What you need to know about torticollis in newborns?
Parents should immediately think about it if the baby turns his head to one side during sleep , and during wakefulness he always looks in one direction.
With this disease, the baby's head is constantly tilted to the affected side , while the face is turned in the opposite direction and slightly tilted back. The back of the head is slanted, often a bald patch forms in the hair on one side of the head.
Facial asymmetry often occurs when the cheek on the side in which the child most often turns his head enlarges, as if swelling. The child becomes capricious, sleeps poorly , and regurgitates food.
If you notice one or more of the above symptoms in your baby, you should immediately consult a doctor. Obviously, in this case, the specialist will diagnose him with torticollis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Massage
A key element of the treatment program, the goal of the procedure is to relieve excessive tension on one side of the neck and create conditions for muscle development on the other side, eliminating asymmetry. To perform a full-fledged therapeutic massage, you need knowledge and experience; in their absence, the procedure will be useless.
Torticollis in newborns can improve with regular massage.
There are a few simple techniques you can use at home:
- Alternately stroking the healthy and sore sides of the neck. Stroking movements can be alternated with light tapping with your fingertips.
- Massage the cheek on the affected side: first, stroking, then light tingling and vibration.
- Back massage in the area of the paravertebral muscles (the main back muscles that run along the spine): first, light stroking movements, then more vigorous rubbing.
- Light kneading of the collar area (shoulders are slightly compressed).
- Stroking the tummy, arms and legs, allowing the baby to relax.
All movements are performed at an average pace, without excessive effort, each of them is repeated 5-20 times. The maximum session duration is 10 minutes. The main rule: the massage should give the child pleasure; if he is worried, the procedure should be stopped immediately.
Causes of the defect
Torticollis can be congenital or acquired . The reasons may be different, but they are all associated with deformation and improper functioning of the neck muscles.
Congenital torticollis
Congenital torticollis develops during pregnancy . It can be caused by prolonged incorrect position of the fetal head in the womb or underdevelopment of the baby's neck muscles. usually appear from birth .
There are two types of congenital torticollis:
- muscular torticollis - when, as a result of underdevelopment, the sternocleidomastoid muscle is shortened;
- bony torticollis – when the cause of the disease is a disruption in the process of skeletal formation during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus.
Acquired torticollis
Acquired torticollis is symptomatically similar to congenital torticollis, but has no age limit for its occurrence . The reasons may be:
- birth injury;
- diseases of the spine;
- dislocation of the cervical vertebra as a result of injury;
- underdevelopment of some groups of neck muscles;
- getting used to incorrect head position;
- skin burn on the neck;
- other reasons.
Do you know why pregnant women can't eat grapes? Find the answer to the question in this article.
This article will tell you about what kind of music pregnant women should listen to.
How to treat with body position
At the same time, sore muscles are developed.
The place to sleep is of great importance. Place your child to sleep on a medium-firm mattress. An orthopedic pillow for newborns with torticollis also helps correct the defect. But it is used only after the doctor’s permission after the child reaches six months of age.
Otherwise, take a regular diaper, fold it in four, and use it as a pillow. Carry the baby in a strictly vertical position, making sure that the hangers are at the same level as mom’s or dad’s. Place the baby on his stomach more often, this improves the condition of the neck muscles.
Defect diagnosis
Torticollis is not difficult to identify. The disease is usually diagnosed closer to two weeks after the baby is born, and the sooner treatment begins, the better.
First of all, you need to find a competent orthopedic doctor and additionally get advice from a pediatric neurologist .
You should know that there is also a so-called false torticollis , when the child’s head is tilted to one side, but there are no changes in the muscles/ligaments/vertebrae of the neck - this is how hypertonicity of the cervical muscles appears against the background of a general increased tone. This disease is treated by a neurologist.
Symptoms and signs
Obvious symptoms and signs of torticollis:
- the child stubbornly turns his head to one side;
- he develops a noticeable deformation of the skull;
- facial asymmetry becomes visually noticeable;
- The child constantly shrugs one shoulder.
As a result, irritability, poor appetite and intermittent restless sleep occur due to discomfort in the neck area.
Redressing technique
The child is placed on the table on his back, his arms are placed along his body, and they are held by an assistant or mother. The doctor approaches from the side of the head, places both palms on the child’s head and cheeks on both sides and, without jerking, smoothly and with increasing force tries to move the head to the correct position, turning the chin towards the torticollis.
In this position, the sternocleidomastoid muscle is maximally stretched. During redressing, the head should not be tilted forward.
Redressation lasts from 5 to 10 minutes, and is carried out no more than 3–5 times per day. After redressing, the head is fixed in the maximum corrected position with cotton-gauze pads, which are secured with a bandage.
After the completion of skin formation (at the age of 2.5–3 months), before the redressing session, paraffin applications are prescribed to thicken the sternocleidomastoid muscle, which improves its elasticity.
In 1.5–2 month old infants, after redressing, the head is fixed with a Shants collar.
Treatment is carried out with gradual stretching of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, so that before the age of one year, a child with congenital torticollis is cured, which is always achieved in mild and moderate forms.
Treatment
Treatment of torticollis in newborns is carried out only non-surgically . With timely and correct conservative treatment, it disappears completely and without any unpleasant consequences.
But in particularly serious and advanced cases, surgical intervention is required. Infants are not operated on; surgical treatment is indicated only after 3 years .
Conservative treatment
In modern medicine, an integrated approach is used to treat torticollis:
- parents should ensure that the baby holds his head correctly during sleep, feeding, and wakefulness;
- regular massage of the neck/collar area;
- use of special pads/rollers to fix the head;
- therapeutic exercises, including in water;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- swimming;
- Shants collar;
- regular visits to the doctor.
All procedures/events must be systematic, only then can a good result be obtained. Usually, after complex treatment (by about one year), the baby’s torticollis completely disappears.
What are the first signs of the onset of labor? We'll tell you!
Should you quit smoking during pregnancy? Read in this article.
Follow the link and you will learn https://puziko.online/beremennost-na-rannih-srokah/problemy-na-rannih-srokah-beremennosti/simptomy-zamershei-beremennosti.html about the symptoms of a frozen pregnancy.
Surgery
If conservative treatment does not bear the desired fruit, then surgical intervention can give the deformed muscle a healthy shape.
There are two main types of surgery, the choice depends on the characteristics of the disease in the child:
- lengthening of the sternocleidomastoid muscle by sewing in synthetic materials;
- dissection of the legs of the sternocleidomastoid muscle for the purpose of lengthening.
Both operations are performed under general anesthesia. After surgery, it is necessary to wear a plaster cast (1-1.5 months), and for six months you will need to use a special head holder.
Possible complications
In infants, if all the doctor’s recommendations are followed, in 80% of cases it is possible to achieve a complete recovery; in children older than one year, the prognosis is less optimistic.
If you do not treat torticollis at all, then when the child reaches the age of 6-7 years, he will have to become familiar with the following consequences:
- strabismus;
- diseases of the spine: scoliosis, kyphosis, osteochondrosis;
- deformation of the skull and bones of the upper body;
- chronic oxygen starvation of the brain and associated developmental delays;
- change in the shape of the ear canal and hearing impairment;
- diction disorders;
- dental problems;
- mental disorders;
- severe headaches are an inevitable consequence of pinched nerves and impaired blood supply to the brain;
- frequent fainting.
We should not forget about purely aesthetic problems - pronounced asymmetry of the face and the whole body: if time is lost, it is completely impossible to eliminate these shortcomings even with the help of surgery: it will only increase the amplitude of head movements. Torticollis in the early stages is easy to treat, but difficult to diagnose. As the child gets older, the symptoms become more severe and treatment becomes more difficult.
To prevent this pathology from causing serious problems, it is necessary:
- regularly show the child to the pediatrician;
- carry out the necessary examinations in a timely manner;
- do not ignore measures aimed at preventing the disease;
- if the first symptoms are detected, immediately show the child to a doctor;
- If the diagnosis is confirmed, strictly follow its requirements regarding the treatment of torticollis.
Then the newborn and older child will have every chance to say goodbye to torticollis before their first birthday and will never again encounter its signs, not only in the photo, but also in later life.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Well-known pediatrician and TV presenter Yevgeny Komarovsky calls on parents to exercise maximum responsibility when it comes to diagnosed torticollis - this is a serious disease that, without correction, can lead to dire consequences. Komarovsky considers therapeutic massage and orthopedic devices very useful. But he urges parents not to go to extremes. In particular, he warns them against turning to an osteopath.
Despite the fact that osteopathy is recognized by the Ministry of Health, unlike homeopathy, it has not become more scientific, says Komarovsky. Therefore, there is not a single intelligible evidence that an osteopath can cure a child with torticollis. But such treatment can harm him: an incompetent osteopath or an undertrained manual therapy specialist can lead to additional injury to the neck, which may then require surgical correction.
There are several known cases of infant deaths in the hands of osteopaths and chiropractors with dubious diplomas and reputations, but high prices for their sessions.
It is much more useful, Komarovsky believes, to visit a qualified medical massage therapist and ask him to show him the technique of therapeutic massage, so that later, in a quiet home environment, the mother herself can do it to the child.
You need to visit exercise therapy specialists and learn exercises for daily gymnastics, with and without a fitball, which should be aimed at the proper development of the neck muscles. All this will beneficially complement the treatment program.
Classification
Depending on the time and causes of development, torticollis in children is divided into congenital, acquired and habitual position of the fetal head.
- Congenital torticollis:
- myogenic (defect in muscle development);
- osteogenic (due to deformation or fusion of the cervical vertebrae);
- dermodesmogenic (due to skin diseases, for example, the so-called congenital skin folds).
- Acquired torticollis:
- myogenic (for myositis, that is, inflammatory muscle diseases);
- neurogenic (with paralysis of the cervical muscles);
- dermodesmogenic (scars on the skin after burns or injuries);
- osteogenic (due to traumatic subluxation of the first cervical vertebra);
- eye diseases (for example, astigmatism);
- otogenic (as a result of diseases of the middle ear).
- Installation torticollis. It begins to develop in newborns with an asymmetrical position of the head, so it can only be acquired. This pathology can progress due to improper care of the baby (constantly carrying him in your arms with his head always turned in the same direction or, for example, placing toys on one side). This positional torticollis is also caused by the newborn lying on the same side for a long time. It has been noted that this form of torticollis develops in babies under one year of age.
Surveys
To establish an appropriate diagnosis, external signs alone are not enough. If parents suspect that their newborn may have torticollis, they should definitely contact their pediatrician. The pediatrician will give referrals for consultations with an orthopedic traumatologist, a neurologist, as well as an ophthalmologist and an ENT specialist to evaluate the baby’s vision and hearing.
The mother will be asked about how the pregnancy proceeded, what the birth was like, whether the baby suffered from myositis, or suffered severe viral infections after birth. After collecting an anamnesis, the baby will be sent for examination.
Usually, an ultrasound of the neck, or more precisely the cervical spine, is quite informative, but sometimes other methods are recommended, for example, an X-ray of the cervical vertebrae, computed tomography or MRI.
An X-ray of the first and second cervical vertebrae is considered very informative: their position usually makes it possible to easily determine whether the pathology is bone or articular, whether there have been dislocations, subluxations, whether there is a fusion, whether the vertebrae are deformed.
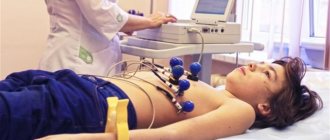
Neurological torticollis is more difficult to diagnose. To understand whether the nerves in this part of the child’s body are working normally, the child is prescribed electroneurography. To assess the condition of muscle tissue - electromyography. Only after obtaining examination data can the type, type and degree of torticollis be established. After this, therapy is prescribed.
Physiotherapy
For newborns at home, in addition to massage, it is recommended to perform gymnastics. It is also performed with the active participation of adults, but under the supervision of an experienced massage therapist. Certain reasons may cause some pain, so gymnastics is performed gently and should not be persistent. It is better to do gymnastics together.
One of the parents holds the child’s arms and body, the other holds the child’s head. While performing gymnastics, the head and neck should be in a suspended state, the shoulders should be parallel to the edge of the table. When performing gymnastics, the head should be in line with the body.
Over time, the support for the head decreases and it begins to gradually droop. The muscles relax more and more, gradually stretching. The hands limit the tilt and rotation of the child's head. Classes are conducted symmetrically for both sides. The baby's head is raised so that the chin touches the chest. Gymnastic exercises are carried out no more than five times, they are performed in the morning and evening.
While the child is in your arms, head support gradually decreases. When a child begins to hold his head, you can influence the reasons by making the head hang down under its own weight, so the muscles will be more stretched. Then the head rises for a while, the muscles should rest a little, then everything is repeated again. Gymnastics is carried out at least 3 times throughout the day.
Electrophoresis and massage courses can be used to supplement gymnastic exercises. After several procedures, the desired result will be noticeable; parents should remember that the disease can sometimes recur. On the side of the injury, the muscles are retarded in growth; in order to consolidate the positive result, four courses of massage in combination with physiotherapy are recommended in the first year of life.