aspiration, the drug “Methylprednisolone” or bone marrow.
Non-osteogenic fibroma:
Formed in the extremities. Discovered accidentally on x-ray. Requires removal only when it weakens the bone.
Soft tissue tumors
Skin fibroma in children
Mainly represented by papular and nodular lesions. Among them are:
A smooth, flesh-colored nodule with a wide base. It is localized on the toes and develops in the first 12 months after birth. Requires differentiation from fibrosarcoma.
The formations are prone to spontaneous regression, as well as relapses after removal, so surgery is not recommended as the main treatment.
A tumor of the cell spindle is presented as a flesh-colored or brown nodule. Diffuse, pigmented or pleximorphic variants are differentiated. The latter are prone to malignant transformation. Especially noticeable is fibroma on a child’s hand, which can be present at birth and occur during adolescence.
Nodules of all shades of red, as well as bluish and purple. Absolutely safe and do not require therapy.
A fibrous papule that forms from the hair follicle and resembles an intradermal nevus. It appears in childhood and gets darker over the years.
Oral benign lesions
Fibrous, non-cancerous growths called tumors. But behind the distinguishing features, it is rather hyperplasia, which is formed as a result of a reaction to some irritant or is genetically determined. Histologically, it is a spherical solid body that can periodically become inflamed.
- Fibroma in a child on the gum:
It has an oval, ovoid appearance and is characterized as sessile or pedunculated. The surface is smooth, but due to frequent injuries it can be ulcerated or covered with hyperkeratosis.
It is a group of infiltrating fibrous proliferations that are intermediate between benign and malignant lesions. Usually diagnosed in patients under 10 years of age. Gingival fibromatosis is a distinct condition that can be hereditary or drug-induced. The growths have a keratinized, inflamed appearance.
Fibroma of the jaw bone
Fibroma in children: treatment and removal
As described above, fibroma in a child requires treatment only in cases where the symptoms interfere with life.
General therapeutic measures include:
The most effective and simple ways to remove fibroids in a child. During surgery, the tumor is scraped off using a special instrument that has a scoop, loop or ring at the tip. Excess liquid is sucked off. The remaining cavity is filled with the patient’s own donor tissues, removed from other parts of the body or with pieces from other materials.
2. Steroid injection:
In some cases, a steroid injection can help cure bone fibroids in a child without surgery. Scientists believe this effect occurs due to the steroids' ability to reduce levels of prostaglandin, a type of fatty acid that forms in cysts.
3. Bone marrow injections:
The necessary substances are sucked out from the hip bones and injected into the cystic seal. This procedure promotes rapid healing. Sometimes used in combination with demineralized bone gel to stimulate the formation of new tissue. The prognosis for treatment is positive, but a small number of relapses occur.
Fibroids in children are not an aggressive disease, which often does not require the use of any radical measures and solutions.
Source: https://orake.info/fibroma-u-detej-foto-udalenie-posledstviya/
Non-osteogenic fibroma
The diagnosis of non-osteogenic bone fibroma is often heard among males. This means that a pathological change has occurred in the femur and tibia.
The disease is characterized by resorption of the cortical part of the tubular bone, followed by its replacement with fibrous tissue.
The development of pathology is usually not accompanied by any symptoms and, without timely diagnosis and treatment, leads to fractures. Non-osteogenic bone lesions tend to self-resorb.
Non-osteogenic fibroma is a neoplasm that has a destructive effect on human bone tissue.
What it is?
Non-osteogenic or non-ossifying fibroma occurs not only in older people, but also in children and adolescents. Such pathological changes in the body require medical intervention. Non-osteogenic fibromas are benign neoplasms consisting of tissues whose cells synthesize extracellular structure.
Non-osteogenic fibroma includes damage to the tibia or femur. The pathology is characterized by the dissolution of the outer bone layer, which forms the bone crust. The tubular section, which is adjacent to the cartilage plate, also dissolves.
After the process of resorption of the tubular section, it is replaced by the epiphyseal line. The outer bone layer is replaced by fibrous tissue, which serves as a building material for tendons and is unable to fully recreate the bone cortex.
Due to such pathological replacement, unnatural fractures of the arms and legs occur.
Fibroma shape
Tibial fibroids have a characteristic elongated appearance. The edges of the damaged bone are surrounded by cells and fibers that look like strange tufts. What are these weaves formed from? shown in the table:
Non-osteogenic fibroma may be composed of fibroblasts, collagen, lipocytes, or a combination of these.
| Biomaterial | Short description |
| Collagen protein fiber | Part of connective tissues. Such fibers perform a mechanical role. They have low elasticity. |
| Cells that produce extracellular substance (fibroblasts) | Extracellular substance is considered the main building material for connective tissues and provides mechanical support for cells. Fibroblasts help release chemical material from the cell (such as elastin). |
| Lipocyte cells | Form scar tissue. |
| Cellular elements | Their presence confirms the inflammatory process in bone tissue. |
Etiology and pathogenesis
Patients who have been diagnosed with neurofibromatosis are at risk. In most cases, non-osteogenic disease occurs in the first 20 years of life; it is rare in older age. Boys suffer from non-osteogenic fibroids much more often than girls.
Non-osteogenic fibroma can go away on its own, but there is a risk of degeneration into oncology.
The causes of tumor changes in the bone are not clear. The disease manifests itself as focal resorption of bone tissue and its transformation into a fibrous structure.
Often, non-osteogenic fibromas disappear on their own.
A benign tumor does not pose a great danger, but there are still several factors that can negatively affect the development of the tumor and further consequences:
- the possibility of degeneration into a malignant tumor;
- excessive growth of fibroids provokes disruption of muscle and bone activity;
- mechanical damage to the tumor (trauma, blow) provokes the onset of the inflammatory process and the development of a secondary infection.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of the development of non-osteogenic fibroma in almost all cases are absent until a pathological bone fracture.
Sometimes non-osteogenic bone fibroma is discovered during an X-ray examination, which is prescribed for other reasons.
The main symptom of non-osteogenic fibroma is unnatural fractures, most of which occur in the lower extremities. Other signs of the disease:
- during an x-ray examination, porous tissues are clearly visible in the image;
- general tests show an insufficient amount of calcium in the body;
- impaired phosphorus-calcium metabolism, and emerging pathological processes that destroy bone tissue and prevent its self-healing.
Features of education in children
Non-osteogenic fibroma reduces bone strength, and this is very dangerous due to the extreme activity of children.
The process of development of non-osteogenic fibroma in children begins with a slow thinning of the outer layer of bone tissue.
The growth of the tumor provokes painless resorption of bone tissue. At the final stage of thinning, the density of bone tissue is radically transformed, which negatively affects the overall structure of the bone.
The plates cease to perform their functions and are no longer aligned along the lines of compression and tension. This condition causes a decrease in resistance to physical activity.
Bone fibroma is considered a defect in the outer layer of bone, which is located in a long, tubular, hard formation in the human body. The defect looks like multi-chamber formations, similar to small holes.
Treatment of non-osteogenic fibroma is prescribed in rare cases. Since the porous tissue gradually heals spontaneously.
At an early stage, the clinical picture will not make it possible to diagnose the disease due to the absence of symptoms and spontaneous resorption of fibroids.
How is non-ossifying fibroma treated?
Non-ossifying fibroma has the unique property of self-resolving. This is considered the most appropriate recovery. The disadvantage of this treatment is that independent restoration of bone tissue sometimes takes a long time.
To speed up recovery, the doctor prescribes medications. Bone resection (removal of the affected part) is performed surgically. Sometimes the affected area is excised above the bone.
In this case, healthy and damaged tissues are separated, the periosteum is peeled off using a parser and sawed off from both ends of the damaged area.
Surgery is performed only in extreme cases, when the cortical bone is depleted by more than half. In case of fractures, the tumor is usually scraped out to speed up the healing of the broken bone.
When surgery is performed on flexible tissue and cartilage, the damaged areas of the joints are removed and replaced with special implants. Radiation therapy is often used to stop or slow tumor growth and to destroy tumor cells.
It is important to remember that the treatment method for non-osteogenic fibroma and its appropriateness should be determined solely by the doctor. Self-medication and violation of medical recommendations can lead to serious consequences.
The tumor has the ability to spread and thereby has a negative impact on the general condition of the body.
Clinical picture of fibrous dysplasia
Fibrocystic dysplasia of the tibia is not congenital. The first signs of the polyostotic form appear in childhood. A sick child experiences changes in skin pigmentation and the functioning of the cardiovascular system is disrupted. He may also complain of pain in his hips. Deformations of the bone apparatus become noticeable quite quickly.
The tibia is most often affected by the polyostotic form; sometimes the disease is complicated by damage to the feet. They are subject to deformation, and the femurs are subject to shortening, this is explained by the difference in loads on them. This leads to a change in the patient’s gait - lameness appears, falling on the healthy leg and pulling up the patient.
The course of the monoosseous form is much easier. There are no pathological manifestations in the periosteal tissues. The degree of deformation and its severity are determined by the characteristics and location of the lesion. Patients with this form are also characterized by lameness and a pronounced feeling of fatigue in the affected segment. Fractures of a pathological nature are common.
Bone fibroma
Bone fibroma is a rare true benign tumor of osteogenic origin, resulting from tumor proliferation of the connective tissue substance. Bone fibromas of non-osteogenic origin are even rarer.
We observed 6 children with bone fibromas of osteogenic origin, two of them were described in 1961 (children aged 11 and 15 years with tumor localization in the frontal and ilium bones, there is histological confirmation of the diagnosis).
The remaining children were aged 10, 13 and two 14 years old with damage to the fibula in two cases, the radius and the femur (in the lower metaphysis). All patients underwent bone resection with homoplasty. Here is a description of an exceptionally rare form of true bone fibroma that we have observed in recent years.
Valery P., 10 years old, was admitted to the clinic of pediatric bone pathology CITO 27/II 1965 with complaints of swelling of the posterior outer surface of the left leg. I have been ill for a year, pain appeared only recently in the area of the head of the fibula. In recent months, the tumor has grown rapidly.
On the x-ray, there is a huge spindle-shaped tumor, occupying almost the entire diaphysis and proximal metaphysis of the fibula, which does not exist as such - it is occupied by a tumor. The latter has a clear shell-like bony border. The structure is homogeneous, with a fine pattern of trabeculae.
Fibroma of the fibula
Fibroma of the fibula in a 10-year-old boy: before treatment and 8 months after resection of the bone fibroma and homoplasty.
Diagnosis: aneurysmal cystic fibrous dysplasia fibroma. On 17/III we performed an operation. The tumor was resected along with the thinned and altered periosteum. The defect was replaced by two thin cortical homografts.
Histological examination : desmoplastic bone fibroma. Macroscopically, the tumor specimen had the appearance of a spindle with clear boundaries.
Macroscopic specimen of bone fibroma
Macroscopic specimen of bone fibroma removed from a patient: general view of the specimen and sectional specimen.
On the section, the tumor is surrounded, like a case, by thinned periosteum and the cortical layer and filled with homogeneous dense connective tissue, divided by thin bone crossbars into lobules. There are no blood cavities and cartilage tissue in the tumor. Plaster immobilization for 4 months. X-ray after 8 months shows good reconstruction of homografts.
This type of lesion is described in the literature as desmoplastic bone fibroma. This observation is interesting due to the painless course of the tumor in stage I of the disease (before compression of the peroneal nerve), which explains the large size of the tumor with which the patient presented.
Acquaintance with the literature showed that many more neoplasms or various variants of skeletal tumors have been described under the name “bone fibroma” and that this term is used much more often than such a tumor is encountered in practice.
The section related to bone fibroids includes diseases that are similar in name, but different in genesis.
In modern literature there are publications of observations referred to as “chondromyxoid bone fibroma”, “osteogenic bone fibroma”, “non-osteogenic bone fibroma”.
These are all “fibromas” of osteogenic origin, despite their unfortunate names (some of them are not fibromas at all from a morphological point of view).
“Bone diseases in children”, M.V. Volkov
Chondroma and osteochondroma (localization)
The localization of chondromas differs significantly from the localization of osteochondral exostoses, which is sometimes one of the clinical and diagnostic signs.
The favorite localization of chondromas are the metatarsal and metacarpal bones, phalanges of the fingers and toes, then the ribs and sternum, i.e.
bones that have the largest amount of cartilage tissue (articular cartilage, cartilaginous composition of the body of the sternum, ribs). Half of our patients were affected...
Chondroblastoma (differential diagnosis)
Differential diagnosis is complicated by the similarity of the histological structure of chondroblastoma and chondromyxoid fibroma, as well as the possibility of the existence of mixed forms described by Dahlin (1957), Lichtenstein and Bernstein (1957), R. E. Zhitnitsky (1964). In one of our cases, a 10-year-old boy, whom we have been observing for the last 9 years, had chondroblastoma of the right tibia. He underwent marginal resection...
Chondroma and osteochondroma (enchondromas)
Enchondromas arise from the cortical region, adjacent to both the diaphysis and metaphysis.
Pain in ecchondromas occurs only after the latter reaches a significant size and compression of the surrounding tissue occurs, while in enchondromas the pain is associated with destruction of the periosteum.
As a result of the proliferation of chondromas, deformations are formed on the hands and feet that interfere with function. At…
The only treatment for patients with chondroblastoma is surgery. Radiation therapy should not be used due to its complete ineffectiveness against chondroblastomas. Hatcher and Campbell in 1951
reported a case of malignancy of benign chondroblastoma after radiation therapy and were strong opponents of this type of treatment. The choice of surgical treatment method is determined by the nature of the tumor.
Of the 23 children with chondroblastoma...
Chondroma and osteochondroma (metaphyseal enchondromas of long tubular bones)
With metaphyseal enchondromas of long tubular bones, the first symptom is pain; they are detected only on an x-ray.
Rarely, enchondroma develops not in the metaphysis, but in the thickness of the epiphyseal growth zone. Caffey (1957) refers to cases of cartilaginous tumor growth in the zone of growth cartilage as a special type of neoplasm - “epiphyseal osteochondroma”.
The tumor causes premature ossification of the epiphyseal cartilage at the site of the lesion….
Source: https://www.kelechek.ru/bolezni_kostey_u_detey/novoobrazovaniya_osteogennogo_proishozhdeniy/4692.html
Chondromyxoid fibroma
Chondromyxoid fibroma
is a very rare cartilaginous benign tumor. It most often occurs in the metaphyses and metadiaphyses of long tubular bones, but it can also develop in other bones of the skeleton.
The course is usually favorable, however, it is prone to recurrence and in some cases can become malignant.
It manifests itself as gradually increasing pain in the affected area; in severe cases (especially in childhood), mild or moderate atrophy of the muscles of the affected limb and limitation of movements in the nearby joint are possible.
Treatment is surgical and carried out as planned. Radical removal of the tumor is performed to prevent relapses and malignant transformation. The prognosis is favorable. Relapses occur in 10-15% of patients, usually in the first two years after surgery.
D16
Benign neoplasm of bones and articular cartilage
Chondromyxoid fibroma is a rare benign neoplasm that arises in the bones and consists of cartilaginous tissue. Accounts for 0.5-1% of the total number of bone tumors.
It can develop in people of any age; men and women are affected equally often. Rapid growth and severe symptoms are more often observed in children.
In 15% of cases, it is asymptomatic and becomes an accidental finding by a traumatologist or orthopedist during an X-ray examination.
Usually localized in the metaphyseal and metaepiphyseal zone of the long tubular bones of the lower extremities. The first place in prevalence is occupied by chondromyxoid fibroma of the proximal end of the tibia.
Often found in the metatarsal bones and calcaneus. Possible damage to the ribs, humerus and pelvic bones, as well as vertebrae, sternum and skull bones. 25% of the total number of cases are affected by flat bones.
The most aggressive growth is characterized by tumors in the spine.
Chondromyxoid fibroma
The clinical picture of the disease largely depends on the age of the patients. In adults, the disease usually develops slowly and occurs with mild symptoms or is completely asymptomatic. Children are characterized by faster tumor growth, progressive increase in pain and pronounced clinical symptoms.
The main complaint of patients is pain, which often appears during movement, however, it can also be bothersome at rest.
The intensity of the pain syndrome varies significantly in different patients - from insignificant, erased to intense, pronounced.
Upon examination, a local increase in temperature, muscle atrophy of the affected limb, limitation of movement in a nearby joint, or pain during movement may be detected.
The clinical picture of this disease is nonspecific, so the diagnosis is made based on the results of additional studies.
Radiographs reveal an exophytic formation with clear scalloped outlines, which is usually localized in the metaphyseal zone and grows towards the epiphysis.
The tumor is a clearly defined focus of destruction, the length of which can vary from 1-2 to 6-8 centimeters. The cortex above the lesion is swollen and thinned.
A sclerotic rim is revealed along the edge of the formation; inclusions of lime and a trabecular pattern may be found in the focus of destruction. If the tumor is located subperiosteally, the cortex becomes uneven. There is usually no periosteal reaction. When the tumor is localized in the vertebral area, periosteal growth is often observed.
The X-ray picture of chondromyxoid fibroma may resemble changes in chondrosarcoma, enchondroma, benign chondroblastoma and chondroblastic variant of osteosarcoma, so a bone biopsy is performed to make a final diagnosis. During the differential diagnosis, highly aggressive malignant chondrosarcoma should first be excluded.
Macroscopically, the tumor tissue is a lobulated formation of dense consistency, bluish-gray or grayish-white, well demarcated from healthy tissue. In appearance it may resemble hyaline cartilage.
Microscopic examination reveals a chondroid or myxoid intercellular substance, within which elongated or stellate cells are located. Areas of connective tissue are located mainly in the layers between the lobules. Small vessels are also found there.
Along with collagen fibers, osteoid and giant multinucleated cells are detected in the tumor tissue.
The structure of the lobules within the same tumor can vary significantly. A variety of fibroblasts are detected - both large and small, some cells have 2 or 3 nuclei.
The cells are located mainly along the periphery of the lobules. In every third case, the cells of benign chondromyxoid fibroma have an atypical structure and resemble the cells of malignant chondrosarcoma in appearance.
In 10% of cases, foci of necrosis are found in the biopsy specimen.
An immunohistochemical study reveals a positive reaction with protein S-100. Cells located at the periphery of the lobules show immunoreactivity with CD 34 and smooth muscle actin. There are cytoplasmic fibrils and cellular processes, and the presence of glycogen is noted. Along with typical myofibroblasts and chondrocytes, intermediate forms of cells are found.
Treatment is only surgical. The operation is performed as planned in the oncology department. The most effective method of surgical intervention, ensuring a minimum number of relapses, is marginal resection of a section of bone followed by plastic surgery of the defect with an autograft or allograft.
In some cases, this disease is treated with curettage (an operation during which the tumor is scraped out with a curette - a surgical instrument that looks like a spoon).
However, this approach is not preferable, since this intervention increases the likelihood that altered tumor cells will remain in the affected area, and chondromyxoid fibroma will recur over time.
Data on the likelihood of chondromyxoid fibroma turning into a malignant tumor are ambiguous. This is due to both the rarity of neoplasia and possible overdiagnosis (cases when, based on the results of a microscopic examination, a removed tumor is mistaken for malignant due to the presence of similar cells). In general, the prognosis for this disease is considered favorable.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/traumatology/chondromyxoid-fibroma
Classification of pathology
Hip dysplasia
According to the international classification, fibrous dysplasia of the fibula is divided into two types:
- Monostotic. Only affects one bone. May appear regardless of age. There are no changes in skin pigmentation.
- Polyostotic. Diagnosed exclusively in children, it is often combined with disorders of the endocrine system and excessive accumulation of melanin pigment.
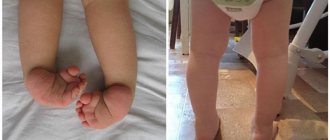
An example of polyostotic dysplasia in a child is a fibrous cortical defect of the tibia. This condition is also called non-ossifying fibroma. It is considered the largest type - the size exceeds 3 cm.
Non-ossifying fibroma is most often diagnosed in adolescents aged 10 to 15 years. Although cases are often observed in children 4-8 years old. The pathology most often affects boys. This distinguishes the fibrous cortical defect of the tibia from other forms of tibial dysplasia, which are detected mainly among females.
The clinical picture of non-ossifying fibroma is practically absent. The exception is large formations, which cause pain. In addition, due to the weakening of the bone under the tumor mass, a pathological fracture may occur.
If you look at a fibroma under a microscope, you can see a lesion with minor areas of hemorrhage and a brown tone.
To make an accurate diagnosis, radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, and scintigraphy are required. In most cases, treatment is not required. It is enough to regularly undergo control examination using one of the listed methods to exclude complications.